Tag Archives: Craig Medred
Bailouts
 The Alaska Congressional delegation is singing praises for a new $100 million bailout of the state’s floundering commercial salmon processing business. In a joint statement from the office of Sen. Lisa Murkowski, the trio applauded the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) move with the state’s senior Republican lawmaker tried to spin it as a new poverty program to provide “almost $100 million of Alaskan seafood for people experiencing food insecurity. “This purchase won’t just bolster Alaska’s seafood industry and support our coastal communities,” Murkowski was quoted as saying, “but will help bring the highest-quality and healthiest seafood products in the world to families in need. I am grateful for the USDA’s investment in our fishermen and the health of Americans.” There has been no actual “investment in our fishermen,” presuming she is talking about Alaska fishermen. But they may benefit from a deal that helps processors clean out some of their inventory before the upcoming fishing season. More, >>click to read<< 13:06
The Alaska Congressional delegation is singing praises for a new $100 million bailout of the state’s floundering commercial salmon processing business. In a joint statement from the office of Sen. Lisa Murkowski, the trio applauded the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) move with the state’s senior Republican lawmaker tried to spin it as a new poverty program to provide “almost $100 million of Alaskan seafood for people experiencing food insecurity. “This purchase won’t just bolster Alaska’s seafood industry and support our coastal communities,” Murkowski was quoted as saying, “but will help bring the highest-quality and healthiest seafood products in the world to families in need. I am grateful for the USDA’s investment in our fishermen and the health of Americans.” There has been no actual “investment in our fishermen,” presuming she is talking about Alaska fishermen. But they may benefit from a deal that helps processors clean out some of their inventory before the upcoming fishing season. More, >>click to read<< 13:06
No-farm farm
 In one of the stranger twists in the strange world of global salmon marketing, Alaska’s non-farm fish farmers played a role in convincing the Canadian city of Ottawa to order removal of billboards protesting farmed salmon. The reason? “False advertising.” And now the same environmental group involved in Ottawa – Wild First – is under fire in British Columbia for running radio advertisements claiming salmon farms have pushed wild Pacific salmon to “the brink of extinction,” according to the news website Business in Vancouver (BIV). That claim is about as far from the truth as one can get. Salmon in the Pacific are today at numbers never seen in recorded history, but most of them are pink salmon. Some scientists contend this explosion of pinks due in part to the free-range fish farming efforts of hatchery operators in Alaska and Russia has reached the point where it is wreaking havoc with the entire North Pacific ecosystem. more, >>click to read<< 07:50
In one of the stranger twists in the strange world of global salmon marketing, Alaska’s non-farm fish farmers played a role in convincing the Canadian city of Ottawa to order removal of billboards protesting farmed salmon. The reason? “False advertising.” And now the same environmental group involved in Ottawa – Wild First – is under fire in British Columbia for running radio advertisements claiming salmon farms have pushed wild Pacific salmon to “the brink of extinction,” according to the news website Business in Vancouver (BIV). That claim is about as far from the truth as one can get. Salmon in the Pacific are today at numbers never seen in recorded history, but most of them are pink salmon. Some scientists contend this explosion of pinks due in part to the free-range fish farming efforts of hatchery operators in Alaska and Russia has reached the point where it is wreaking havoc with the entire North Pacific ecosystem. more, >>click to read<< 07:50
Sea change – Major study links pink salmon and ocean chaos
 Pink salmon and the hatcheries helped boost their numbers to never-before-seen highs were Thursday singled out for disrupting the ecosystem of the North Pacific Ocean to the detriment of other species of salmon, seabirds, whales and more in a peer-reviewed study published in the journal Marine Ecology Progress Serices (MEPS). The study titled “From diatoms to killer whales: impacts of pink salmon on North Pacific ecosystems” concluded that “the evidence is consistent and strong that pink salmon can exert competitive dominance for common-pool prey resources shared by four forage fish species, all five species of Pacific salmon and steelhead trout, and 11 species of seabirds. “It further indicates that pink salmon can have a strong influence on ecosystem structure and function by, for example, initiating pelagic trophic cascades.” >>click to read<< 10:20
Pink salmon and the hatcheries helped boost their numbers to never-before-seen highs were Thursday singled out for disrupting the ecosystem of the North Pacific Ocean to the detriment of other species of salmon, seabirds, whales and more in a peer-reviewed study published in the journal Marine Ecology Progress Serices (MEPS). The study titled “From diatoms to killer whales: impacts of pink salmon on North Pacific ecosystems” concluded that “the evidence is consistent and strong that pink salmon can exert competitive dominance for common-pool prey resources shared by four forage fish species, all five species of Pacific salmon and steelhead trout, and 11 species of seabirds. “It further indicates that pink salmon can have a strong influence on ecosystem structure and function by, for example, initiating pelagic trophic cascades.” >>click to read<< 10:20
Warming bonus
 A warmer ocean continues to smile on Alaska commercial salmon fishermen, but the fish market is sadly another story. The 49th state these days finds itself vying with Russia to become the world’s biggest supplier of cheap salmon to stuff into cans and pouches while upscale consumers spend their money on nice, fat salmon filets. Norwegian salmon farmers – Leroy, Mowi and others who specialize in six-and-a-half to 13-pound Atlanatic – are posting record profits and worry about being taxed by the Norwegian government the way Alaska taxes oil, and Alaska fishermen are waiting to find out just how low the final price for the bulk of their catch, pink salmon that have in recent years averaged 3.4 pounds, according to Alaska Department of Fish and Game data. >>click to read<<
A warmer ocean continues to smile on Alaska commercial salmon fishermen, but the fish market is sadly another story. The 49th state these days finds itself vying with Russia to become the world’s biggest supplier of cheap salmon to stuff into cans and pouches while upscale consumers spend their money on nice, fat salmon filets. Norwegian salmon farmers – Leroy, Mowi and others who specialize in six-and-a-half to 13-pound Atlanatic – are posting record profits and worry about being taxed by the Norwegian government the way Alaska taxes oil, and Alaska fishermen are waiting to find out just how low the final price for the bulk of their catch, pink salmon that have in recent years averaged 3.4 pounds, according to Alaska Department of Fish and Game data. >>click to read<<
. >>click to read<< 11:55

