Tag Archives: North Pacific Fishery Management Council
Federal judge dismisses Alaska trawlers’ lawsuit that sought to overturn halibut limits
 A federal judge has dismissed a lawsuit that sought to overturn new halibut bycatch limits on deep-sea trawlers that fish in federal waters off Alaska. The lawsuit was filed by Groundfish Forum Inc., a Seattle-based trawl trade group, after the North Pacific Fishery Management Council passed a rule that reduces halibut bycatch limits for many trawlers when there are fewer halibut in Alaska waters. The National Marine Fisheries Service, in charge of implementing the rule, moved to dismiss the lawsuit, and U.S. District Court Judge Sharon Gleason ruled in favor of the agency on Nov. 8. Intrafish, a trade publication, first reported on the ruling. The lawsuit has been a major issue in fishing communities across the Gulf of Alaska. Some of those communities joined the federal government in defense, as did various fishing and conservation organizations. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 10:22
A federal judge has dismissed a lawsuit that sought to overturn new halibut bycatch limits on deep-sea trawlers that fish in federal waters off Alaska. The lawsuit was filed by Groundfish Forum Inc., a Seattle-based trawl trade group, after the North Pacific Fishery Management Council passed a rule that reduces halibut bycatch limits for many trawlers when there are fewer halibut in Alaska waters. The National Marine Fisheries Service, in charge of implementing the rule, moved to dismiss the lawsuit, and U.S. District Court Judge Sharon Gleason ruled in favor of the agency on Nov. 8. Intrafish, a trade publication, first reported on the ruling. The lawsuit has been a major issue in fishing communities across the Gulf of Alaska. Some of those communities joined the federal government in defense, as did various fishing and conservation organizations. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 10:22

Multiple groups urge seafloor protections from pelagic trawling
A diverse group of harvesters, conservation entities and others are calling on federal fisheries managers to do more to protect seafloor habitats from midwater trawl nets they say are dragging the bottom of the ocean floor. Midwater, or pelagic trawling — used to catch schooling fish like pollock, is supposed to be fished in the water column rather than on the seafloor. For this reason, pelagic trawling is allowed in most conservation areas closed to bottom trawling — a form of fishing where nets are purposely dragged on the seafloor and damage corals, sponges and other living seafloor habitats in the process. An analysis by the National Marine Fisheries Service indicates that 40% to 100% of the width of pelagic trawl gear fished in the Gulf of Alaska and Bering Sea has been in contact with the seafloor, and that these nets, which range from 50 to 190 yards wide, are dragged for miles. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 20:12

In surprising move, Bering Sea snow crab fishery to reopen after 2 year closure
The Alaska Department of Fish and Game announced Friday afternoon that Bering Sea fishermen will be allowed to harvest a total of about 4.7 million pounds of opilio, also known as snow crab, for the first time in two years. According to Fish and Game, estimates of total mature male biomass are above the threshold required to open the fishery. The announcement comes as a surprise to many fishermen, after roughly 10 billion snow crabs disappeared from the Bering Sea over a span of four years, and Fish and Game closed the fishery in 2022. Recently, scientists have learned that the disappearance was likely due to ecological shifts, and there’s been little hope within the industry that stocks would recover anytime soon. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 10:49

Biden administration rejects top Inslee choice for Alaska fish commission, reappoints trawl ally
The Biden administration has rejected a nominee for a key Alaska fisheries management post who could have tipped decisions toward the interests of tribes and conservation groups and away from the priorities of the large-boat, Seattle-based trawl industry. U.S. Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo skipped over the top choice of Washington Democratic Gov. Jay Inslee, conservation advocate Becca Robbins Gisclair, and instead reappointed the last-ranked nominee on a slate of four candidates that Inslee offered: Anne Vanderhoeven, a trawl industry employee who has served on the panel for several years. Raimondo’s choice for the open North Pacific Fishery Management Council seat, which was confirmed Tuesday by Inslee’s natural resources advisor Ruth Musgrave, comes after what advocates describe as weeks of intense lobbying by supporters of both Gisclair and Vanderhoeven. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 11:47
Alaska’s declining crab population due to trawlers catches attention of lawmaker
