Tag Archives: United States
Lobster harvesters in Atlantic Canada to vote on increasing minimum legal size this year
 At stake is maintaining access to the United States market. “It will be an individual vote. That’s a big decision that every single enterprise and owner has to look at from their own business,” said Heather Mulock, executive director of the Coldwater Lobster Association, which represents fishermen in lobster fishing area 34 (LFA 34). In late May or June, the 979 licence holders in the area will be asked to vote on whether to match increases in allowable U.S. catch measurements that will come into effect Jan. 1, 2025, and again in 2027. Live Canadian lobster that fall under the new limits would not be allowed into the U.S. That includes bonded shipments of lobster under the new minimum in the U.S., according to an information package sent to fishermen in southwestern Nova Scotia. That could block trucking of “undersized” Canadian lobster across the border for flights to Asia from airports in Boston or New York. more, >>click to read<< 08: 57
At stake is maintaining access to the United States market. “It will be an individual vote. That’s a big decision that every single enterprise and owner has to look at from their own business,” said Heather Mulock, executive director of the Coldwater Lobster Association, which represents fishermen in lobster fishing area 34 (LFA 34). In late May or June, the 979 licence holders in the area will be asked to vote on whether to match increases in allowable U.S. catch measurements that will come into effect Jan. 1, 2025, and again in 2027. Live Canadian lobster that fall under the new limits would not be allowed into the U.S. That includes bonded shipments of lobster under the new minimum in the U.S., according to an information package sent to fishermen in southwestern Nova Scotia. That could block trucking of “undersized” Canadian lobster across the border for flights to Asia from airports in Boston or New York. more, >>click to read<< 08: 57
From Bubba Gump to bust? American shrimpers face extinction.
 On a chilly December morning, the captain of the Miss Patti is ready to throw his lines and go shrimping – well, almost. Brian Jordan’s deckhand is in a foul mood, and it’s no wonder why. Is any of this worth it? Here on the tiny working waterfront of Tybee Island, Georgia, the hesitancy is logical. Shrimp prices cratered this year, and hundreds of boats from Brownsville, Texas, to Harkers Island, North Carolina, remained dockside. The problem hasn’t been a lack of shrimp or the price of diesel. Instead, freezers across the United States are filled to the gills. A glut of imported shrimp has dropped the price to about half of what shrimp boats received in the 1980s. At stake is the livelihood of Mr. Jordan and shrimpers like him nationwide. They can’t compete with overseas rivals who raise and harvest shrimp in lower-cost “aquaculture’’ farms. more, >>click to read<< 13:06
On a chilly December morning, the captain of the Miss Patti is ready to throw his lines and go shrimping – well, almost. Brian Jordan’s deckhand is in a foul mood, and it’s no wonder why. Is any of this worth it? Here on the tiny working waterfront of Tybee Island, Georgia, the hesitancy is logical. Shrimp prices cratered this year, and hundreds of boats from Brownsville, Texas, to Harkers Island, North Carolina, remained dockside. The problem hasn’t been a lack of shrimp or the price of diesel. Instead, freezers across the United States are filled to the gills. A glut of imported shrimp has dropped the price to about half of what shrimp boats received in the 1980s. At stake is the livelihood of Mr. Jordan and shrimpers like him nationwide. They can’t compete with overseas rivals who raise and harvest shrimp in lower-cost “aquaculture’’ farms. more, >>click to read<< 13:06
Rogue wave hits Canadian lobster industry as U.S. moves to increase minimum legal size
 An unexpected decision to increase the minimum legal size of lobster in the United States has appeared like a rogue wave on the Canadian industry, threatening to curtail live exports south of the border. With total Canadian live shipments worth $545 million in 2022, the potential trade implications was the first item on the agenda in the annual U.S.-Canada lobster town meeting being held in Moncton, N.B., this week. “Effectively we will not be able to ship a certain size lobster there that we always have. So their action will create an action that we have to respond to in Canada,” said Geoff Irvine, executive director of the Lobster Council of Canada. The U.S. move to increase the minimum legal size of a lobster carapace, or outer shell, from 82 millimetres to 84 millimetres in January 2025 — and to 86 millimetres in 2027 — would create a mismatch in the closely integrated two-way trading between the countries. photos, more, >>click to read<< 10:22
An unexpected decision to increase the minimum legal size of lobster in the United States has appeared like a rogue wave on the Canadian industry, threatening to curtail live exports south of the border. With total Canadian live shipments worth $545 million in 2022, the potential trade implications was the first item on the agenda in the annual U.S.-Canada lobster town meeting being held in Moncton, N.B., this week. “Effectively we will not be able to ship a certain size lobster there that we always have. So their action will create an action that we have to respond to in Canada,” said Geoff Irvine, executive director of the Lobster Council of Canada. The U.S. move to increase the minimum legal size of a lobster carapace, or outer shell, from 82 millimetres to 84 millimetres in January 2025 — and to 86 millimetres in 2027 — would create a mismatch in the closely integrated two-way trading between the countries. photos, more, >>click to read<< 10:22
