Tag Archives: marine-mammal-protection-act
In the Pacific Northwest, killing sea lions is a necessity
 Don’t let their adorable faces and playful personalities fool you: California and Steller sea lions are capable of having disastrous impacts on nonnative ecosystems. In places like the Columbia River Gorge, these so-called dogs of the sea have been encroaching on native fish habitats for decades. Making homes in the Pacific, in coastal areas like the beaches of California, Alaska and Japan, these sea lions especially thrive on the West Coast, where population numbers are estimated to have grown from 75,000 to 257,000 in the last 30 years. This population boom has meant increased nutritional needs, sending thousands of sea lions inland in search of prey. One of the easiest targets for sea lions is the Columbia River, one of North America’s largest rivers and a key migration route for North American fish. The picturesque river valley abounds with seafood, including 13 federally protected species. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 10:12
Don’t let their adorable faces and playful personalities fool you: California and Steller sea lions are capable of having disastrous impacts on nonnative ecosystems. In places like the Columbia River Gorge, these so-called dogs of the sea have been encroaching on native fish habitats for decades. Making homes in the Pacific, in coastal areas like the beaches of California, Alaska and Japan, these sea lions especially thrive on the West Coast, where population numbers are estimated to have grown from 75,000 to 257,000 in the last 30 years. This population boom has meant increased nutritional needs, sending thousands of sea lions inland in search of prey. One of the easiest targets for sea lions is the Columbia River, one of North America’s largest rivers and a key migration route for North American fish. The picturesque river valley abounds with seafood, including 13 federally protected species. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 10:12
Final Incidental Take Regulations for the Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind Commercial (CVOW-C) Project, Offshore Virginia
 On Monday, January 22, 2024, NOAA Fisheries published the final incidental take regulations related to Dominion Energy’s Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind Commercial (CVOW-C) Project. The effective dates for these regulations are February 5, 2024 through February 4, 2029. Pursuant to the Marine Mammal Protection Act, these regulations will govern the “take” of small numbers of marine mammals exposed to elevated underwater noise generated by the project’s activities over a five-year period. NOAA Fisheries has determined the take that may be authorized under the final rule will have a negligible impact on all affected marine mammal species and stocks. more, >>click to read<< 14:50
On Monday, January 22, 2024, NOAA Fisheries published the final incidental take regulations related to Dominion Energy’s Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind Commercial (CVOW-C) Project. The effective dates for these regulations are February 5, 2024 through February 4, 2029. Pursuant to the Marine Mammal Protection Act, these regulations will govern the “take” of small numbers of marine mammals exposed to elevated underwater noise generated by the project’s activities over a five-year period. NOAA Fisheries has determined the take that may be authorized under the final rule will have a negligible impact on all affected marine mammal species and stocks. more, >>click to read<< 14:50
NOAA Fisheries releases more information about ‘high level’ of killer whales caught this year by Alaska trawl fleet
 Six killer whales caught in trawl net gear this year in waters off Alaska died as a result of their entanglement, while a seventh whale was seriously injured by this gear, according to a NOAA Fisheries statement released Friday. The trawl fishing industry’s 2023 take of killer whales, first made by public NOAA Fisheries in September, is significantly higher than in recent years past, according to a review of NOAA Fisheries death tolls through 2021. Bering Sea killer whales are not listed under the Endangered Species Act but are protected under the Marine Mammal Protection Act. John Gauvin, fisheries science director for the Alaska Seafood Cooperative, “We want to conduct our fisheries without harming orcas and we’re taking steps to avoid future mortalities,” more, >>click to read<< 10:19
Six killer whales caught in trawl net gear this year in waters off Alaska died as a result of their entanglement, while a seventh whale was seriously injured by this gear, according to a NOAA Fisheries statement released Friday. The trawl fishing industry’s 2023 take of killer whales, first made by public NOAA Fisheries in September, is significantly higher than in recent years past, according to a review of NOAA Fisheries death tolls through 2021. Bering Sea killer whales are not listed under the Endangered Species Act but are protected under the Marine Mammal Protection Act. John Gauvin, fisheries science director for the Alaska Seafood Cooperative, “We want to conduct our fisheries without harming orcas and we’re taking steps to avoid future mortalities,” more, >>click to read<< 10:19
72 whales have died on the East Coast in a year. NOAA must take action.
 So, what have we learned from the recent whale deaths off the East Coast — 72 since December 2022? They have compelled local communities to question the risks and benefits of offshore wind. Sadly, these same deaths have revealed a disturbing lack of curiosity among the oil-companies-turned-offshore-wind-developers, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and even some marine scientists who rush to the cameras every time a whale dies to point fingers away from offshore wind development along the eastern seaboard. Proponents of offshore wind are quick to blame global warming (to which of course their solution is offshore wind turbines) moving feeding grounds into shipping lanes and general episodic “vessel strikes” for these deaths. Many hope to close the investigation within the same day or two because the last thing they need is to have two dead whales, less than 30 miles apart, stealing the headlines for a full week. Proponents of these systems are also quick to claim that offshore wind will not harm marine mammals, yet their own action seemingly contradicts that. >>click to read<< 16:49
So, what have we learned from the recent whale deaths off the East Coast — 72 since December 2022? They have compelled local communities to question the risks and benefits of offshore wind. Sadly, these same deaths have revealed a disturbing lack of curiosity among the oil-companies-turned-offshore-wind-developers, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and even some marine scientists who rush to the cameras every time a whale dies to point fingers away from offshore wind development along the eastern seaboard. Proponents of offshore wind are quick to blame global warming (to which of course their solution is offshore wind turbines) moving feeding grounds into shipping lanes and general episodic “vessel strikes” for these deaths. Many hope to close the investigation within the same day or two because the last thing they need is to have two dead whales, less than 30 miles apart, stealing the headlines for a full week. Proponents of these systems are also quick to claim that offshore wind will not harm marine mammals, yet their own action seemingly contradicts that. >>click to read<< 16:49
Biden admin’s new rule could put pinch on lobster fishermen while letting others off the hook: critics say
 The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration is planning to enact a new federal rule under the Marine Mammal Protection Act – which would expand an existing restricted area off the coast of Maine where lobster fishing is already banned for three months each year. The move would cut the lobstermen’s’ business by at least 25% of the already declining industry, critics say. The plans come as an attempt to protect the endangered North Atlantic Right Whale, but a group of fishermen say the agency have no data to support the tightening restrictions. They also claim the federal agency is playing favorites by greenlighting offshore wind developments even though recent studies show can be harmful to marine life. “The federal government treats foreign offshore wind developers much better than lobstermen. The corporations have official authorization to disturb and displace marine life. Working lobstermen aren’t as lucky as our friends,” Video, >>click to read<< 07:55
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration is planning to enact a new federal rule under the Marine Mammal Protection Act – which would expand an existing restricted area off the coast of Maine where lobster fishing is already banned for three months each year. The move would cut the lobstermen’s’ business by at least 25% of the already declining industry, critics say. The plans come as an attempt to protect the endangered North Atlantic Right Whale, but a group of fishermen say the agency have no data to support the tightening restrictions. They also claim the federal agency is playing favorites by greenlighting offshore wind developments even though recent studies show can be harmful to marine life. “The federal government treats foreign offshore wind developers much better than lobstermen. The corporations have official authorization to disturb and displace marine life. Working lobstermen aren’t as lucky as our friends,” Video, >>click to read<< 07:55

