Tag Archives: NOAA

Up to 70 North Atlantic right whales were spotted in Cape Cod Bay
About one-fifth of the world’s entire population of North Atlantic right whales were all spotted hanging out in Cape Cod, Mass., heading into the weekend. Between 60 to 70 right whales, including a mother and calf, were seen feeding outside the east end of the Cape Cod Canal in the Cape Cod Bay on Friday, according to the Massachusetts Environmental Police. The wildlife officials sent out two patrol vessels to protect the whales from boat traffic. By Saturday, the whales had seemingly moved on. >click to read< 11:00

Dem senators from 4 states ask NOAA to address whale deaths
Democratic U.S. Senators from four states want federal environmental officials to address a spate of whale deaths on both coasts, urging “transparency and timeliness” in releasing information about whale deaths and their causes. The call late Tuesday by New Jersey Sens. Robert Menendez and Cory Booker; Connecticut Sen. Richard Blumenthal, Oregon Sen. Jeff Merkley, and Rhode Island Sen. Sheldon Whitehouse for action by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration marked the first large-scale request for action by Democratic federal lawmakers on an issue that has rapidly become politicized. Thus far, mostly Republican lawmakers have called for a pause or an outright halt to offshore wind farm preparation work, which they blame for the deaths of whales along the U.S. East Coast since December. But in their letter to a NOAA administrator, the Democratic senators conspicuously did not blame — or even mention — offshore wind as a potential cause of the deaths. >click to read< 16:52

EXCLUSIVE: Federal Regulator Acknowledges Danger to Wildlife Caused by Offshore Wind Farms
Captain Jerry Leeman, who heads the fishing vessel F/V Teresa Marie IV, sent a copy of the Norwegian haddock study to Nies in a January 9 letter. “Thank you for your January 9 letter … A federal fisheries council acknowledged that some power cables for offshore wind turbines could harm certain fish, according to a letter seen by the DCNF. Multiple recent studies have demonstrated that a variety of commercially popular fish can be negatively impacted by their exposure to magnetic fields emitted by high voltage direct current cables, which can confuse their ability to navigate and, in some cases, leave them exposed to predators. “We were previously aware of this study and agree that it has concerning implications for the possible effects of high voltage direct current cabling on larval behavior and resulting predation rates,” Thomas Nies, executive director of the New England Fishery Management Council (NEFMC), said in a January 18 letter. >click to read< 20:01

‘The people’s fish’: Atlantic mackerel stocks have collapsed – can a moratorium bring them back?
Canada’s Atlantic mackerel population is a shadow of what it once was, and its decline threatens the well-being of the people who depend on it. Mackerel supports one of Atlantic Canada’s top recreational fisheries, and one of its oldest commercial fisheries. The fish is also used for bait, and it has an important place in Indigenous cultures. The same migratory stock supports recreational and commercial fisheries in the U.S. Last March, the federal Department of Fisheries and Oceans closed Canada’s commercial and bait mackerel fisheries for one year and placed daily personal limits on the recreational fishery, to give the population time to rebound. But the U.S. fishery remains open, albeit with a reduced quota. Next week, federal Fisheries Minister Joyce Murray will decide whether to reopen the Canadian fishery. The DFO’s latest studies have found no sign of recovery in the mackerel stock. Photos, >click to read< 13:09

Resistance to Offshore Wind Is Growing on US Coasts
A growing chorus of interest groups is calling for a pause in offshore wind activities to allow further assessment of the sector’s impacts on the marine ecosystem. Fishing groups and local residents have filed five lawsuits against proposed or under-construction wind projects along the Atlantic seaboard. A leading body for the U.S. Pacific fishing industry is urging the federal government to call off its proposed auction for offshore wind off the Oregon coast. And the United States’ largest lobbying group for Native Americans recently called for a halt to all offshore wind scoping and permitting. Wind energy is a key component of the Biden Administration’s climate agenda. >click to read< 08:10

On Demand Gear – Cape Cod Lobstermen Would Rather Wait Than Switch
21-year-old North Atlantic right whale known as Porcia was observed in Cape Cod Bay on March 18. The whale was seen swimming with her 2023 calf by her side. That means Cape Cod lobstermen are on land, waiting out the whales. Elsewhere in Massachusetts waters, however, the NOAA is running an experiment that gives lobster fishermen exempted fishing permits to work in areas that are otherwise restricted. What they are testing is something called on-demand fishing gear. “I think it’s a Star Wars idea that will not work,” said Dana Pazolt, a Truro-based lobsterman who sets his traps on the bay side in the fall and on the ocean side in the spring and summer. Pazolt’s 800 lobster traps have 50 miles of rope. >click to read< 11:10