Op-Ed: Engineering insights when building a trawler
 Constructing a new factory trawler fishing vessel in the United States is not an undertaking for the faint of heart. Thinking back to an article written about 10 years ago, industry scholars predicted a boom in shipbuilding to replace the Alaskan fishing fleet. While naval architects, shipyards and equipment suppliers saw a boom in their immediate future, the renewal of the fishing fleet has barely begun. In fact, less than 5% of the fishing trawlers in the Alaskan fishery have been replaced. The refrigerated seawater (RSW) catcher fleet has seen one large conversion join the ranks. The Amendment 80 fleet has seen three new construction vessels, along with one sponsoning and one conversion project. The American Fisheries Act (AFA) fleet has seen one new-build project completed. Vessels in all three fleets have seen significant upgrades in this time, but the underlying hulls still date from the 1980s and 90s with some going back as far as the 1960s and 70s. more, >>click to read<< 10:16
Constructing a new factory trawler fishing vessel in the United States is not an undertaking for the faint of heart. Thinking back to an article written about 10 years ago, industry scholars predicted a boom in shipbuilding to replace the Alaskan fishing fleet. While naval architects, shipyards and equipment suppliers saw a boom in their immediate future, the renewal of the fishing fleet has barely begun. In fact, less than 5% of the fishing trawlers in the Alaskan fishery have been replaced. The refrigerated seawater (RSW) catcher fleet has seen one large conversion join the ranks. The Amendment 80 fleet has seen three new construction vessels, along with one sponsoning and one conversion project. The American Fisheries Act (AFA) fleet has seen one new-build project completed. Vessels in all three fleets have seen significant upgrades in this time, but the underlying hulls still date from the 1980s and 90s with some going back as far as the 1960s and 70s. more, >>click to read<< 10:16
Canada pledges to work with U.S. over competing claims to Arctic sea floor
 The federal government is pledging to work with its American counterparts after the U.S. claimed parts of the Arctic sea floor that Canada also wants. Grantly Franklin, spokesman for Global Affairs Canada, said in an email that Canada expects to follow the process set out in a United Nations treaty despite the fact the U.S. hasn’t ratified the Convention on the Law of the Sea. “Canada and the U.S. are in frequent communication with regards to the continental shelf in the Arctic and have expressed their commitment along with other Arctic states to the orderly settlement of overlapping claims,” Franklin wrote. more, >>click to read<< 19:43
The federal government is pledging to work with its American counterparts after the U.S. claimed parts of the Arctic sea floor that Canada also wants. Grantly Franklin, spokesman for Global Affairs Canada, said in an email that Canada expects to follow the process set out in a United Nations treaty despite the fact the U.S. hasn’t ratified the Convention on the Law of the Sea. “Canada and the U.S. are in frequent communication with regards to the continental shelf in the Arctic and have expressed their commitment along with other Arctic states to the orderly settlement of overlapping claims,” Franklin wrote. more, >>click to read<< 19:43
First Nations seek salmon return to Columbia Basin in new treaty with U.S.
 Representatives from the Ktunaxa and Syilx Okanagan nations say they continue to bring up salmon restoration in negotiations for a modern Columbia River Treaty and will not stop until a solution can be reached within or outside a new agreement. The U.S.-Canada treaty regulates the cross-border Columbia River to prevent flooding and generate hydro power. A key component of the 62-year-old treaty is set to expire in September 2024, lending urgency to the ongoing talks. “I think what we are doing in the fight to bring salmon back is vital to us moving forward,” said Lower Similkameen Indian Band Chief Keith Crow, who is a member on the Syilx Okanagan Nation’s Chiefs Executive Council and the Nation’s lead in the Columbia River Treaty talks. >>click to read<< 14:25
Representatives from the Ktunaxa and Syilx Okanagan nations say they continue to bring up salmon restoration in negotiations for a modern Columbia River Treaty and will not stop until a solution can be reached within or outside a new agreement. The U.S.-Canada treaty regulates the cross-border Columbia River to prevent flooding and generate hydro power. A key component of the 62-year-old treaty is set to expire in September 2024, lending urgency to the ongoing talks. “I think what we are doing in the fight to bring salmon back is vital to us moving forward,” said Lower Similkameen Indian Band Chief Keith Crow, who is a member on the Syilx Okanagan Nation’s Chiefs Executive Council and the Nation’s lead in the Columbia River Treaty talks. >>click to read<< 14:25

