Tag Archives: ship strikes
War On Maine’s Lobstermen?
 If you want an emblem of the “man’s man,” larger than life, daring and doing, self-reliant, depend-on-nature, a make-it-happen guy, who rises with the dawn, works hard, asks little, wants little, values independence, and will never fly a desk… that’s the Maine lobsterman or woodsman. Now, they are being scapegoated for wind farms – or some other cause – apparently killing Right whales. Go figure. A more cynical irony is hard to imagine. The wind subsidy crowd, sure they will make money off the taxpayer-funded “green wave” with gold at the end of a government-funded rainbow, has decided – in Washington and “activist cells” around America – to hit Maine’s lobstermen. Wrong. more, >>click to read<< by Robert B. Charles 07:17
If you want an emblem of the “man’s man,” larger than life, daring and doing, self-reliant, depend-on-nature, a make-it-happen guy, who rises with the dawn, works hard, asks little, wants little, values independence, and will never fly a desk… that’s the Maine lobsterman or woodsman. Now, they are being scapegoated for wind farms – or some other cause – apparently killing Right whales. Go figure. A more cynical irony is hard to imagine. The wind subsidy crowd, sure they will make money off the taxpayer-funded “green wave” with gold at the end of a government-funded rainbow, has decided – in Washington and “activist cells” around America – to hit Maine’s lobstermen. Wrong. more, >>click to read<< by Robert B. Charles 07:17

Why are the whales dying? Sea mammal deaths hit record in New York and New Jersey
As whales wash up along East Coast shores at alarming rates, researchers dissect decomposing carcasses, logging whether ship strikes or fishing gear factored into each demise, while some beachgoers wonder if their favorite coastline will be next. At least 14 humpbacks and minke whales have been found dead thus far in 2023 in waters off New York and New Jersey — up from 9 in the entirety of last year. The most recent deaths were two humpbacks, whose corpses were spotted May 31, in Raritan Bay off Keansburg, New Jersey, and Wainscott on Long Island. >click to read< 11:52

Ship Strikes: Thousands of whales are being killed by passing ships. Can we save them?
A collision with a vessel is one of the main threats to whales and if the whale does not die on impact, it is usually only a question of time. In Moon’s case, Wray knows she made the 3,000 mile migration to Hawaii. “We’re actually hoping that she has passed,” says Wray. She has not been seen since December. With potentially thousands of whales hit every year, and with the number of ships rapidly increasing across the globe, the problem is only getting worse. But as the recent UN high seas treaty shows, there is increasing political will to protect the world’s oceans and their inhabitants. The question is whether it is even possible to save the whales from dying at the bows of ships. New technology suggests yes – but it’s going to take all hands on deck. >click to read< 08:01

Whale death confusion abounds, and some is deliberate
Press coverage of the tragic whale deaths is a supreme study in confusion, especially the foolish attempts to somehow exonerate offshore wind development. Here are some prominent examples. The evergreen New York Times wins the race for worst coverage by claiming to explain the numerous recent whale deaths as due to online shopping. I am not making this up. Their headline promises an explanation: “Why 23 Dead Whales Have Washed Up on the East Coast Since December”. The primary reason claimed is that East Coast shipping has increased due to people buying lots of stuff post Covid, especially online, and ship strikes account for a lot of the deaths. >click to read< 13:11

Canada is doing its part to protect right whales
Since 2017, the Canadian lobster industry feels like it’s been trapped in a “South Park” episode. There has been a steady drumbeat eager to “Blame Canada” for the plight of North Atlantic right whales. Right whales were rarely observed in the Gulf of St. Lawrence until recently. All that changed in 2017 when a large number unexpectedly moved to the Gulf. Tragically, we lost 17 right whales: 12 in Canadian waters and five in the United States. Two of the 12 Canadian fatalities were found to be caused by crab gear entanglements. Our Maine peers have made huge strides and sacrifices in recent years to protect right whales. Canada has also been leading the way, with the most aggressive management measures in the world. >click to read< By Geoff Irvine and Nat Richard 15:55