Big ripples – The Pebble Mine saga continues
In a move sure to anger Lower 48 environmentalists and much of Alaska, Gov. Mike Dunleavy has decided to sue the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) over its blocking of a proposed Pebble Mine in the Iliamna Lake drainage of Southwest Alaska. And though the lawsuit is sure to upset many Alaska, it might be the last, best chance the state will ever get to secure the rights to self-government that Alaskans thought were granted at statehood in 1959. A variety of Alaska legal experts, both left and right, this week agreed the state’s appeal to the U.S. Supreme Court is a crapshoot. One called it a classic “hail Mary.” Lots of links,>click to read< 13:01

Dividing the baby
Alaska’s Kenai River is today a textbook example of the problems of managing mixed-stock fisheries right down to commercial set gillnetters protesting they catch comparatively few of the weak stock. The weak stock is in this case Chinook, or what Alaskans usually just call king salmon, and it just happens to be the same fish that gets caught as trawl bycatch in the Gulf of Alaska and the Bering Sea. To date this year, according to National Marine Fisheries Service data, trawlers in the Bering Sea have caught about 11,000 Chinook on their way to a harvest of nearly 1 million metric tons, or about 2.2 billion pounds of pollock. >click to read< 09:04
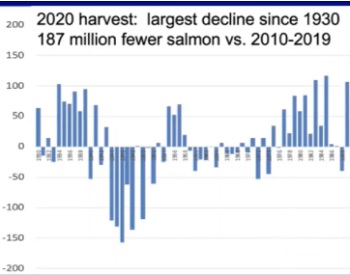
The big bust
The 2020 decline in North Pacific salmon numbers appears to have been the greatest in recorded history, according to a trio of scientists who’ve spent much of their careers studying the secret lives of salmon in the ocean. They suggested to the North Pacific Anadromous Fish Commission (NPAFC), an international monitoring group, that the crash was likely driven by warmer ocean waters and an explosion of pink salmon in 2018 and 2019.,, “Unexpectedly, the high abundance of Pacific salmon came to an abrupt end in 2020. Preliminary commercial catch statistics for all salmon species indicate Pacific salmon harvests, which provide an index of abundance, declined more in 2020 than in any other period on record since 1930. >click to read< 11:01
Common property
Almost four decades ago, a Juneau salmon seiner by the name of Wayne Alex filed a lawsuit aimed at blocking the state of Alaska from taxing commercial fishermen to finance hatcheries. The tax, which the Alaska Legislature obliging called an “assessment” in an effort to avoid an Alaska Constitutional prohibition on dedicated taxes, was intended to benefit private, non-profit aquaculture corporations controlled by commercial fishermen. As the scheme was designed, the hatchery corporations, or “associations” as they were officially called, would run a system of hatcheries to fill the ocean off the 49th state with a bounty of “common property” salmon to benefit Alaskans of all sorts – commercial fishermen, personal-use fishermen, sport fishermen, even subsistence fishermen. Though Alex sued over the tax, it wasn’t his real concern. His fear was that the hatcheries would one day come to replace fishermen like himself. Jump ahead now 39 years and turn your attention north from Juneau for 550 miles to the city of Seward at the head of Resurrection Bay. >click to read< 16:01
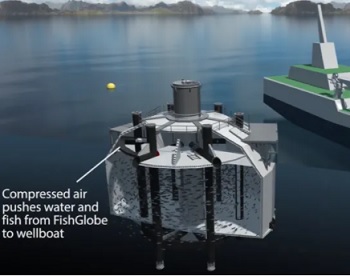
The last cowboys – a replay of the story of cattle in the American West