DFO says thousands of illegal shark fins found during Pacific patrol
Canadian fisheries officers discovered more than 3,000 shark fins while conducting a maritime surveillance and enforcement mission in the North Pacific Ocean, according to Fisheries and Oceans Canada. The agency says the fins were illegally possessed or stored on multiple vessels that were inspected during a two-month patrol of the high seas between British Columbia and Japan. Some of the fins were from threatened species, including the oceanic whitetip shark, the DFO said in news  release Thursday. The annual enforcement mission, known as Operation North Pacific Guard, included fishery and coast guard officers from the United States and Japan, as well as a Canadian patrol aircraft temporarily based out of Japan. >>click to read << 16:21
release Thursday. The annual enforcement mission, known as Operation North Pacific Guard, included fishery and coast guard officers from the United States and Japan, as well as a Canadian patrol aircraft temporarily based out of Japan. >>click to read << 16:21

How Shark Meat Is Prepared In US Restaurants
Shark meat is not one of those things we instinctively think of as being good eating. However, like any other kind of athletic fish, shark offers an excellent amount of flavorful, high-protein meat for consumption. Though it is eaten the world over, in the United States it often comes bearing a different name. Though it is prepared in a number of different ways, chances are that, if you’re eating out, you won’t have any idea that there is a shark on your plate. Though it varies between species, shark meat generally has a very meaty texture and is quite mildly flavored. It is therefore easy for shark to substitute for other types of fish. For example, shark is often used to make fish and chips. >>click to read<< 09:38
William R. Miller: Why don’t we restore commercial fishing in Erie?
 There are two kinds of jobs, those that “create wealth” by bringing money into the region from outside the region and those jobs that “circulate wealth” within the region. Fish we take from the lake, crops that we grow, minerals that we extract from the ground, products that we manufacture, retirees we convince to live here, services provided to outside individuals and organizations, and tourists who we attract, all create wealth for the region. Each wealth-creation job typically supports about three wealth-circulating job in the region. We’ll focus here on one potential source for wealth-creating jobs. In 1890, Erie was the largest, in tonnage, freshwater fishing port in the entire world. Today, my understanding is that Erie is down to one commercial fisherman and the Canadian Great Lakes fishing industry is now about a $1 billion industry. What happened? >click to read< 15:45
There are two kinds of jobs, those that “create wealth” by bringing money into the region from outside the region and those jobs that “circulate wealth” within the region. Fish we take from the lake, crops that we grow, minerals that we extract from the ground, products that we manufacture, retirees we convince to live here, services provided to outside individuals and organizations, and tourists who we attract, all create wealth for the region. Each wealth-creation job typically supports about three wealth-circulating job in the region. We’ll focus here on one potential source for wealth-creating jobs. In 1890, Erie was the largest, in tonnage, freshwater fishing port in the entire world. Today, my understanding is that Erie is down to one commercial fisherman and the Canadian Great Lakes fishing industry is now about a $1 billion industry. What happened? >click to read< 15:45

Seafood legislation would ban import of Russian-origin seafood products
Legislation introduced in the U.S. House and Senate this week would impose a ban on the import of all Russian-origin seafood products still making their way into the United States. An executive order signed in March of 2022 by President Biden prohibited the import of unaltered seafood originating in Russia. That order did not, however, block Russian seafood that has been substantially changed through reprocessing in another country. The U.S.-Russian Federation Seafood Reciprocity Act of 2023 was introduced by Sens. Lisa Murkowski and Dan Sullivan, both R-Alaska. Companion legislation was introduced in the House by Reps. Mary Sattler Peltola, D-Alaska, and Garret Graves, R-LA. >click to read< 10:20