Save Right Whales from Radical Environmentalists Who Exploit Them
Americans agree with protecting the endangered Northern Atlantic right whale. But true conservation efforts don’t necessitate displacing lobstermen and recreational anglers in the process. With fewer than 350 whales left, ambulance-chasing opportunists masquerading as conservationists conveniently swoop in on the whale’s behalf only to leave economic —and environmental—destruction in their paths. This endangered whale requires protection from radical environmentalists who exploit them. Preservationists purporting to care about its well-being, however, distort the threats posed to the whales. >click to read< 08:06

New restrictions on ships to protect whales coming
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has been reviewing the speed regulations it uses to protect North Atlantic right whales, and according to spokesperson Allison Ferreira, the agency will publish new proposed rules within the coming weeks. A public comment process would follow. More than 50 of the whales were struck by ships between spring 1999 and spring 2018, NOAA records indicate. >click to read< 09:36

Ship strikes a cause of whale shark decline
Scientists are looking to better track whale sharks in New Zealand to determine how vulnerable they are to ship strikes after an international study found it may be the cause of their decline. The report, led by the Marine Biological Association of the UK and the University of Southampton, tracked 348 satellite-tagged whale sharks. The tags showed individual whale sharks, which are an endangered species, moving into shipping lanes and then sinking slowly to the sea floor, hundreds of metres below, backing the theory that they were struck by tankers or cargo vessels. >click to read< 10:36
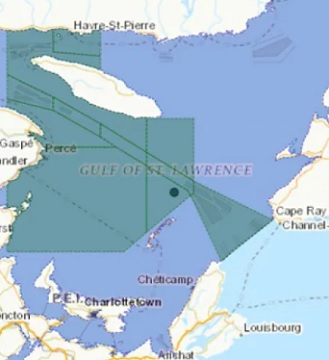
1st Right whale of season spotted in Gulf of St. Lawrence, triggers fishing closure
A surveillance aircraft spotted the whale in the Gulf, north of the Magdalen Islands, on Tuesday, the federal government announced Wednesday afternoon. There is now a 15-day fishing closure in specific fishing grids in the southern Gulf, north of the islands, according to a news release issued by Fisheries and Oceans Canada and the Canadian Coast Guard. In March, the Canadian government announced its fishery and vessel management measures for the 2022 season to protect the endangered whales from entanglements and ship strikes as they migrate into Canadian waters. >click to read< 18:22

Ship strikes may be the difference between extinction and survival for whales
Ship strikes pose a serious threat to whales and have the potential to cause highly endangered subspecies to go extinct. The remaining 1.3 million whales left in our oceans are facing an increasing amount of shipping traffic when coming to the surface and travelling to their feeding or breeding areas. Global maritime traffic increased fourfold between 1992 and 2012. In some corners of the world, such as the Arctic, it actually doubled between 2013 and 2018. The number of whales, in the meantime, is on the decline. >click to read< 07:43
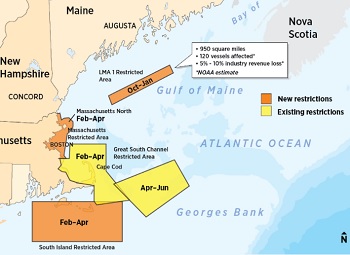
Gulf of Maine: Whale scientists fire back – Marine biologists disagree with a judge’s decision
Lobster industry professionals, elected officials and now a federal judge have expressed doubts as to whether the National Marine Fisheries Service used the best available science in imposing the closure, and whether the whales even frequent the area. They all argue that the statistical modeling used by federal regulators leaves much to be desired. Sean Todd, a marine biologist and director of Allied Whale, a marine mammal research group located at the College of the Atlantic in Bar Harbor, disagrees with both the decision to block the closure and the claim that there are insufficient data to justify it. >click to read< 09:27

Opinion: Federal rules are sinking Maine’s lobster industry
As a lifelong Maine lobsterman, I understand the inherent dangers of my job. I keep watch on the forecast knowing that sudden weather changes can make the difference between a successful day at work and putting my crew’s life at risk. These days, however, the hazard posed by Mother Nature does not compare with the perfect storm of regulations coming out of Washington that threaten my job, our way of life and may eventually sink a fishery that has supported communities and generations of families here in Maine. By Kristan Porter >click to read< 15:18