Norway, a country less than a quarter the size of Alaska, is on pace to bring 1.2 million tonnes of salmon to market this year, and the technologists in that country are talking about the potential to grow their production to 3 million tonnes per year by 2030. Chile, Scotland, the Faroe Islands, and Canada are all significant producers with lesser production in Australia, New Zealand, Iceland, France, Ireland and Finland. Meanwhile, land-based, recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) farms are threatening to lead to an explosion in salmon aquaculture almost everywhere. To truly understand the threat these farmers pose to the future of one of Alaska’s oldest and still largest industries,,, >click to read< 08:52
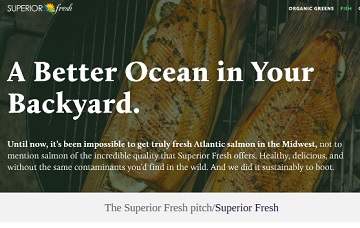
A dark horizon
If you’re an Alaska commercial salmon fishermen, be forewarned; the farmers in Wisconsin are coming for you. Enter the marketers. “A Better Ocean in Your Backyard” is the new marketing theme of Superior Fresh, a recirculating aquaculture system (RAS) farm in America’s Heartland: “Until now, it’s been impossible to get truly fresh Atlantic salmon in the Midwest, not to mention salmon of the incredible quality that Superior Fresh offers. Healthy, delicious, and without the same contaminants you’d find in the wild. And we did it sustainably to boot.” The word that will, or should, jump out to Alaskans (everyone, everywhere) there is “wild.” >click to read< 10:33

Hatchery misfits
Scientists studying pink salmon in Alaska’s Prince William Sound have come to a startling conclusion: Female hatchery fish gone feral reproduce at only about half the rate of their wild cousins. The finding, if confirmed by further studies, could have broad implications for the management of mixed stocks of wild and hatchery salmon. Why hatchery fish perform so poorly in their natural environment is unknown, Alaska Department of Fish and Game biologist Chris Habicht said Friday. The agency researcher cautioned, as well, that the latest finding is based on data from only one reproductive cycle. The dismal spawning success of hatchery fish during 2014-2016 could be a statistical anomaly. Future studies could find higher returns and even out the results when averaged over the years. >click to read<21:41

Framed?
Already struggling financially and facing unhappy neighbors in Alaska’s Kachemak Bay, the Cook Inlet Aquaculture Association (CIAA) now finds itself being drawn into a public-relations mess with four board members charged in an explosive case of illegal fishing. And one of the men charged believes CIAA efforts to grow more salmon is at the heart of the issue.“This is all about politics,” commercial seiner Mark Roth said Thursday. Fishermen regularly fish too close to open-closed lines, stray across and get ticketed. As Mark noted, those cases almost never make the news. ,, For the 64-year-old Mark, sons Paul, 35, and Robert, 39, and friend Eric Winslow, a 61-year-old Alaska fishermen whose home is in Florida, it was different. They this week made the news in a big way,,, >click to read<14:46

Unexpected bounty
Good news at last for salmon-loving Alaskans who’ve watched sockeye returns to the fabled Copper River spurt and falter this year. No, the Copper hasn’t witnessed the miraculous return of tens of thousands of overdue fish, but there are now indications that the disastrously weak run there might be limited to the wild, 26,000-square mile watershed near the Canadian border. An unexpected bounty of sockeye has shown up at Bear Lake on the Kenai Peninsula and the early return of sockeye to the Kenai’s Russian River looks to be tracking the 2017 return, albeit it a week late.,,, Commercial fishermen had harvested 125,000 Bear Lake sockeye through Thursday – about seven times as many as through the same date last year, according to Fish and Game. >click to read<12:34