Federal fisheries service agrees to deal aimed at curbing whale entanglements in fishing gear
A legal agreement finalized Tuesday over the protection of humpback whales is expected to help the threatened animals thrive while maintaining the ocean’s health. The deal stricken between the National Marine Fisheries Service and Center for Biological Diversity will create a team to reduce the number of whales that get tangled in a West Coast federal fishery. The service will form the team by Oct. 31, 2025, a press release stated. A federal court in March sided with the center after it filed suit last year against the fisheries service. The center argued the service failed to protect Pacific humpback whales from getting entangled in sablefish pot gear off the California, Oregon and Washington coasts. >click to read< 09:33

Canadian Company Pleads Guilty to Illegally Selling Harp Seal Oil in the United States
FeelGood Natural Health Stores Ltd. (FeelGood) pleaded guilty today to one count of violating the Lacey Act by knowingly transporting and selling harp seal oil capsules in violation of the Marine Mammal Protection Act (MMPA). According to the plea agreement, FeelGood is a Canadian corporation located in Whitby, Ontario, Canada. Between at least April 2019 and May 2021, FeelGood offered harp seal oil capsules for sale in the United States on both its own webpage and a third-party platform. It did so even though its website on the third-party platform acknowledged, “NOT ship to USA,” and though FeelGood received a notice that some shipments had been seized by the federal government for violation of the MMPA. >click to read< 18:55