Tanker/Whale Strike Update: ENGO says number of whales killed by ships each year in the 1000s
We posted a story about a 32-foot whale carcass was found wedged on the bow of a Japanese tanker as it pulled into harbour. Shocking images, wasn’t much there. The article today has information that is useful to commercial fishermen trying to survive the ridiculous, engo inspired rules regarding fishery restrictions, and rule changes. Ship strikes are known to be one of the leading causes of death for endangered and vulnerable whale populations, according to WWF. Michael Fishbach, executive director and co-founder of the Great Whale Conservancy, an environmental NGO based in North Carolina, told Insider that a dozen whales are killed by a ship for each one that is recorded. >click to read< 10:46

Lobster industry is anxious over upcoming North Atlantic right whale protection rules
The federal government is working on new rules designed to reduce risk to North Atlantic right whales,,, One of the threats the whales face is entanglement in ropes that connect to lobster and crab traps in the ocean. Early indications show that the changes required by the rules could be significant. They’re also vulnerable to ship strikes, and face the looming threat of warming oceans. Acting NOAA Fisheries Assistant Administrator Paul Doremus said in June that the U.S. and Canada, which also harvests lobsters, must “take and sustain additional efforts to reduce right whale mortalities and serious injuries.” >click to read< 10:39

Lobster industry changes require more evidence on North Atlantic right whale deaths
Environmentalists and the lobster industry have rarely agreed on anything related to the effort to save the North Atlantic right whale. So when they do, people should pay attention. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration is now taking comment on its Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan, aimed at reducing risk of rope entanglements and ship strikes to the endangered mammal by at least 60%. But members of both sides say no one has enough information to say that the sweeping changes would be effective. Our comment? Don’t pass a plan that puts the deaths of right whales on the backs of Maine lobstermen unless you can show that’s where it should be. >click to read< 08:14

Evidence shows Maine lobster gear has not contributed to decline in Right whale population
In today’s world, it is hard to discern truth from opinion, or fact from calculated lies.,, The fact is also that no documented right whale death has ever been attributed to Maine lobstermen. There has only been one known entanglement in the past 20 years (2012). That whale was disentangled and set free.,,, The combination of ship strikes and snow crab gear entanglement was catastrophic, but had nothing to do with Maine lobster gear. The “guilt by association” assumption by environmental groups and NOAA/NMFS is unwarranted and unacceptable. By Jack Merrill. >click to read< 07:55

Enviros sue for North Atlantic Right Whale protections from ship strikes
Four conservation groups filed an injunction in a Washington, D.C., court last week asking the National Marine Fisheries Service to expand its efforts to protect right whales and their calves from being hit by ships. Although entanglement in fishing lines gets a lot of headlines, ship strikes have emerged as a prime killer of the right whales, whose numbers have dropped from a peak of 481 in 2011 to 356 this year. Eleven calves, including two that were spotted Wednesday off Amelia Island, Florida, so far this calving season are not accounted for in that estimate. >click to read< 09:50

From the sea floor to the courtroom, the fight to save right whales
The North Atlantic right whale is one of the most endangered species on the planet. Scientists announced last month that there are only about 360 of the animals left, down roughly 50 from the previous year’s survey. They live along the East Coast, from northern Florida to Canada, where the 50-foot-long, 140,000-pound leviathans must navigate through millions of commercial fishing lines primarily, lobster traps, and one of the world’s most crowded shipping channels. Too often they become tangled in those lines, or are struck by a ship, (Ships, A LOT of ships). The fight to save them, led by biologists and conservation groups, has grown urgent — in the water and in the courts. >click to read< 11:28

