Tag Archives: Canada’s East Coast

Senate report says government must implement rights-based Indigenous fisheries
A new report from the Senate is calling on the federal government to implement Mi’kmaq, Wolastoqiyik and Peskotomuhkati rights-based fisheries on Canada’s East Coast and overhaul its approach to negotiations. One of the report’s 10 recommendations is that discussions with First Nations be immediately transferred to Crown-Indigenous Relations from the Department of Fisheries and Oceans, which is something Indigenous communities have been calling for. >click to read< 15:45
First Nations shouldn’t have to negotiate with Fisheries and Oceans, committee says – Key to the proposed plan is to sideline DFO and leave it to the Department of Crown-Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs to negotiate rights-based fishing agreements. DFO could act as advisers. “As long as you both have First Nations fisheries and non-First Nations fisheries under DFO, it’s never going to work,” >click to read<
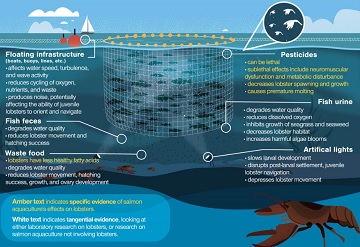
How Might Fish Farms Be Affecting the Lobster? Let us count the ways.
“There is a tremendous amount of waste generated by fish farms,” Milewski says. “I don’t think people have a sense of the scale.” A fairly typical farm of about 600,000 fish will generate around 40 tonnes of waste every month during its 22-month production cycle. “It’s understandable how that waste can change lobsters’ behavior, distribution, and abundance,” she adds. But the review also identified serious gaps in our understanding of the interactions between aquaculture operations and lobsters. While some aspects, such as the use of chemical pesticides, have been well studied, information on others, including waste discharges, disease, and noise, are limited or entirely lacking. >click to read< 11:02

Coronavirus: Reverberations from COVID-19 reach Canada’s East Coast and its lobster fishery
Lobster fishermen, like Fralick, are facing a crunch. In the last month, the coronavirus epidemic in China has precipitated a drop in lobster prices. “It dropped from $10.50 all the way down to $6, and now it’s back up to $7,” says Fralick. “That takes all the profit out of it.” Quarantines and lack of restaurant traffic has slowed lobster demand from China. Customer orders have dried up. As a result, fewer cargo planes are making the trip. >click to read< 07:54














