 Alaska Rep. Mary Peltola’s mounting frustration with the largely Seattle-based pollock industry’s decades-old issue of inadvertently damaging the state’s rapidly declining crab populations and critical habitat for many other species may result in legislation a move heralded by the scientific and conservation communities. Members of the scientific community concerned with sustainability and conservation are currently in a deadlock with industrial pollock trawler fleets and the North Pacific Fishery Management Council over federal fishery regulations, including pelagic, or “mid-water” trawling, which uses wide-mouthed nets designed to target schools of Bering Sea Alaskan pollock. The Alaska Marine Conservation Council released a report in February 2023 analyzing the trawlers’ impact on red king crab habitats following the 2022 closure of the Alaska snow crab fisheries, which is still ongoing, and a two-year closure for Bristol Bay king crab that ended in 2023, underscoring the devastating environmental and financial toll. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 19:17
Alaska Rep. Mary Peltola’s mounting frustration with the largely Seattle-based pollock industry’s decades-old issue of inadvertently damaging the state’s rapidly declining crab populations and critical habitat for many other species may result in legislation a move heralded by the scientific and conservation communities. Members of the scientific community concerned with sustainability and conservation are currently in a deadlock with industrial pollock trawler fleets and the North Pacific Fishery Management Council over federal fishery regulations, including pelagic, or “mid-water” trawling, which uses wide-mouthed nets designed to target schools of Bering Sea Alaskan pollock. The Alaska Marine Conservation Council released a report in February 2023 analyzing the trawlers’ impact on red king crab habitats following the 2022 closure of the Alaska snow crab fisheries, which is still ongoing, and a two-year closure for Bristol Bay king crab that ended in 2023, underscoring the devastating environmental and financial toll. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 19:17
The federal government is assuming management of salmon fishing in parts of Alaska’s Cook Inlet
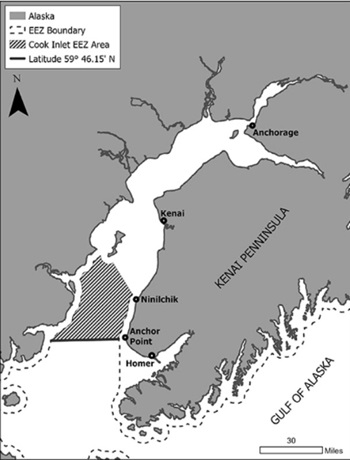 Commercial and recreational salmon fishing in the federal waters of Cook Inlet will resume this summer, but under new management by the federal government, according to a rule made final this week. Until now, the state had managed salmon fisheries in both state and federal waters of the inlet. But the switch in management was ordered by federal courts, as a result of litigation stretching back a decade. The United Cook Inlet Drift Association, or UCIDA, which is made up of commercial salmon fishers, sued the federal government in 2013 for failing to develop a salmon harvest management plan for the federal waters of the inlet. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 13:11
Commercial and recreational salmon fishing in the federal waters of Cook Inlet will resume this summer, but under new management by the federal government, according to a rule made final this week. Until now, the state had managed salmon fisheries in both state and federal waters of the inlet. But the switch in management was ordered by federal courts, as a result of litigation stretching back a decade. The United Cook Inlet Drift Association, or UCIDA, which is made up of commercial salmon fishers, sued the federal government in 2013 for failing to develop a salmon harvest management plan for the federal waters of the inlet. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 13:11
Alaska lawmakers, residents ask feds to limit how much salmon industrial trawlers catch
 U.S. Rep. Mary Peltola, Alaskan Natives, and family-owned fisheries are looking for a sea change in the fishing rights battle between local fishermen and industrial trawling fishing operations after a federal council recently denied a tribe-approved reduction in chum salmon catches. In western Alaska, local communities are facing a significant decline in salmon populations. The cause of this decline remains a subject of intense debate between industry leaders, subsistence communities, conservation scientists, and local fishermen. Residents point to the Seattle-based trawler fleets in the Bering Sea fishing for pollock but unintentionally catching thousands of chum salmon as bycatch instead. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 11:31
U.S. Rep. Mary Peltola, Alaskan Natives, and family-owned fisheries are looking for a sea change in the fishing rights battle between local fishermen and industrial trawling fishing operations after a federal council recently denied a tribe-approved reduction in chum salmon catches. In western Alaska, local communities are facing a significant decline in salmon populations. The cause of this decline remains a subject of intense debate between industry leaders, subsistence communities, conservation scientists, and local fishermen. Residents point to the Seattle-based trawler fleets in the Bering Sea fishing for pollock but unintentionally catching thousands of chum salmon as bycatch instead. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 11:31
NOAA Fisheries Denies Request for Emergency Action on Bering Sea Chinook Salmon Bycatch