The Judge has ruled! NMFS must list the North Atlantic Right Whale entanglement facts on paper. Case Closed!
Judge Boasberg has ruled! A new accurate ESA analysis has been ordered by next June. The National Marine Fisheries Service just needs to put the lobster entanglement facts on paper and it’s “Case Closed” Not only was there an unusual mortality event in the Gulf of St Lawrence. The Right Whales stopped reproducing. Basically the whales moved up into the South West Gulf of Saint Lawrence in 2015 and took the crab fishermen by surprise and also they set up feeding on copious copepods at the mouth of the St Lawrence River where the Spring flood of nutrients kicks off phytoplankton blooms. Unfortunately this is directly under a shipping lane used solely by cruise ships who traveled at night starting at the end of April.,, by Jim O’Connell, >click to read< 20:26

Whale info way off, by Maine Lobsterman Leonard Young
Reading Bill McWeeny’s July 23 commentary bothered me a great deal. His statement that right whales have never been so close to extinction since they were hunted is untrue. I’ve been a lobsterman for almost 50 years, and we’ve been dealing with the whale issue for almost two decades. When we started this process, we were told there were 200 of these animals. Mr. McWeeny decided to omit the fact that we had modified our gear many years ago with sinking ground lines, breakaways in our end lines and more traps on end lines to decrease end lines. Since we did this, entanglements decreased considerably. These animals had increased to almost 500. Then they changed their feeding ground,, by Maine Lobsterman Leonard Young, Corea >click to read< 11:20

Report: 4 of 5 Gulf of St. Lawrence area right whale deaths investigated last year were caused by ship strikes
The report, compiled by the Marine Animal Response Society and Canadian Wildlife Health Cooperative, says vessel strikes caused four out of the five whale deaths investigated last year. A total of nine right whales were found dead in and around the Gulf of St. Lawrence in 2019. The report released Wednesday focused on the necropsy results for five right whales, all found dead between June and July 2019. It found vessel strikes caused the death of four of them, but the necropsy investigation could not determine the cause of death of the fifth. >click to read< 14:42
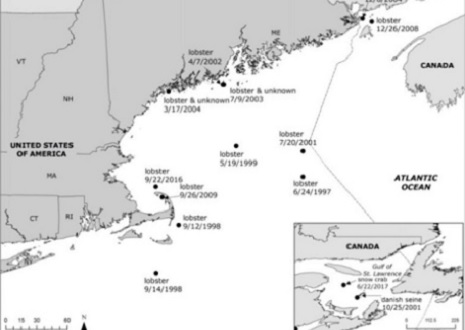
North Atlantic Right Whale: How to kill a species with Fake News, from National Geographic of all places!
“Fishing without vertical lines is what is going to save this species.“ says CT Harry of the IFAW who work hand in hand with NOAA. A ridiculous statement in view of the 18 cruise ship strikes in the Gulf of St. Lawrence (GSL) in the past few years, in all of NE over 20 years. ¼ whale per year by the lobster industry. Eighteen ship strikes in the GSL over the past 3 years averages 6 per year. These people are killing 24 whales while those people kill one. by Jim O’Connell >click to read< 13:22
 Most likely Carnival Cruise Lines is responsible for 18+ Right Whale deaths in the past 3 year, at which rate they would soon be extinct. – Human caused Right whale deaths have suddenly, in sync with a plummeting whale birthrate, put the right whale on the path to extinction. Why their birth rate, births per year, declined since a tremendous surge in 2000-2009 from 350 to 500 is unknown. In 2018 it hit bottom as no calves were born. >click to read<
Most likely Carnival Cruise Lines is responsible for 18+ Right Whale deaths in the past 3 year, at which rate they would soon be extinct. – Human caused Right whale deaths have suddenly, in sync with a plummeting whale birthrate, put the right whale on the path to extinction. Why their birth rate, births per year, declined since a tremendous surge in 2000-2009 from 350 to 500 is unknown. In 2018 it hit bottom as no calves were born. >click to read<
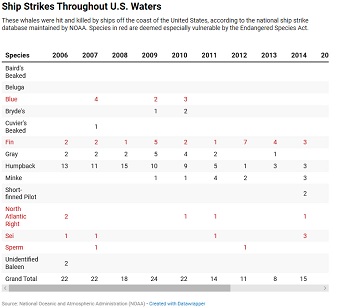
‘Ship Strikes’ Killing Whales! A voluntary slow-down program for passing ships is frequently ignored
According to NOAA, these “ship strikes” are blamed for at least 88 whale deaths in California. Since 2006, 239 whales were killed in all U.S. waters over the same time period. Of those whales killed, nearly one in three was a member of an endangered species. Scientists, however, believe the true number of deaths is far higher than the official counts. “The majority of reported ship strikes probably represents a tenth or less of the true number occurring,” said Calambokidis. “The majority of whales that die, in fact, sink and disappear and are never documented.” Check the chart that says how many estimated by NOAA! >click to read< 14:16