Tons of fish caught in Russia is sold in America, despite import ban
President Joe Biden signed an import ban on Russian seafood last year, but fish valued at several hundred millions of dollars are able to evade the ban by diverting to another another country before arriving on American shores. “There has been a huge loophole where the Russians have been now sending their fish – it’s pollock, it’s salmon, a little bit less crab – to other countries for reprocessing, primarily China,” U.S. Sen. Dan Sullivan told reporters Thursday. The ban was intended to ensure Americans aren’t indirectly financing Russia’s war on Ukraine through their purchases. >click to read< 11:07

Today is National Lobster Day
In colonial times and in the early years of the republic, lobster was most often eaten by the lower classes, servants, slaves, and apprentices—it was not until much later that it became a delicacy. This was largely because lobster was so plentiful and cheap. European settlers reported they found them washed ashore in piles two feet high. In these early years, they were known as the “cockroach of the ocean,” and prisoners were even known to refuse to eat them. Although Native Americans ate crustaceans, they also commonly used lobster as fertilizer and on fishing hooks. >click to read< 09:39

Canadian Wildfire Season Is Upon Us (A Few Engineering Notes on the Season)
In case you haven’t noticed the smell of burnt flannel and soft wood in the air, it is definitely Canadian fire season. This French fried time of year is accompanied by acrid smoke, heavy fog like conditions, and a feeling of having smoked a pack of non-filtered camels without actually being a smoker. With the ocean looking like the backstage of a Snoop Dogg concert it is time to take stock of a few issues that may occur. By JJ Johnson, photos, >click to read< 18:44

Canadian and American lobster industry confronts ‘ropeless’ traps after whale entanglements
Injuries to endangered North Atlantic Right Whales ensnared in fishing gear have fueled a prominent campaign by environmental groups to pressure the industry to adopt on-demand equipment that only suspends ropes in the water briefly before traps are pulled from the water. To address the problem, the U.S. and Canadian governments have imposed new regulation on lobster and crab fisheries in recent years, including the use of weak links in rope that break if a whale swims through, color-coded rope for tracing, adding more traps per buoy line, and zone closures during whale migration. Washington and Ottawa are now promoting ropeless fishing as a possible long-term solution. But lobstermen, particularly in Maine where 80% of U.S. lobster is caught, are not enthusiastic. >click to read< 08:49

Contrary to mainstream belief, wind turbines are neither effective nor, in many cases, good for the environment
Claims of wind power being pro-environment often do not consider the damaging effects these projects can have on wildlife and ecosystems, thus hiding the “true cost” of such initiatives. Wind power projects can threaten birds that fly within their vicinity and trigger a decline in their population; it can harm marine life due to noise pollution and affect the growth of plants in the region where it is located. Driven by subsidies granted by the federal government, the growth of wind projects has triggered concerns about the cumulative impacts they have on the environment. There have been growing protests against wind power projects across the world. In the United States, people have opposed setting up wind turbines in Lake Erie due to concerns about the environmental impact of the project. In New Jersey, protestors have asked to pause the development of an offshore wind farm which they claim has led to dolphins and whales washing ashore. >click to read< 12:38

Fishers crabby over Japan’s Russian imports, but Tokyo says Canada exports negligible
Atlantic fishers are feeling the pinch as Japan brings in cheap Russian product rather than Canadian snow crabs, with federal ministers and provincial premiers saying they are raising the issue with Japanese officials. Snow crab prices have dropped in Newfoundland and Labrador from $7.60 per pound at the start of last year’s season to an opening price of $2.20 this year. Fishers in the province have refused to start harvesting this year as they scramble to sell off last year’s surplus, although the price could still rise. Meanwhile, Moscow has flooded other parts of the international market with cheap product. >click to read< 07:58