 NOAA Fisheries denied a request for emergency action to institute a cap of zero on Chinook salmon bycatch in the Bering Sea pollock fishery. The request was submitted on January 17, 2024. It effectively asked Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo to close the Bering Sea pollock fishery, which opened on January 20, 2024. It was submitted by: Association of Village Council Presidents, Kuskokwim River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission, Tanana Chiefs Conference, Yukon River Drainage Fisheries Association, Yukon River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission. The petition also requested that the Department of Commerce urge the North Pacific Fishery Management Council to evaluate and update current Chinook salmon bycatch management. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 13:08
NOAA Fisheries denied a request for emergency action to institute a cap of zero on Chinook salmon bycatch in the Bering Sea pollock fishery. The request was submitted on January 17, 2024. It effectively asked Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo to close the Bering Sea pollock fishery, which opened on January 20, 2024. It was submitted by: Association of Village Council Presidents, Kuskokwim River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission, Tanana Chiefs Conference, Yukon River Drainage Fisheries Association, Yukon River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission. The petition also requested that the Department of Commerce urge the North Pacific Fishery Management Council to evaluate and update current Chinook salmon bycatch management. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 13:08

Fishery council seeks more information before deciding on chum bycatch in Bering Sea pollock fishery
The North Pacific Fishery Management Council, which manages federal fisheries in Alaska, will continue to explore options for how to manage chum salmon bycatch in the Bering Sea pollock fishery. The council, facing rising pressure from western Alaska communities who depend on chum as a cornerstone of subsistence, released a statement Wednesday summarizing their decision from their April meeting. Dismal western Alaska salmon returns have reached crisis levels. And while the council listened to scores of harrowing testimonies recalling empty rivers and vacant fish camps, the council was also presented with research that suggested bycatch limits wouldn’t do much to help the crisis. “Available science indicates recent declines in chum salmon populations across many regions of the North Pacific, including Canada, Japan, Russia, Korea, and the U.S., appear to be driven by warmer water temperatures in both the marine and freshwater environments,” the council said in the statement. more, >>click to read<< 12:38
Western Alaska tribes, outraged by bycatch, turn up the heat on fishery managers and trawlers
 Earlier this spring, Maurice McGinty, a tribal leader from the village of Nulato, pulled out his last mason jar of smoked Yukon king. “We have no more now,” said McGinty, 80. He added: “They are pushing us, and our traditional way of life, into a hole.” Imagine hearing and reading versions of McGinty’s story dozens of times, told by Indigenous people who live along the Yukon and another iconic subsistence river in Southwest Alaska, the Kuskokwim. That’s the reality this week for the policymakers on the North Pacific Fishery Management Council, the federal commission that regulates commercial fishing in the American waters of the Bering Sea. On one side are tribal leaders from the Yukon and Kuskokwim, On the other side are representatives for the trawlers, more, >>click to read<< 13:51
Earlier this spring, Maurice McGinty, a tribal leader from the village of Nulato, pulled out his last mason jar of smoked Yukon king. “We have no more now,” said McGinty, 80. He added: “They are pushing us, and our traditional way of life, into a hole.” Imagine hearing and reading versions of McGinty’s story dozens of times, told by Indigenous people who live along the Yukon and another iconic subsistence river in Southwest Alaska, the Kuskokwim. That’s the reality this week for the policymakers on the North Pacific Fishery Management Council, the federal commission that regulates commercial fishing in the American waters of the Bering Sea. On one side are tribal leaders from the Yukon and Kuskokwim, On the other side are representatives for the trawlers, more, >>click to read<< 13:51
Federal judge to rule on reduction in trawler halibut bycatch
 A U.S. District court judge is expected to issue a decision this spring on a lawsuit filed by the Groundfish Forum challenging a National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS) decision setting abundance-based limits on halibut bycatch in the Amendment 80 Bering Sea trawl fishery. The Groundfish Forum, based in Seattle, filed its complaint with the U.S. District Court in Anchorage on Dec. 19, challenging the new halibut bycatch rules that were first adopted by the North Pacific Fishery Management Council and subsequently approved by NMFS. On Feb. 29, the Halibut Defense Alliance intervened on the side of NMFS over concerns about the number of halibut taken as bycatch by Amendment 80 vessels in the Bering Sea, saying the limits on halibut bycatch would ensure more equitable access to halibut fisheries. The alliance is a broad coalition of commercial harvesters, charter operators, processors and community organizations representing halibut-dependent communities in Alaska and the Pacific Northwest. more, >>click to read<< 19:52