Where have all the dead whales gone? By Nils Stolpe, FishNet-USA
Beginning in December of last year and extending through most of the first quarter of 2023, New Jersey and New York beaches were inundated with abnormally high numbers of dead or dying whales and smaller marine mammals. These majestic creatures-though not so majestic when being pushed about willy-nilly by tides, wind, waves and various types of earth moving machines-have never expired in such large numbers in such publicly accessible locations in local residents’ memories. Perhaps coincidently, intensive hydroacoustic surveys to determine the suitability of potential sites for the construction of thousands of gigantic windmills and their supporting infrastructure (supposedly to help us all survive what is being sold as an imminent energy/climate crisis) were being committed offshore of the beaches where all of these marine mammal deaths and strandings have been concentrated. To us inveterate observers of that hunk of Atlantic Ocean real estate known as the New York Bight, and the critters that temporarily or permanently live there, and of the actions of the public agencies charged with-and entitled to tens of millions of taxpayer dollars each year to do so-administering the Endangered Species and the Marine Mammal Protection Acts, that surely hints at, at best, ineptitude at that’s ineptitude at a fairly advanced level. >click to read the article< 16:14

Lawsuit claims US federal government violated regulations in approving Massachusetts offshore wind project
A Texas non-profit research institute that aims to promote free enterprise in Texas and the nation is acting on behalf of fishing companies in Massachusetts, a state 2,000 miles away, in a lawsuit that seeks to stop development of the Vineyard Wind offshore wind project. The Texas Public Policy Foundation (TPPF) has named the US Department of the Interior, the US Department of Commerce, the US Department of Defense and other agencies and individuals as defendants in the suit. The lawsuit, filed in December 2021, claims the defendants violated the Outer Continental Shelf Lands Act, the Endangered Species Act, the Clean Water Act, the Marine Mammal Protection Act, the National Environmental Policy Act, and their respective rules and regulations. >click to read< 10:54

Whales win in federal fight over sablefish net permit
A federal judge has awarded summary judgment to environmental advocates over the National Marine Fisheries Service’s handling of endangered Pacific humpback whales that get tangled in fishing gear off the Pacific coast. U.S. District Judge James Donato ruled in favor of the Center for Biological Diversity, which sued the feds in 2022 over a permit that authorized the incidental taking of endangered humpback whales in a sablefish fishery without also putting plans into place to reduce the number of entanglements. The organization said the permit was unlawful because the service “did not first ensure that a take reduction plan for the whales had been developed or was being developed, as required.” >click to read< 11:05

Seafood industry urges ‘extreme caution’ on controlling seals to avoid consumer backlash
Canada’s seafood industry is urging Ottawa to use “extreme caution” when considering measures to control the growing seal population, warning they could jeopardize market access and acceptance of Canadian seafood. But according to Conservative fisheries critic Clifford Small, a member of parliament from Newfoundland and Labrador, those concerns are overblown. “It is immensely important that as the government considers potential steps moving forward, its actions do not disrupt either the market access or acceptance of Canadian fish and seafood products, both internationally and domestically,” said Paul Lansbergen, president of the Fisheries Council of Canada. Lansbergen said both the U.S. and the European Union have strict rules regarding the harming of marine mammals during fishing. >click to read< 14:50

Maine delegation to fight bill that would repeal ‘pause’ in lobstering regulations
When Congress passed a law in December that included a six-year reprieve from new federal regulations for the lobster industry, the fishery heaved a sigh of relief. But if a new bill introduced this week in the House of Representatives is approved, that relief would be short-lived. Maine’s congressional delegation says they are committed to ensuring that doesn’t happen. On Monday, Rep. Raul Grijalva, D-Arizona, introduced The Restoring Effective Science-based Conservation Under Environmental Laws Protecting Whales Act, or the RESCUE Whales Act. If passed, the bill would repeal the protections for the lobster fishery that were included in the 2022 federal omnibus spending law. The omnibus poses an “existential threat” to the North Atlantic right whale, undermines the science-based protections of both the Endangered Species Act and the Marine Mammal Protection Act, and ignores possible solutions like “ropeless gear,” Grijalva said in a statement. >click to read< 11:31

Sea lions, seals might be hampering WA salmon recovery. What can be done?
State officials are now exploring whether to kill sea lions and seals in the Salish Sea and outer coast in a desperate effort to save salmon species from extinction. A new report commissioned by the state Legislature and completed by the Washington Academy of the Sciences says seals and sea lions are likely impeding salmon recovery, and the full impacts of predation on salmon may not be fully understood without lethal intervention. Three mammals specifically have skyrocketed. From 1975 to 2015, the harbor seal population in the Salish Sea exploded from about 6,000 to around 50,000. And California sea lions rose from 50,000 to somewhere around 300,000 on the West Coast of the U.S., according to the Northwest Indian Fisheries Commission. Populations of Steller’s sea lions living around Washington, Oregon and California steadily rose from an estimated 15,000 in 1982 to more than 43,000 in 2019. >click to read< 09:14