Horrible timing
The Alaska Department of Fish and Game was Wednesday lobbying Alaska residents to buy Chitina dipnet permits to fish the Copper River even as the troubled, 2018 return of sockeye salmon to that big, muddy drainage was fading so badly that Cordova commercial fishermen pleaded to have the dipnet fishery shut down. “As of today sonar counts are well below projected counts and remain below the minimum threshold of 360,000 sockeye salmon for spawning escapements,” the Cordova District Fishermen United said in a letter to state officials. “In light of the weak early run component, restrictive closures on commercial fishing openers, and no noticeable increase in counts at the sonar currently, it is in the best interest of our sockeye runs to close the Copper River personal use and sport fisheries.” >click to read<18:26

Cordova disaster?
The Copper River commercial salmon fishery will remain closed on Monday, leaving about 550 gillnet fishermen in Cordova to sit in port and ponder what is increasingly looking like a disaster for what is pound-for-pound Alaska’s most valuable sockeye run. Favored fad-fish of high-scale restaurants, Copper sockeye had a reported price on their heads of $8.50 to$9.50 per pound when the season opened, and everything looked good-to-go despite a below-average, pre-season sockeye forecast. >click to read<09:53

Copper failure
The commercial fishing season for Copper River salmon – the most coveted of Alaska fish – is shaping up as a disaster for the isolated fishing community of Cordova. Prices paid to fishermen are now reported at $9.50 per pound for prime fish, but there just aren’t many fish to be had and most of them are small. “Absolutely unprecedented” is how Stormy Haught, the area research biologists for Alaska Department of Fish and Game described the situation Wednesday. Haught is well aware of the long, detailed history of Cooper River commercial fisheries because he’s been back through all the data looking for a parallel to this season that might indicate to fishery managers how they can expect the run to play out going forward. >click to read<08:18

Smoke-filled rooms
With the fishing season beginning in the 49th state, Alaska Gov. Bill Walker has been holding private meetings to forge an agreement between commercial, sport and other fishing interests on how to manage salmon in Cook Inlet. The reason why is unclear. By law, the regulation of state fisheries falls solely under the jurisdiction of the Alaska Board of Fisheries. One of the first acts of the Alaska Legislature after Statehood in 1959 was to establish a Board of Fish and Game – later split into the separate boards for fish and wildlife management – to insulate resource decisions from backroom politicking. >click to read<10:37

Halibut trash
Only in Alaska, which likes to claim title to the world’s “best-managed fisheries,” would halibut now retailing at prices in excess of $20 per pound be ground into fish meal to feed animals, shrimp and maybe even farmed salmon – the bane of Alaska commercial fishermen. Photos of halibut and other, trawl-caught bottomfish headed for the grinder emerged from Kodiak this weekend as Alaska fishermen started into a fishing season where the targeted harvest of halibut by both commercial fishermen and anglers has been seriously restricted because of conservation concerns. >click to read<18:20

Evermore salmon
More research is needed into the interactions of hatchery and wild fish in Alaska before the Alaska Department of Fish and Game approves the dumping of additional pink salmon fry into Prince William Sound, an advisory committee to state regulators decided here this week. Virgil Umphenour, the chair of the committee and a former member of the state Board of Fisheries, says it is troubling that a state which has long prided itself on best-in-the-world, scientific management of its fisheries is allowing ever more salmon ranching with little clue as to the impacts on wild fish.,, There are obvious impacts, says Nancy Hillstrand of Homer, who has become an activist for wild fish. >click to read<08:45

Deadly success?
Twenty-eight years ago, the state of Alaska banned fish farming in favor of salmon ranching. The idea was simple: Catch a bunch of fish, squeeze out their eggs and sperm, mix the two together, hatch the eggs, raise the little fish in a hatchery, dump them in the ocean, wait for them to come back, and net the money. What could possibly go wrong? Maybe this: From 1985 to 1994, before the hatchery program seriously geared up in the Prince William Sound, the commercial catch of sockeye (red) salmon in Cook Inlet averaged about 5.3 million fish per year.>click to read<10:34