A U.S. District court judge is expected to issue a decision this spring on a lawsuit filed by the Groundfish Forum challenging a National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS) decision setting abundance-based limits on halibut bycatch in the Amendment 80 Bering Sea trawl fishery. The Groundfish Forum, based in Seattle, filed its complaint with the U.S. District Court in Anchorage on Dec. 19, challenging the new halibut bycatch rules that were first adopted by the North Pacific Fishery Management Council and subsequently approved by NMFS. On Feb. 29, the Halibut Defense Alliance intervened on the side of NMFS over concerns about the number of halibut taken as bycatch by Amendment 80 vessels in the Bering Sea, saying the limits on halibut bycatch would ensure more equitable access to halibut fisheries. The alliance is a broad coalition of commercial harvesters, charter operators, processors and community organizations representing halibut-dependent communities in Alaska and the Pacific Northwest. more, >>click to read<< 19:52
Regional council says it won’t tighten fishing regulations in Bristol Bay red king crab savings area
 The North Pacific Fishery Management Council will not move forward with a request to close the Bristol Bay red king crab savings area to all commercial fishing. At its February meeting, the regulatory council looked at the effectiveness of closing the 4,000-square-nautical-mile section of the eastern Bering Sea to commercial trawl, pot and longline fishing, but decided not to tighten regulations in the area. The savings box was established in 1996 as a haven for the massive crab species. It is already permanently closed to bottom trawling, but it remains open to midwater, or pelagic trawlers, pot fishing and longlining. Non-pelagic, known as bottom trawling, is allowed in a small section within the savings area — known as the savings subarea — when crabbers are harvesting the species. The council also evaluated a pot gear closure of a large section in the eastern portion of Bristol Bay, known as Area 512, to address drops in the Bristol Bay red king crab stock. All trawling is already prohibited in that area. more, >>click to read<< 12:38
The North Pacific Fishery Management Council will not move forward with a request to close the Bristol Bay red king crab savings area to all commercial fishing. At its February meeting, the regulatory council looked at the effectiveness of closing the 4,000-square-nautical-mile section of the eastern Bering Sea to commercial trawl, pot and longline fishing, but decided not to tighten regulations in the area. The savings box was established in 1996 as a haven for the massive crab species. It is already permanently closed to bottom trawling, but it remains open to midwater, or pelagic trawlers, pot fishing and longlining. Non-pelagic, known as bottom trawling, is allowed in a small section within the savings area — known as the savings subarea — when crabbers are harvesting the species. The council also evaluated a pot gear closure of a large section in the eastern portion of Bristol Bay, known as Area 512, to address drops in the Bristol Bay red king crab stock. All trawling is already prohibited in that area. more, >>click to read<< 12:38
Trade groups and state unhappy with federal NOAA Fisheries management plan plan in public comments
 Public comment is in for a NOAA Fisheries management plan for Cook Inlet’s most productive drift fishing waters. In nearly 90 submitted public comments, cities, tribes, trade organizations and the state commissioner of Fish and Game express mixed and negative reactions to the plan. The Cook Inlet Exclusive Economic Zone, or EEZ, was the subject of a lawsuit by the United Cook Inlet Drift Association over management of the fishery, which starts three miles offshore and stretches from south 0 f Kalgin Island to Anchor Point. In response, the federal North Pacific Fishery Management Council closed the fishery in 2020, which was met with protest by Kenai Peninsula commercial fishermen. more, >>click to read<< 10:52
Public comment is in for a NOAA Fisheries management plan for Cook Inlet’s most productive drift fishing waters. In nearly 90 submitted public comments, cities, tribes, trade organizations and the state commissioner of Fish and Game express mixed and negative reactions to the plan. The Cook Inlet Exclusive Economic Zone, or EEZ, was the subject of a lawsuit by the United Cook Inlet Drift Association over management of the fishery, which starts three miles offshore and stretches from south 0 f Kalgin Island to Anchor Point. In response, the federal North Pacific Fishery Management Council closed the fishery in 2020, which was met with protest by Kenai Peninsula commercial fishermen. more, >>click to read<< 10:52
Ecosystem reports show continuing effects of warming in Alaska’s marine waters