Commission cuts halibut limits across Alaska, Canada
The International Pacific Halibut Commission adopted its annual catch limits for halibut in 2023 from California to the Bering Sea at its meeting Jan. 27. Coastwide, the total constant exploitation yield, a term for how many total halibut longer than 26 inches are removed from the population, regardless of reason, is just shy of 37 million pounds, a 10% drop from 41.2 million pounds last year. Every regulatory area received a cut except for 2A, which covers California, Oregon and Washington. Area 3A, which covers the central Gulf of Alaska, and area 4A, which covers the eastern Aleutians, saw the largest cuts at 17% each. Southeast Alaska only saw a 1% cut, while the western Gulf, western Aleutians and central Bering Sea each saw 6% cuts. The Canadian coast saw a 10.3% cut. >click to read< 11:50

SEA-NL calls on Ottawa to lift mackerel moratorium; at least match U.S. quota for 2023
Seaward Enterprises Association of Newfoundland and Labrador is calling on Fisheries and Oceans to lift the moratorium on Atlantic mackerel in 2023 and set a quota at least equal to the total allowable catch set this week by the United States. “It’s a senseless sacrifice for Canadian mackerel fishermen to remain under a moratorium when their U.S. cousins have never stopped fishing,” says Ryan Cleary, SEA-NL’s Executive Director. The CBC reports that earlier this week the United States set the 2023 TAC for Atlantic mackerel at 3,639 tonnes, a 27% decrease from that country’s 2022 quota of 4,963 tonnes. Meanwhile, Canada slapped a moratorium on the same Atlantic mackerel stock last year, and Ottawa has yet to announced whether there will be a commercial fishery this year. >click to read the rest< 15:33

U.S. announces reduced East Coast commercial mackerel quota for 2023
The United States will proceed with a commercial fishery of the depleted East Coast mackerel stock it shares with Canada in 2023. The U.S. quota was released this week, putting pressure on Canada which has yet to decide whether it will continue a total moratorium it imposed in 2022 to help rebuild the population. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, the U.S. equivalent of the Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO), announced on Tuesday a total allowable catch of 3,639 metric tonnes. It was 27 per cent cut from 2022 in recognition that the transboundary stock remains in trouble and is overfished. >click to read< 19:01

How new fishing technology could help save North Atlantic right whales
Captain Martin Noel and his crew have returned to the fishing grounds to retrieve their crab traps from the Gulf of St. Lawrence, about 140 kilometres off Shippagan, N.B. At the press of a button on Noel’s smartphone, an acoustic signal from a floating transducer pings an oxygen tank at the bottom of the ocean. That cues the tank to inflate a buoy, in turn, sending to the surface a line of traps from 300 feet below. Brimming with one of Canada’s most lucrative seafood catches, snow crab, these on-demand traps are pivotal to Canada’s plans to protect one of the world’s most critically endangered populations of large whales. >click to read< 10:06

Canada, U.S. fail to reach agreement on quota for shared haddock stock in 2023
Canada and the United States have, for the first time, failed to agree on a shared quota for the transboundary haddock stock on the Georges Bank fishing grounds off southern Nova Scotia. The two countries have jointly managed the haddock fishery and two other straddling stocks, since 2000, but were unable to reach a consensus for the 2023 haddock quota. “While Canada and the U.S. tried to negotiate a shared haddock total allowable catch … our countries will be setting our own total allowable catch independently of the other,” The disagreement centred on the size of the quota cut. >click to read< 07:25
Fisheries minister pushes for joint Canada-U.S. management of depleted Atlantic mackerel stock
“We don’t support the fact that we had closures because the stock was in critical condition and the United States were fishing essentially that same stock,” Canada’s Fisheries and Oceans Minister Joyce Murray told a parliamentary committee Friday. Murray’s remarks are a more public stance on what has been a quiet effort by Canada to persuade the United States to jointly manage a species both countries say is in trouble. Murray said she expressed her concerns in a virtual meeting earlier on Dec. 2 with her U.S. counterpart, Richard Spinrad, who leads the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration or NOAA. “He wants to invoke the precautionary principle, which in my view, wasn’t happening adequately. We agreed that we share our approach to this and in two months there will be meetings between NOAA and DFO to discuss our assessments and build a better approach to rebuilding mackerel.” >click to read< 10:03