Faulkingham Pitches $1,000,000 State Contribution to Lobster Legal Defense Fund
A public hearing will be held Thursday to discuss a bill aimed at providing financial support to the Maine Lobstermen’s Association (MLA), a group that represents Maine’s lobster industry. The bill, proposed by House Minority Leader Billy Bob Faulkingham (R-Winter Harbor), would provide the MLA with a one-time contribution of $1,000,000 to offset large expenses the organization has incurred in recent years as it fights against burdensome federal regulations. Faulkingham expressed his concern for the Maine lobster industry, which he says is “under attack” and facing potentially devastating regulations and lawsuits. >click to read< 08:57

Maryland, Virginia race to save dwindling commercial fisheries in the Chesapeake Bay
Alarmed by plummeting stocks of commercial fisheries in the Chesapeake Bay, officials in Maryland and Virginia are scrambling to control invasive fish species that are causing at least part of the problem. On Thursday, Gov. Wes Moore asked the federal government to carry out an evaluation to determine if the situation amounts to a declaration of a “commercial fishery disaster,” which would qualify the state for federal assistance. In a letter to Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo, Moore said the state is increasingly concerned about the explosive growth of invasive fish species in the Chesapeake Bay, including blue catfish, flathead catfish and snakehead. >click to read< 09:11

Seafood industry urges ‘extreme caution’ on controlling seals to avoid consumer backlash
Canada’s seafood industry is urging Ottawa to use “extreme caution” when considering measures to control the growing seal population, warning they could jeopardize market access and acceptance of Canadian seafood. But according to Conservative fisheries critic Clifford Small, a member of parliament from Newfoundland and Labrador, those concerns are overblown. “It is immensely important that as the government considers potential steps moving forward, its actions do not disrupt either the market access or acceptance of Canadian fish and seafood products, both internationally and domestically,” said Paul Lansbergen, president of the Fisheries Council of Canada. Lansbergen said both the U.S. and the European Union have strict rules regarding the harming of marine mammals during fishing. >click to read< 14:50

Whale death confusion abounds, and some is deliberate
Press coverage of the tragic whale deaths is a supreme study in confusion, especially the foolish attempts to somehow exonerate offshore wind development. Here are some prominent examples. The evergreen New York Times wins the race for worst coverage by claiming to explain the numerous recent whale deaths as due to online shopping. I am not making this up. Their headline promises an explanation: “Why 23 Dead Whales Have Washed Up on the East Coast Since December”. The primary reason claimed is that East Coast shipping has increased due to people buying lots of stuff post Covid, especially online, and ship strikes account for a lot of the deaths. >click to read< 13:11

Alaska Halibut Season Opens March 10
Pacific halibut season opens Sunday, March 10 statewide in Alaska. NOAA Fisheries filed notice of their effectiveness in the Federal Register today, which will publish March 7, 2023. The regulations, adopted at the annual meeting of the International Pacific Halibut Commission (IPHC) in January, took effect when the Secretary of State accepted them, with the Secretary of Commerce’s concurrence. Included in this season’s federal regulations are the catch limits established by the IPHC and basic regulations for the commercial and sport halibut fisheries. >click to read< 18:03

In Depth: Alaska’s Fisheries Are Collapsing. This Congresswoman Is Taking on the Industry She Says Is to Blame.
The late 1990s and early 2000s were boomtimes for halibut fishermen in Alaska. Over 80 million pounds of the flatfish were being harvested annually. Deckhands could earn $250,000 a season. The small boat harbor in the southcentral city of Homer, known as the “halibut capital of the world,” was bustling. Erik Velsko, 39, was one of those fishermen. He started buying annual shares in 2001 when the halibut population was at near historic highs. But within a few years, the stock plummeted by more than half and the quotas for commercial fishermen were slashed accordingly. Halibut wasn’t the only so-called directed fishery to experience such a catastrophic drop. The crab fleet — made famous in the reality show “Deadliest Catch” — has been mostly stuck in port for two years after the near total collapse of the snow crab population and the decades long decline of red king crab. Photos, >click to read< 11:42