With bill’s passage, lobster industry welcomes 6-year break from new regulations
Hours before a stopgap spending measure was set to expire, Congress voted to pass the $1.7 trillion omnibus package to fund the government through September 2023. The package passed in the Senate Thursday afternoon with a large bipartisan majority, 68-29. Maine’s delegation was able to include a rider in the package that protects lobstermen for six years from rules that the industry says would decimate the state’s iconic fishery and coastal economy. The provision essentially reverses a federal court decision this summer on new lobstering regulations by preventing them from taking effect until Dec. 31, 2028. >click to read< 09:14

Proposed Virginia offshore wind farm threatens North Atlantic Right Whales
The proposed Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind Project is directly in the NARWs’ annual migration path. Dominion Energy has applied to erect 176 wind turbines, covering an area of approximately 10 miles by 15 miles—equal to the size of 85,000 football fields or the city of Tampa, Florida—located 27 miles off the coast of Virginia Beach. Each turbine will sit atop a monopole extending a minimum of 80 feet into the water and about 120 feet into the ocean floor, and its height above the water will top 620 feet. That’s higher than the Washington Monument, which is 555 feet tall. “How to kill whales with offshore wind?” Wojick asks. “Just push them into traffic. The collision deaths would not be directly attributable to the wall of noise created by the OSW project, so who would know?” >click to read< 08:55

Reminder: Scoping Meeting for the Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan on Tuesday, 4:30 PM
We will be conducting a virtual scoping meeting to collect public input on modifications to the Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan to reduce the risk of death and serious injury caused by U.S. commercial fishing gear to endangered North Atlantic right whales in compliance with the mandates of the Marine Mammal Protection Act. Register to attend the virtual public scoping meeting. >Click to read the notice< and access the links. 16:45

Fishery interests urge judge to rule in lobster lawsuit
Parties in a lobster industry lawsuit filed against federal regulators are urging a judge to make a decision in the case because its outcome affects a parallel case that the parties have to act on. The federal judge considering this decision was the same who ruled last month that new regulations to protect endangered right whales do not go far enough and violate both the Endangered Species Act and Marine Mammal Protection Act. In that case, U.S. District Judge James Boasberg asked the parties to propose remedies. The lobster association’s case takes aim at newly enacted and proposed federal regulations to protect the whales, which the association says are invalid because they are based on flawed assumptions and calculations. The parties need to know the court’s opinion so they can develop proposed remedies that Boasberg ordered in the parallel lawsuit brought by conservation groups. >click to read< 17:01

N.L. MP vows he’s ‘gonna keep pushing’ forward on seal management legislation
Clifford Small may have lost a battle in his bid to convince the House of Commons of the need for legislation to manage seal populations, but the Newfoundland and Labrador Conservative MP says he’s not about to give up the fight. Small’s private members’ bill, Act for the Conservation of Fish Stocks and Management of Pinnipeds (seals), or Bill C-251, died when it came to the House for second reading on June 15. There’s more than one way to move a bill through the parliamentary process, said Small. Bills can start in the House or they can be introduced through the Senate, he said, indicating that’s the path he may pursue next. >click to read< 14:20

North Atlantic Right Whale: Oceana Wins First Step In USMCA Complaint
The Secretariat for the Commission for Environmental Cooperation, part of the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), has agreed to move forward with the first step in a two-step process to investigate the USA’s failure to uphold its environmental laws to protect North Atlantic right whales, according to an Oceana announcement this week. The decision was in response to Oceana’s filing the first-ever “Submission on Enforcement Matters” against the US government under the USMCA last October. The ocean advocacy organization claimed the government has violated the USMCA by failing to enforce environmental laws to protect critically endangered North Atlantic right whales, of which only around 330 remain. >click to read< 14:53

Golden asks for more lobstermen on panel
U.S. Rep. Jared Golden (ME-02) called on the National Marine Fisheries Services March 16 to expand representation of lobstermen on its Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Team by including members of Maine Lobstering Union Local 207. The Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Team is charged with making recommendations to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration for addressing rising North Atlantic right whale mortalities. Only four of the members of the 60-person team are Maine lobstermen. >click to read< 17:46

Maine lobster industry fights lawsuit that aims to shut down fishery
While Maine’s lobster industry has been fighting an offensive legal battle against impending rules to protect endangered North Atlantic right whales, it also is playing defense in a case brought by environmentalists that seeks to shut down the lobster fishery entirely. Lobster industry groups are intervening in a case brought in Washington, D.C.’s U.S. District Court by the Center for Biological Diversity and other plaintiffs that argues the new federal restrictions aren’t adequate, and that the fishery’s continued operation poses an existential threat to the whales. >click to read< 19:15