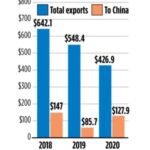
China’s fish
The national seafood media was Monday atwitter with speculation China might impose tariffs on American seafood, and Alaska Commissioner of Commerce Mike Navarre was trying to spin the state’s proposed liquified natural gas (LNG) project as some sort of shelter against a looming U.S.-China trade war. “For now, China appears to be leaving Alaska seafood alone,” added reporter Liz Raines. There was no “appears” about it.,, Why? Because China – sometimes with the help of North Korean serfs – has turned Alaska fish into a moneymaker for China. >click to read< 14:16

Stormy horizons – Salmon farms
Good news for Alaska commercial fishermen: Salmon last year ranked as the favorite fish at Japanese conveyor-belt sushi restaurants for the sixth year in a row, according to a survey by seafood processor Maruha Nichiro. Bad news for Alaska fishermen: “Ninety percent of that salmon is imported from Chile and Norway, but its popularity is now spurring domestic fish farming,” Nikkei Asian Review reported earlier this month. The report of Japanese domestic fishing farming might be the worst news of all. >click to read<09:02

No kings
Snow and ice still cover the tributaries of the Susitna River basin, but already the Alaska Department of Fish and Game is talking about closing the Chinook salmon fishery for the 2018 season. The agency’s fear for the drainages of both the Susitna and Little Susitna mirrors the 2017 fear for the 24,000-square-mile Copper River basin : No king salmon. In the case of the Copper last year, the state was faced with a scientifically calculated Chinook forecast calling for the return of 29,000 of the fish – only 5,000 more than were needed for spawning in streams located behind a gauntlet of commercial, subsistence, personal-use dipnet, and rod-and-reel fisheries. >click to read<14:48

Little red salmon
The wolves of Southwest Alaska share something in common with the wolves of Denali, according to a new National Park Service-sponsored study, they love fish – salmon to be specific. Following on the pioneering work of U.S. Geological Survey biologist Layne Adams in Denali National Park and Preserve in 2010, researchers who spent five years monitoring the diets of six wolf-packs in Lake Clark National Park and Preserve have documented high use of salmon by wolves there. A few Lake Clark area wolves even appear to have adapted to a prey-switching strategy that takes advantage of the decades that Alaska state salmon managers have devoted to boosting salmon runs to streams draining into Bristol Bay. click here to read the story 14:38
Prelude to war – A news analysis
 The mayor of Kenai, Alaska is “extremely disappointed” with the Alaska Board of Fisheries, and the mayor of the Matanuska-Susitna Borough less than pleased but “satisfied” with the Board’s big compromise. The big compromise itself? The Board will avoid both Wasilla and Kenai in favor of a 2020 meeting in Anchorage. So contentious has become the issue of Cook Inlet fishery management that politicians now argue over minutiae while the bigger issues plaguing the Inlet’s fisheries are ignored. click here to read the story 10:46
The mayor of Kenai, Alaska is “extremely disappointed” with the Alaska Board of Fisheries, and the mayor of the Matanuska-Susitna Borough less than pleased but “satisfied” with the Board’s big compromise. The big compromise itself? The Board will avoid both Wasilla and Kenai in favor of a 2020 meeting in Anchorage. So contentious has become the issue of Cook Inlet fishery management that politicians now argue over minutiae while the bigger issues plaguing the Inlet’s fisheries are ignored. click here to read the story 10:46
Pebble rising?
 Once thought to be on the verge of death, Alaska’s proposed Pebble prospect copper and gold mine seems to be taking on a new life. First came the July announcement by the Environmental Protection Agency of President Donald Trump that it planned to lift a proposed ban on the mine ordered by the EPA of President Barrack Obama.,,, The Pebble Limited Partnership sued the Obama administration and the EPA of Trump – taking a page from the playbook of enviromental organizations fond of filing lawsuits to leverage legal settlements – in this case negotiated an agreement allowing Pebble to apply for the necessary permits. click here to read the story 09:37
Once thought to be on the verge of death, Alaska’s proposed Pebble prospect copper and gold mine seems to be taking on a new life. First came the July announcement by the Environmental Protection Agency of President Donald Trump that it planned to lift a proposed ban on the mine ordered by the EPA of President Barrack Obama.,,, The Pebble Limited Partnership sued the Obama administration and the EPA of Trump – taking a page from the playbook of enviromental organizations fond of filing lawsuits to leverage legal settlements – in this case negotiated an agreement allowing Pebble to apply for the necessary permits. click here to read the story 09:37