The great US offshore wind-power boom has begun to falter
Plans for massive offshore wind farms that President Joe Biden hopes will power as many as 10 million American homes by 2030 are starting to wobble. On Monday, New Jersey utility Public Service Enterprise Group Inc. said it’s deciding whether to pull out of Ocean Wind 1, a proposed project in the Atlantic Ocean that would generate 1.1 gigawatts – enough for 500,000 homes. Less than two weeks earlier, New England utility Avangrid Inc. said its similarly sized Commonwealth Wind project was no longer viable because of higher costs and supply chain woes. Offshore wind projects are “facing a number of headwinds,” Soaring inflation, rising interest rates and supply chain snarls around the world are threatening to hobble the offshore wind boom that both federal and local policy makers have been planning for years off the US East Coast. >click to read< 13:28

North Atlantic right whale’s decline slows, but population falls again
The decline of an endangered species of whale slowed last year, as it lost about 2% of its population, but scientists warn the animal still faces existential threats and is losing breeding females too fast. The North Atlantic right whale’s population was more than 480 in 2010 and fell by more than 25% over the following decade. The North Atlantic Right Whale Consortium, a group of scientists, government officials and industry members, said Monday that the population fell to an estimated 340 last year. That is a decline of eight animals from the previous year, when the population was initially thought to be even fewer. >click to read< Meanwhile in Canada, no right whale deaths have been reported in Canadian waters in three years. >click to read< 08:02
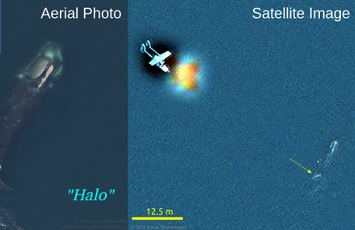
New satellite imagery first to identify North Atlantic right whale from space
New satellite imagery research led by the University of Ottawa is the first to identify a specific endangered Gulf of St. Lawrence North Atlantic right whale from space. Matus Hodul: “The North Atlantic right whale is critically endangered, with about 336 individual whales accounted for. Mortality comes from whales being hit by ships and becoming entangled in fishing gear, so being able to detect and monitor their location is important to conservation efforts. Knowing where the whales are at any given time enables fisheries to open or close to avoid the whales and enables ships to bypass them to prevent collisions.” >click to read< 07:46 ‘Individual North Atlantic right whales identified from space’ >click<

The U.S. is not harvesting as many fish as it could, driving up imports
In 2020, the global fishing industry reached an all-time record of production worth an estimated $406 billion, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Fish is a key source of protein, making it essential in feeding the growing world population. In the United States, New Bedford, Massachusetts, is the country’s most valuable fishing port, bringing in a whopping $376.6 million worth of seafood in 2020. “Fishing stocks did have a collapse in the ’90s. It changed the species that we were offering. It changed the availability. It changed the pricing,” Laura Foley Ramsden, fourth generation “fish mongress” of Foley Fish in New Bedford, 15-minute video, >click to read< 09:52

ENGO recommends against consuming lobster over danger to whales
Seafood Watch, a program out of the Monterey Bay Aquarium, says entanglement in fishing gear is the leading cause of death of the critically endangered North Atlantic right whale population, and US and Canadian lobster fisheries aren’t doing enough to prevent it. Jennifer Dianto Kemmerly is vice president of global ocean conservation at the Aquarium. “We really want consumers and businesses to be aware of how dire the situation is,” Kemmerly said. Meanwhile, the international conservation group Oceana blamed the National Marine Fisheries Service for failing to update safeguards that would protect both right whales and lobster fisheries. To remove the red listing, it recommends using ropeless gear, expanding seasonal closures where whales are present, and improving transparency and monitoring of fishing vessels. >click to read< 18:11

B.C. fishermen fume as their Americans counterparts fish
Commercial salmon fishers and environmentalists are crying foul, for opposite reasons after U.S. fisheries officials let American fishers hit the water while the Canadian government kept their counterparts ashore. After several years of historically low runs, the Pacific Salmon Commission (PSC), an international fisheries management organization, estimated last week that enough sockeye, about 4.4 million, would return to the Fraser River to support a commercial fishery. American fisheries managers adopted the commission’s estimate, opening a small commercial fishing window over the weekend. But in a rare disagreement, Canadian officials did not, citing concerns the run would be nearly one million fish smaller than predicted, and kept Canada’s waters closed. >click to read< 10:16
Concern for BC sockeye salmon as return estimates drop by millions – The Pacific Salmon Commission’s pre-season estimate of 9.8 million returning fish went down to 5.5 million Monday, prompting environmentalists and fishers alike to express concern. >click to read<