 The waters off Alaska’s Aleutian Islands registered the warmest winter temperatures in over a century, part of a decade-long period of warming, according to a report issued by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The Aleutians report is one of three annual ecosystem status reports issued by NOAA Fisheries for marine areas of Alaska. The reports, compiled by large teams of scientists, were released earlier this month and presented to the North Pacific Fishery Management Council, the panel that sets regulated commercial fishing in federal waters off Alaska. The Bering Sea remains warmer than the long-term average, though it has cooled since the heatwaves, NOAA Fisheries biologist Elizabeth Siddon told the North Pacific Fishery Management Council in her presentation of the report. more, >>click to read<< 07:53
The waters off Alaska’s Aleutian Islands registered the warmest winter temperatures in over a century, part of a decade-long period of warming, according to a report issued by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The Aleutians report is one of three annual ecosystem status reports issued by NOAA Fisheries for marine areas of Alaska. The reports, compiled by large teams of scientists, were released earlier this month and presented to the North Pacific Fishery Management Council, the panel that sets regulated commercial fishing in federal waters off Alaska. The Bering Sea remains warmer than the long-term average, though it has cooled since the heatwaves, NOAA Fisheries biologist Elizabeth Siddon told the North Pacific Fishery Management Council in her presentation of the report. more, >>click to read<< 07:53
Bering Sea trawl fleet files lawsuit over new halibut bycatch limits
 A trade association representing the Bering Sea bottom-trawl fleet filed a lawsuit this week in federal court, arguing that new halibut bycatch limits are unfair and unlawful. The North Pacific Fishery Management Council in December 2021 approved a new halibut bycatch quota system based on annual surveys of the valuable flatfish. Instead of the current fixed limits, a new abundance-based system means that when halibut stocks are low, bycatch caps could be cut by up to 35%. Based in Washington state, Groundfish Forum — representing five companies and 17 bottom-trawl vessels — sued the National Marine Fisheries Service on Tuesday in response to the new limits, which are set to go into effect Jan. 1. Attorneys argue that the trawl fleet was unfairly singled out by the new rules that could result in “drastic economic consequences.” more, >>click to read<< 08:04
A trade association representing the Bering Sea bottom-trawl fleet filed a lawsuit this week in federal court, arguing that new halibut bycatch limits are unfair and unlawful. The North Pacific Fishery Management Council in December 2021 approved a new halibut bycatch quota system based on annual surveys of the valuable flatfish. Instead of the current fixed limits, a new abundance-based system means that when halibut stocks are low, bycatch caps could be cut by up to 35%. Based in Washington state, Groundfish Forum — representing five companies and 17 bottom-trawl vessels — sued the National Marine Fisheries Service on Tuesday in response to the new limits, which are set to go into effect Jan. 1. Attorneys argue that the trawl fleet was unfairly singled out by the new rules that could result in “drastic economic consequences.” more, >>click to read<< 08:04
Federal fisheries managers hold Bering Sea pollock quota steady
 The total amount of pollock allowed to be scooped up by trawlers in the Bering Sea will stay the stotal allowable catchame in 2024. In its Dec. 9 meeting in Anchorage, the North Pacific Fishery Management Council moved to keep the total allowable catch for pollock at its current level of 1.3 million metric tons, a move that has generated criticism from conservationists, tribes, and the trawling industry alike. Alaska’s pollock fishery is responsible for the vast majority of salmon bycatch in the region. And amid alarming declines in returns of multiple species of salmon to Western Alaska rivers, the pollock trawl fishery has faced increasing criticism for its perceived role driving the crisis. But federal fisheries managers and the trawling industry pushed back, asserting that the claims are unfounded. more, >>click to read<< 08:12
The total amount of pollock allowed to be scooped up by trawlers in the Bering Sea will stay the stotal allowable catchame in 2024. In its Dec. 9 meeting in Anchorage, the North Pacific Fishery Management Council moved to keep the total allowable catch for pollock at its current level of 1.3 million metric tons, a move that has generated criticism from conservationists, tribes, and the trawling industry alike. Alaska’s pollock fishery is responsible for the vast majority of salmon bycatch in the region. And amid alarming declines in returns of multiple species of salmon to Western Alaska rivers, the pollock trawl fishery has faced increasing criticism for its perceived role driving the crisis. But federal fisheries managers and the trawling industry pushed back, asserting that the claims are unfounded. more, >>click to read<< 08:12
NOAA Fisheries releases more information about ‘high level’ of killer whales caught this year by Alaska trawl fleet
