Tag Archives: Gulf of Maine

Scientists expect some decline in Gulf of Maine lobster numbers, but ‘no calamity’
Concern about the effects of climate change have reached Maine’s lobster industry, where there are questions whether the state’s record lobster catches can be sustained. There has been wide agreement among fishermen and scientists in recent years that the waters of the Gulf of Maine have been getting steadily warmer as a result of the changing climate. In fact, researchers say the Gulf water have warmed more quickly than most other parts of the ocean. University of Maine researcher Dr. Rick Wahle said warmer water in the Gulf has been one factor in the big jump in lobster landings. He said a reduction in the number of lobster predators and conservation efforts by fishermen are also factors. click here to read the story 14:53
New rules aim to boost herring supply prized as lobster bait
 The Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission adopted many of the same measures that Maine implemented last year to try to “stretch out” the limited quota of inshore Atlantic herring into late summer, when lobster boat captains in Maine, New Hampshire and Massachusetts are clamoring for what many fishermen say is the best, and formerly cheapest, kind of lobster bait. The commission voted to allow regulators to set weekly herring quotas, to limit fishing to certain days of the week, and to give the three states that regulate the inshore herring fishery in the southern Gulf of Maine the ability to limit or ban the use of so-called “carrier vessels” that transfer herring landed by a licensed boat so it can keep fishing instead of heading back to port to unload its haul. click here to read the story 08:35
The Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission adopted many of the same measures that Maine implemented last year to try to “stretch out” the limited quota of inshore Atlantic herring into late summer, when lobster boat captains in Maine, New Hampshire and Massachusetts are clamoring for what many fishermen say is the best, and formerly cheapest, kind of lobster bait. The commission voted to allow regulators to set weekly herring quotas, to limit fishing to certain days of the week, and to give the three states that regulate the inshore herring fishery in the southern Gulf of Maine the ability to limit or ban the use of so-called “carrier vessels” that transfer herring landed by a licensed boat so it can keep fishing instead of heading back to port to unload its haul. click here to read the story 08:35
Series of coral protection hearings planned for New England
 Federal fishery managers will hold a host of public hearings in New England and New York about a plan to protect corals in key East Coast fishing areas. The New England Fishery Management Council is hosting seven public hearings about alternatives it is considering about the protection of corals in the Gulf of Maine and Georges Bank. The hearings will take place from May 22 to 25 in Montauk, Narragansett, New Bedford, Gloucester, Portsmouth, and Ellsworth. There will also be a web-based hearing on May 26. The fishery council says it wants to collect feedback from fishermen and other stakeholders about the coral protection Link 21:28
Federal fishery managers will hold a host of public hearings in New England and New York about a plan to protect corals in key East Coast fishing areas. The New England Fishery Management Council is hosting seven public hearings about alternatives it is considering about the protection of corals in the Gulf of Maine and Georges Bank. The hearings will take place from May 22 to 25 in Montauk, Narragansett, New Bedford, Gloucester, Portsmouth, and Ellsworth. There will also be a web-based hearing on May 26. The fishery council says it wants to collect feedback from fishermen and other stakeholders about the coral protection Link 21:28
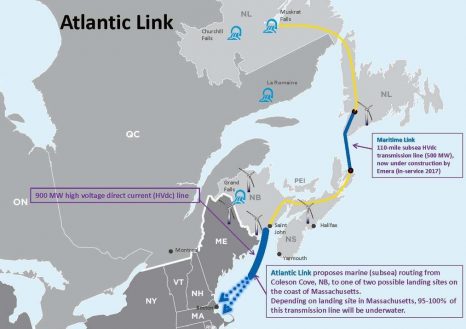
Maine fishermen could feel impact of proposed undersea cable
A Canadian company is proposing a 350-mile, sub-sea power transmission cable that could interfere with commercial fishing along the coast of Maine. If the project is approved, the Atlantic Link cable would be buried about 25 miles offshore of Harpswell, running between New Brunswick, Canada, and Plymouth, Massachusetts. It would affect about 400 lobstermen from Cape Elizabeth to Phippsburg, according to spokesman Gerald Weseen of the Nova Scotia-based energy services company Emera. Weseen and other project representatives, and staff from the Maine Coast Fishermen’s Association, conducted a meeting about the project April 21 that drew only two area lobstermen. click here to read the story 13:12
Meanwhile in the Straight of New Brunswick, Scallop fishermen worried about short- and long-term impact of electric cable installation. “Are we going to have a fishery there in the future, or are we going to have wait seven years to get it back up again?” Barlow asked. click here to read the story 14:20