North Atlantic Right Whale: Extinction Is Looming. Everyone’s Fighting.
This May, new rules created for the lobster industry by the National Marine Fisheries Service will become official policy for boats operating in right whale territory. The agency estimates that lobster and Jonah crab traps are responsible for 95 percent of vertical end-line ropes in the areas where whale protections apply and therefore pose the most risk for entangling whales. The Fisheries Service says these changes will reduce the risk of death and serious injury by 69 percent. But in the months after the rules were finalized, the agency has seen pushback from conservation groups, who argue the new protections aren’t enough, and lobster fishing crews, who say the rules will harm their business. >click to read< 14:22

What Is the Marine Mammal Protection Act?
The Marine Mammal Protection Act, or MMPA, is the U.S. federal law restricting human actions that affect marine mammals. The MMPA was signed into law in 1974 by President Richard Nixon, making it one of many environmental policies established by the Nixon administration. One of the most significant actions taken under the MMPA was the establishment of an “optimum sustainable yield” (OSY). Instead of the traditional single-species approach to marine mammal management, OSY focuses on the role of marine mammals in the health of an ecosystem. The ecosystem-based approach remains widely implemented across the fishery industry today. >click to read< 11:03
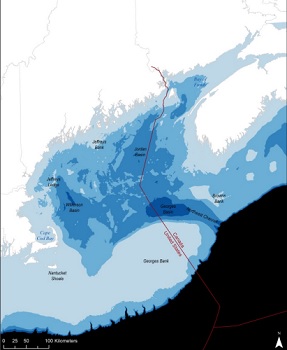
N.E. Aquarium Scientists urge NOAA to consider more aggressive Right Whale steps
In response to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Proposed Rule to amend the regulations implementing the Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan to reduce the incidental mortality and serious injury to North Atlantic right whales, fin whales, and humpback whales in northeast commercial lobster and crab trap/pot fisheries to meet the goals of the Marine Mammal Protection Act and the Endangered Species Act, the New England Aquarium submits this comment to express our strong reservations that the measures outlined in the Proposed Rule and accompanying Draft Environmental Impact Statement (DEIS) are not nearly aggressive enough to change the fate of North Atlantic right whales in U.S. waters. Based on our decades of NARW expertise, the Aquarium strongly urges NOAA to revise this Proposed Rule substantially before finalizing it. >click to read< 07:07

Maine’s booming seal population concerns local fishermen, biologists. Cod predation isn’t mentioned
Biologists say there are three points to consider: While the increase in harbor seals is creating a healthier ecosystem for the Gulf of Maine, it’s also creating problems for local lobstermen who say they’re a threat to their livelihoods, and it’s drawing new and potentially dangerous fish into our waters at a rate the state has never seen before. “I’ve had guys call me and say, ‘Are you having a problem with bait bags being ripped out because of the seals?’ and I say, ‘Yeah. I’ve had five or six.’ he says, ‘Rusty, I just had twenty traps in a row right, in a row. The seals went bang bang, bang, bang, bang right down through and ripped all the bags out,'” Court said. >click to read< Bait bags? What about cod fish bellies?!!

DFO working to keep U.S. markets open to northern fisheries
The Department of Fisheries and Oceans is working to ensure that fisheries in Nunavut and Nunavik will be able to export their products to markets in the United States after next year. Beginning on Jan. 1, 2022, the U.S. Marine Mammal Protection Act’s import provisions rule will take effect. Four Greenland halibut (turbot), three Arctic char fisheries, and a shrimp fishery will all need to comply. “This rule ensures that the U.S. will only accept imports of fish and fish products originating from foreign countries that have enacted management measures to reduce marine mammal bycatch”,,, DFO submitted a progress report to NOAA and proposed that three Arctic char gillnet fisheries be exempt based on their location in river estuaries, short time in the water and shallow depth. NOAA rejected the request for an exemption. >click to read< 14:00

Herrera Beutler lauds NOAA decision on sea lion removal
NOAA announced Aug. 14 that a task force had endorsed implementing the Endangered Salmon Predation Prevention Act, legislation signed into law in 2018. The administration stated that the new law amends the Marine Mammal Protection Act, allowing for removal of sea lions in a stretch of the Columbia River and its tributaries intended to cut down on predation of salmon and steelhead. With NOAA’s approval of these permits, wildlife managers can now finally take action and implement the sea lion control measure that tribes, fishermen, scientists, conservationists and local leaders have been calling for to preserve our native fish runs,” U.S. Rep Herrera Beutler >click to read< 10:46