 Six killer whales caught in trawl net gear this year in waters off Alaska died as a result of their entanglement, while a seventh whale was seriously injured by this gear, according to a NOAA Fisheries statement released Friday. The trawl fishing industry’s 2023 take of killer whales, first made by public NOAA Fisheries in September, is significantly higher than in recent years past, according to a review of NOAA Fisheries death tolls through 2021. Bering Sea killer whales are not listed under the Endangered Species Act but are protected under the Marine Mammal Protection Act. John Gauvin, fisheries science director for the Alaska Seafood Cooperative, “We want to conduct our fisheries without harming orcas and we’re taking steps to avoid future mortalities,” more, >>click to read<< 10:19
Six killer whales caught in trawl net gear this year in waters off Alaska died as a result of their entanglement, while a seventh whale was seriously injured by this gear, according to a NOAA Fisheries statement released Friday. The trawl fishing industry’s 2023 take of killer whales, first made by public NOAA Fisheries in September, is significantly higher than in recent years past, according to a review of NOAA Fisheries death tolls through 2021. Bering Sea killer whales are not listed under the Endangered Species Act but are protected under the Marine Mammal Protection Act. John Gauvin, fisheries science director for the Alaska Seafood Cooperative, “We want to conduct our fisheries without harming orcas and we’re taking steps to avoid future mortalities,” more, >>click to read<< 10:19
Opinion: The tragic mismanagement of bycatch in Alaska
 The commissioner of the Alaska Department of Fish & Game’s recent opinion piece on bycatch would make for good comedy if the topic wasn’t so serious. Doug Vincent-Lang extolled the North Pacific Fishery Management Council’s handling of bycatch in trawl fisheries off the coast of Alaska. As examples, he mentioned existing bycatch caps for chinook salmon and halibut bycatch measures that are not yet in effect. Other than that, here are the council “actions” he espouses. The council, of which he is a key member, has “initiated an analysis” concerning caps on chum bycatch, is “considering further fishing restrictions” related to crab in the Bering Sea and is “evaluating whether further protections are needed” for Tanner crab in the Gulf. He also notes that the council “support(s) further research” into the causes of the declines in these seminal Alaska fisheries stocks. >>click to read<< 12:29
The commissioner of the Alaska Department of Fish & Game’s recent opinion piece on bycatch would make for good comedy if the topic wasn’t so serious. Doug Vincent-Lang extolled the North Pacific Fishery Management Council’s handling of bycatch in trawl fisheries off the coast of Alaska. As examples, he mentioned existing bycatch caps for chinook salmon and halibut bycatch measures that are not yet in effect. Other than that, here are the council “actions” he espouses. The council, of which he is a key member, has “initiated an analysis” concerning caps on chum bycatch, is “considering further fishing restrictions” related to crab in the Bering Sea and is “evaluating whether further protections are needed” for Tanner crab in the Gulf. He also notes that the council “support(s) further research” into the causes of the declines in these seminal Alaska fisheries stocks. >>click to read<< 12:29
OPINION: North Pacific Fishery Management Council is acting to reduce bycatch
 In a recent opinion piece, Brooke Woods, Linda Behnken and Nanci Morris Lyon stated, “Federal fisheries off Alaska are managed via the dictates of the North Pacific Fishery Management Council (NPFMC), which has done little to address the trawl fleet’s enormous bycatch of species immeasurably important to Alaskans.” Nothing could be further from the truth The council adopted hard caps for chinook salmon in the Bering Sea trawl pollock fisheries that vary depending upon the expected returns to western Alaska rivers. When expected returns are low, the caps are adjusted downward. Additionally, the fishing industry has stepped forward to implement chinook salmon avoidance measures that hold each vessel accountable for limiting bycatch to below the caps. In fact, the fleet is well below their caps, recognizing the need to rebuild these stocks. >>click to read<< 15:55
In a recent opinion piece, Brooke Woods, Linda Behnken and Nanci Morris Lyon stated, “Federal fisheries off Alaska are managed via the dictates of the North Pacific Fishery Management Council (NPFMC), which has done little to address the trawl fleet’s enormous bycatch of species immeasurably important to Alaskans.” Nothing could be further from the truth The council adopted hard caps for chinook salmon in the Bering Sea trawl pollock fisheries that vary depending upon the expected returns to western Alaska rivers. When expected returns are low, the caps are adjusted downward. Additionally, the fishing industry has stepped forward to implement chinook salmon avoidance measures that hold each vessel accountable for limiting bycatch to below the caps. In fact, the fleet is well below their caps, recognizing the need to rebuild these stocks. >>click to read<< 15:55
Doug Vincent-Lang
With little movement on salmon bycatch, Alaska advocates look to Biden administration for executive action