The Risk of Ship Strikes: Maine Congressional Delegation Ask Feds To Shift Focus Of Right Whale Protections
In a letter to top officials at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) this week, the delegation calls on the agency to provide more information about reducing the risk of ship strikes off the United States and Canada – strikes that they say are as much a threat to the whales’ survival as entanglement with lobster fishing gear. >click to read< 10:13
 Most likely Carnival Cruise Lines is responsible for 18+ Right Whale deaths in the past 3 year, at which rate they would soon be extinct – >click to read<
Most likely Carnival Cruise Lines is responsible for 18+ Right Whale deaths in the past 3 year, at which rate they would soon be extinct – >click to read<

Researchers, marine pilots work to prevent vessel strikes from killing Alaska whales
Over the past decade, federal officials have logged 77 incidents of vessels hitting whales in Alaska waters. About three-quarters of those, were endangered humpbacks. But, it’s not clear why those strikes keep happening. A group of federal researchers and marine pilots have teamed up to combine what scientists know about whale behavior with what marine pilots know about ships.,,, That’s important as NOAA has logged 182 whale strikes in U.S. waters over the last decade. But that’s an undercount: ships aren’t legally required to report when they hit whale. And sometimes they don’t even know it’s happened. >click to read< 12:18

Most likely Carnival Cruise Lines is responsible for 18+ Right Whale deaths in the past 3 year, at which rate they would soon be extinct.
Human caused Right whale deaths have suddenly, in sync with a plummeting whale birthrate, put the right whale on the path to extinction.,,, There is the simple answer, to halt the march towards extinction. There is an easy way to prevent those 18 deaths and at least bring that -18 up to 0. We can stop the majority of the anthropogenic Whale deaths with a simple Cruise Ship lane modification between PEI and the tip of the Gaspe Peninsula. Prior to 2007 ships were almost solely responsible for Right whale deaths, but since 2008 fishing line entanglement deaths have increased and fishermen have become the main target. However data from the past 3 years indicate many more ship strike deaths than entanglement deaths. >click to read< 12:41

‘Find some good solutions’: governments, experts, fishermen prepare for 2020 right whale regulations
An annual roundtable meeting held by officials with the Department of Fisheries and Oceans has wrapped up after discussing how to deal with the declining North Atlantic right whale population. The subject has become controversial after at least nine confirmed deaths in 2019, with several preliminary findings indicating vessel strikes were the cause. Some of the deaths came despite the Canadian government cracking down tighter on fisheries closures and speed restrictions, but the impact on the fishing industry is part of what makes regulations such a controversial topic. >click to read< 08:43
Whale Deaths and Ship Strikes: The casualty of a global problem
A humpback whale was recently spotted in the River Thames near London. This unusual sighting sparked national media interest, similar to “Benny” the beluga who also called the river home for several weeks last year. However, while Benny eventually left the Thames and headed home to the Arctic, the humpback whale was not so lucky. Ironically, despite the human-interest factor, the whale died as a result of human impact. In doing so, it had the dubious honor of being the first humpback whale known to have died in UK waters from being hit by a vessel. >click to read< 08:41

Lobstermen, environmentalists weigh in on right whale rules
Some of the largest and most powerful animal and environmental groups – including the Pew Charitable Trust, the U.S. Humane Society, the Conservation Law Foundation and Oceana – sent representatives to the hearing. They urged National Marine Fisheries Service to take immediate action to protect the whale, including proposals that even the team tasked by the fisheries service to come up with its whale protection plan had dismissed, such as offshore closures and ropeless lobster fishing. >click to read< 20:58