Landlocked Congressman Targets Maine’s Lobstermen Over Whales
When a senior congressman from a land-locked state in the American West drops a bill pertaining to the Atlantic right whale out of the blue, it just seems fishy. But that is exactly what happened when Rep. Raul Grijalva (D-NM) introduced a bill for the sole purpose of undoing the six-year pause on enforcement of NOAA rules that Maine’s congressional delegation had wrestled out of budget negotiations late last year. Why? A long-time progressive, Grijalva until recently chaired the House Committee on Natural Resources, where he welcomed the testimony of Monterey Bay Aquarium Executive Director Julie Packard. Home to Seafood Watch, the group that “red-listed” Maine lobster last year, Packard’s Monterey Bay Aquarium has made fast enemies in the Pine Tree State. >click to read< 08:07

Panel discusses impact of offshore wind on West Coast fisheries
The Biden administration has called for deploying 30 gigawatts of offshore wind energy to combat climate change by 2030. Depending on where the turbines are placed, they could displace highly productive fishing grounds that account for billions of dollars and thousands of jobs in Oregon, Washington and California. Projects must be planned carefully using the best available science to mitigate potential damage, according to a panel of experts who spoke March 1 at the Northwest Offshore Wind Conference in downtown Portland. >click to read< 11:52

Another dead whale seen floating off Jersey Shore, this time in Seaside Park
Another dead humpback whale — the ninth dead whale to be reported or come ashore in New Jersey since Dec. 1 — was seen Wednesday afternoon floating about a half-mile off of the shoreline near the L Street beach. The whale was reported to the Marine Mammal Stranding Center of Brigantine and then to federal authorities at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, or NOAA, said NOAA spokeswoman Allison Ferreira. Wednesday’s stranding is at least the 18th sighting or beaching of a dead whale or dolphin in the New Jersey-New York region since the beginning of December. >click to read< 08:09

Blue State Enviro Groups Demand Answers From Green Biden Administration On Whale Deaths
Nonprofit groups in the state’s coastal towns have spent months trying to get the administration to place a moratorium on offshore wind projects until a thorough, transparent investigation can be completed to see if there is a connection to recent whale strandings. Since December 2022, over 20 whales have washed up along east coast shores near survey sites for future offshore wind projects in an unusual mortality rate, according to NOAA. “The low-frequency sonar used in the windmills is causing deafness in the whales. It’s one of those things that science is only going to pick up on years after the fact, in the meantime, whales are being killed,” James Lovgren, board of trustee member of Clean Ocean Action and retired commercial fisherman, told the DCNF. “You have to pause and ask, ‘why are we doing this?’” >click to read< 09:17

Many voices weigh in on offshore wind plan
Three days after Governor Janet Mills unveiled an offshore wind roadmap, a “comprehensive plan that offers detailed strategies” for offshore wind power in the Gulf of Maine, a handful of unconvinced citizens gathered at the Sustainable Maine Fishing Foundation Feb. 26 on Bar Harbor Road in Trenton. The idea was to inform lobstermen and interested people on offshore wind development before a Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) presentation that opens the Fishermen’s Forum March 2 in Rockport, board member Ginny Olsen said. Energy operations consultant George Stover of Freeport, who has worked in the state’s energy industry for decades, discussed the Maine power grid and its energy sources and why, to his mind, offshore wind power is not a good fit or needed here. “If they continue down this road, it scares me,” he said. He is not alone. The idea of floating offshore wind installations in the Gulf of Maine has raised fears and concerns from environmentalists and fishermen alike. >click to read< 12:42
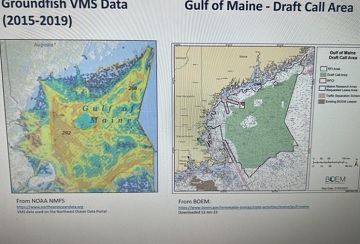
Gloucester webinar tackles concerns about wind farm projects
At the nascent stage of wind farm development in the Gulf of Maine, a webinar last week looked at the possible impacts to marine life, coastal communities and fisheries while acknowledging there are many unknowns to such projects. Capt. Al Cottone, a commercial fisherman and executive director of the Gloucester Fisheries Commission, said the industry has “a ton of questions that haven’t been answered yet. And I don’t think these questions will be answered in the time frame that was shown earlier in the presentation and it’s very concerning to the industry.” “We are very concerned about the displacement of vessels,” Cottone said. “Once you start losing access to fishing grounds, it puts a lot of pressure on other fishing grounds.” >click to read< 12:28