 Amid catastrophic shortfalls in salmon harvests in some of Alaska’s rural, Indigenous communities, advocates have pleaded for a crackdown on unintentional catch of those same salmon by the trawl vessels that harvest billions of pounds of whitefish in the Bering Sea. But the politically appointed regional council that manages Bering Sea fisheries has largely resisted those requests. So instead, advocates are now taking another approach. They’re pushing the Biden administration for a workaround: a rewrite of the federal guidelines that tell the regional council, and its counterparts across the country, how to manage all the fisheries under their supervision. >>click to read<< 18:40
Amid catastrophic shortfalls in salmon harvests in some of Alaska’s rural, Indigenous communities, advocates have pleaded for a crackdown on unintentional catch of those same salmon by the trawl vessels that harvest billions of pounds of whitefish in the Bering Sea. But the politically appointed regional council that manages Bering Sea fisheries has largely resisted those requests. So instead, advocates are now taking another approach. They’re pushing the Biden administration for a workaround: a rewrite of the federal guidelines that tell the regional council, and its counterparts across the country, how to manage all the fisheries under their supervision. >>click to read<< 18:40
Alaska fishermen will be allowed to harvest lucrative red king crab in the Bering Sea
 Alaska fishermen will be able to harvest red king crab for the first time in two years, offering a slight reprieve to the beleaguered fishery beset by low numbers likely exacerbated by climate change. There was no such rebound for snow crab, however, and that fishery will remain closed for a second straight year, the Alaska Department of Fish and Game announced Friday. “The Bristol Bay red king crab fishery for the prior two seasons were closed based on low abundance and particularly low abundance of mature-sized female crabs,” said Mark Stichert, the state department’s ground fish and shellfish management coordinator, “Based on survey results from this year, those numbers have improved, some signs of modest optimism in terms of improving abundance in Bristol Bay red king crab overall and that has allowed for a small but still conservative fishery for 2023 as the total population size is still quite low,” he said. >>click to read<<11:52
Alaska fishermen will be able to harvest red king crab for the first time in two years, offering a slight reprieve to the beleaguered fishery beset by low numbers likely exacerbated by climate change. There was no such rebound for snow crab, however, and that fishery will remain closed for a second straight year, the Alaska Department of Fish and Game announced Friday. “The Bristol Bay red king crab fishery for the prior two seasons were closed based on low abundance and particularly low abundance of mature-sized female crabs,” said Mark Stichert, the state department’s ground fish and shellfish management coordinator, “Based on survey results from this year, those numbers have improved, some signs of modest optimism in terms of improving abundance in Bristol Bay red king crab overall and that has allowed for a small but still conservative fishery for 2023 as the total population size is still quite low,” he said. >>click to read<<11:52

Alaska cancels snow crab harvest again due to population concerns
Crabbers from the Pacific Northwest who fish in Alaska had been watching and waiting for recommendations from the North Pacific Fishery Management Council, which met Thursday and Friday. Following the meetings, the Alaska Department of Fish and Game said Bering snow crab season will be closed for 2023-2024; Bristol Bay red king crab will open. Tanner crab will also be open for commercial fishermen. Both the snow crab and Bristol Bay red king crab seasons were closed in 2023. Crabbers and industry associations warned of the massive impact the decision would have on many small businesses, prompting calls by Congressional officials for an emergency declaration and federal aid. Video, >>click to read<< 08:18

Bristol Bay red king crab fishery could return after two years on ice
The Alaska Department of Fish and Game is set to decide Friday whether or not to reopen the Bristol Bay red king crab fishery, which has been closed since 2021. Their decision will be based on recommendations from the North Pacific Fishery Management Council, which is meeting through Oct. 11 in Anchorage. During the Council’s meeting Tuesday, the Crab Plan Team presented data and analysis on Bristol Bay crab stocks from the summer trawl survey to the Scientific and Statistical Committee. Mike Litzow is a co-chair for the team and the shellfish assessment program manager and director at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Kodiak Lab. Litzow said while male and female crab are still at historic lows, the fishery is not at or approaching an “overfished” status. >>click to read<< 08:48
New quota system to start for trawl harvests of cod in Bering Sea and Aleutians
 Commercial fishermen netting Pacific cod from the Bering Sea and Aleutians region will be working under new individual limits starting next year designed to ease pressure on harvests that regulators concluded were too rushed, too dangerous and too prone to accidentally catch untargeted fish species. The new system will require fishers who harvest cod by trawl – the net gear that scoops up fish swimming near the bottom of the ocean – to be part of designated cooperatives that will then have assigned quota shares. The fisheries service at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration said it has notified eligible participants and is asking for applications. >click to read< 08:54