NOAA and BOEM; Ignorance is Bliss. By Jim Lovgren
For about twenty years the Natural Resources Defense Council [NRDC] engaged the US Navy in a legal battle over the effects of the Navy’s use of Mid Frequency Sonar in training exercises and its impact on marine mammals and other creatures, with one case even reaching the US Supreme court. While there are many different aspects of NRDC’s legal actions, the results of the litigation have produced an enormous amount of scientific data and research regarding the effects of underwater sound on marine creatures, with an emphasis on Sonar and marine mammals. They forced the Navy to admit that their use of sonar had resulted in the unintentional mass strandings of many different marine Mammals in a dozen different instances around the world, primarily involving Beaked whales, that are classified as being low to mid frequency cetaceans. >click to read< 08:48

Crabbers seek solutions as harvest closures impact business
An amount of emergency relief is being sent to help crabbers affected by the historic closure of the Bering Sea snow crab fishing and the Bristol Bay red crab harvest in Alaska. However, the Washington-based fisherman says more long-term care, research and action is needed to preserve the industry as a sustainable way of life for small businesses for generations. Mark Casto owns the fishing boat Pinnacle and says he’s been fishing since graduating from high school in 1986. “I grew up in it, when I was a kid, I used to do it when I was growing up, it was in my blood and it was just my way of life,” said Casto. He’s been grappling with the same teammates for years – some decades – and they’ve become a team that can predict each other’s next move. When the Bering Sea snow crabs were cancelled, they were scattered – all forced to find other ways to make a living during the season. >click to read< 16:50

NOAA, ADFG, Bering Sea Crabbers Teaming Up On Red Crab Fishery Research
Tempestuous weather and icy seas make winter research on Bristol Bay red king crab challenging. This winter, crab fishermen are working together with scientists to make it possible. The Bering Sea crab industry is partnering with NOAA Fisheries’ Alaska Fisheries Science Center and the Alaska Department of Fish and Game to meet a critical need for winter data on Bristol Bay Red king crab. Scientists and fishermen will work together on the month-long field research, set to launch in March. The research responds directly to data requests from the North Pacific Fishery Management Council to inform their management decisions. Photos, >click to read< 10:12

Offshore Wind Supporters Angered by ‘Misleading’ Information from R.I.-Based Opposition Group
A handful of property owners in the East Bay has been publicizing a torrent of data arguing against offshore wind projects, causing alarm and anger from oceanographers, environmental regulators, and climate activists who say the group’s arguments are wrong, misleading, and tainted with negative innuendo, false linkages, and guilt by association. The small group, called Green Oceans and organized last December as a nonprofit, believes offshore wind projects are the “industrialization of the ocean” and “100% destructive,” said one member, Bill Thompson, who owns a house in Tiverton. The group includes five other members, four of whom own houses in Little Compton and one with a Boston address. Green Oceans has produced a white paper against offshore wind, presenting 31 objections:,, >click to read< 21:00

How Many More Whales Need To Wash Up Before We Wake Up? NOAA Shrugs Responsibility Regarding Spike In Whale Deaths
If you’ve taken the time to read anything the NOAA has published to address the spontaneous spike in whale deaths, and whales washing up on East Coast beaches, you may have noticed that the report skirts around the cause of the whales’ deaths. While they do acknowledge the public’s concerns connecting the whales’ health and the recent establishment of offshore wind energy development, they say, “At this point, there is no evidence that noise resulting from wind development-related site characterization surveys could potentially cause mortality of whales, and no specific links between recent large whale mortalities and currently ongoing surveys.” (All sources are linked below – I highly encourage you to look into them!) >click to read< 08:41

Save The Whales rally planned at Point Pleasant Beach after 9th whale found dead

2 whales found dead along Atlantic Coast were likely hit by boats, NOAA says.
Necropsies on two whales found dead along the Atlantic coast this week revealed that both marine mammals showed evidence of vessel strikes. Both whales, a critically endangered North Atlantic right whale and a humpback, were already beginning to decompose, but preliminary results show internal injuries consistent with the blunt force trauma of a vessel strike, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration said Tuesday. The deaths are among a flurry of 21 whale deaths along the length of the Atlantic coast since Dec. 3. >click to read< 09:20




















