Commercial fishermen netting Pacific cod from the Bering Sea and Aleutians region will be working under new individual limits starting next year designed to ease pressure on harvests that regulators concluded were too rushed, too dangerous and too prone to accidentally catch untargeted fish species. The new system will require fishers who harvest cod by trawl – the net gear that scoops up fish swimming near the bottom of the ocean – to be part of designated cooperatives that will then have assigned quota shares. The fisheries service at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration said it has notified eligible participants and is asking for applications. >click to read< 08:54

Council to reconsider red king crab closure options
Regulators are inching closer to closing areas of Bristol Bay to commercial groundfish fishing in an attempt to help conserve the depleted red king crab there. The North Pacific Fishery Management Council has requested more information for a second evaluation of options for what to do about the Bristol Bay Red King Crab fishery. At its meeting from June 6-11 in Sitka, the council tweaked some of the options for closures and asked its staff to gather more information for another review at its next meeting. The current options issue annual closures for part of Bristol Bay to all commercial groundfish gear types, though one option excludes non-pelagic trawl. >click to read< 09:40

These are Alaska’s priorities for fishery management council
Based on discussions with a diverse range of user groups, delegations from our coastal communities, fishermen, processor representatives and other Alaskans, it is clear our fisheries are facing a number of challenges. These challenges include unprecedented declines in Bering Sea crab stocks and ongoing low harvestable levels of Pacific cod and other economically valuable stocks that are causing economic hardship for fishery participants and affected communities. We also heard ongoing concerns about the impacts of federal fisheries on key species like halibut, salmon, and crab. This input was valuable to better understand the issues and to identify priorities and potential solutions. >click to read< 16:01

Fisheries protester removed from Alaska Capitol in handcuffs, arrested after fight
A man urging Alaska lawmakers to take action against trawling was removed from the state Capitol in handcuffs and banned from the building after disrupting a committee hearing on Monday. After his removal, former fisheries worker Eric Osuch went to the nearby State Office Building and was arrested by the Juneau Police Department after a fight was reported there. He was charged with criminal trespass, the department said. Osuch has been a regular figure outside the Capitol since last week, advocating action against deep-sea trawling in order to preserve salmon returns. That topic was addressed by the North Pacific Fishery Management Council last week, with limited immediate action taken. Osuch said he was dissatisfied by that result and called for the abolition of the council. On Monday, he was in front of the Capitol as early as 8:45 a.m., yelling at passersby. >click to read< 09:52

Alaska tribal groups sue federal fisheries managers, seeking action on salmon crisis
Two of Alaska’s largest tribal groups have sued the federal government, alleging federal regulators are mismanaging Alaska’s billion-dollar pollock and cod fishery amid an ongoing salmon crisis in central and southwestern Alaska. The Association of Village Council Presidents, which includes 56 tribes in the Yukon-Kuskokwim delta, and the Tanana Chiefs Conference, which includes 42 tribes in Interior Alaska, filed suit Friday in U.S. District Court against the National Marine Fisheries Service and Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo. The two tribal groups are asking a federal judge to require the agency to update the assessments used to set catch limits for federally managed groundfish fisheries in the Bering Sea and Aleutian Islands. >click to read< 14:57

In Depth: Alaska’s Fisheries Are Collapsing. This Congresswoman Is Taking on the Industry She Says Is to Blame.
The late 1990s and early 2000s were boomtimes for halibut fishermen in Alaska. Over 80 million pounds of the flatfish were being harvested annually. Deckhands could earn $250,000 a season. The small boat harbor in the southcentral city of Homer, known as the “halibut capital of the world,” was bustling. Erik Velsko, 39, was one of those fishermen. He started buying annual shares in 2001 when the halibut population was at near historic highs. But within a few years, the stock plummeted by more than half and the quotas for commercial fishermen were slashed accordingly. Halibut wasn’t the only so-called directed fishery to experience such a catastrophic drop. The crab fleet — made famous in the reality show “Deadliest Catch” — has been mostly stuck in port for two years after the near total collapse of the snow crab population and the decades long decline of red king crab. Photos, >click to read< 11:42




















