No shrimp today: Maine’s waters are warming and it’s costing fishermen money
David Goethel wishes he could retire. At 63, he’s been fishing off the Gulf of Maine for over 34 years. Shrimp used to be plentiful there. Back in 2000, Goethel remembers seeing 100 commercial boats out in the harbor. Now, he’s just one of a handful of local fisherman struggling to make a living. “There was life on the docks, there were people working,” lifelong fisherman Arnold Gamage, 64, agrees. “Now, it looks like a ghost town.” Maine’s fishing industry has been declining for years due to factors like overfishing and increased regulation, but there’s another culprit eating away at profits: Maine’s ocean waters are warming — and it’s killing northern shrimp. Why is the Gulf of Maine warming? Scientists aren’t certain, but Appelman and other experts suspect climate change is playing a role.,, Shrimping used to account for around 30% of Goethel’s income. While he recognizes that the ban is necessary, he still misses that extra cash. Lifelong fisherman Gary Libby is also feeling the squeeze. He’s been trying to sell his shrimp boat but no one is buying. He’s lost between 30% to 40% of his annual income since the ban was instituted. click here to read the story 08:52

Could the Gulf of Maine’s Ground Fishery Rebound?
“The English had discovered living resources that would attract, shape, and sustain the communities of the coast of Maine for the next four centuries,” wrote journalist and historian Colin Woodard of the bounty that once existed in the Gulf of Maine in the 17th century in his book “The Lobster Coast.” “Early explorers were flabbergasted by the largesse of the Gulf of Maine, a semienclosed sea stretching from Cape Cod to Nova Scotia. They saw great pods of whales, acres of thrashing tuna, vast schools of salmon, herring and mackerel, clouds of puffins and terns, shoals of mussels and oysters, vast mudlfats infested with fat clams, cod and haddock biting at the hook, and enormous lobsters foraging in the rockweed. The waters off England and France seemed barren by comparison.” As Woodard noted, the geology and climate of the Gulf of the Maine with its 7,500-mile coastline made the area perfectly suited for a thriving fishery — a “fertile oasis in a world ocean that is, ecologically speaking, largely desert.” click here to read the story 09:27
Lobster fishing in Gulf of Maine coral canyons gets initial approval
 The New England Fisheries Management Council voted 14-1 to ban most fishing in the canyons and plateaus where slow-growing, cold-water coral gardens flourish in the dark waters of the Gulf of Maine. But pleas from Maine lobster fishermen who say a trap ban in fertile fishing grounds off Mount Desert Rock and Outer Schoodic Ridge would cost them millions helped sway an initially resistant council to grant a lobstering exemption. Fishermen also said closing these areas would have led to more traps, and fishing lines, being dropped in nearby waters traveled by endangered right whales, which can suffer injuries or die if they become entangled in lobster fishing lines. Opponents, including environmentalists and some who fish for other species that would not get an exemption in the coral zones,,, click here to read the story. 14:50
The New England Fisheries Management Council voted 14-1 to ban most fishing in the canyons and plateaus where slow-growing, cold-water coral gardens flourish in the dark waters of the Gulf of Maine. But pleas from Maine lobster fishermen who say a trap ban in fertile fishing grounds off Mount Desert Rock and Outer Schoodic Ridge would cost them millions helped sway an initially resistant council to grant a lobstering exemption. Fishermen also said closing these areas would have led to more traps, and fishing lines, being dropped in nearby waters traveled by endangered right whales, which can suffer injuries or die if they become entangled in lobster fishing lines. Opponents, including environmentalists and some who fish for other species that would not get an exemption in the coral zones,,, click here to read the story. 14:50
From the Council – NEFMC Selects Deep-Sea Coral Amendment Preferred Alternatives, Click here to read 15:43
Wake Up, Fishermen! Proposed closure of coral grounds in Gulf of Maine has lobster industry on edge
 Over the past 10 years, the issue of how to protect endangered whales from getting tangled in fishing gear has been a driving factor in how lobstermen configure their gear and how much money they have to spend to comply with regulations. Now federal officials have cited the need to protect deep-sea corals in a proposal to close some areas to fishing — a proposal that, according to lobstermen, could pose a serious threat to how they ply their trade. “The [potential] financial impact is huge,” Jim Dow, a Bass Harbor lobsterman and board member with Maine Lobstermen’s Association, said Wednesday. “You’re talking a lot of the coast that is going to be affected by it.” The discovery in 2014 of deep-sea corals in the gulf, near Mount Desert Rock and along the Outer Schoodic Ridges, has prompted the New England Fisheries Management Council to consider making those area off-limits to fishing vessels in order to protect the coral from damage. According to Maine Department of Marine Resources, fishermen from at least 15 harbors in Hancock and Washington counties could be affected by the proposed closure. click here to read the story Wake Up, Fishermen! 11:15:30
Over the past 10 years, the issue of how to protect endangered whales from getting tangled in fishing gear has been a driving factor in how lobstermen configure their gear and how much money they have to spend to comply with regulations. Now federal officials have cited the need to protect deep-sea corals in a proposal to close some areas to fishing — a proposal that, according to lobstermen, could pose a serious threat to how they ply their trade. “The [potential] financial impact is huge,” Jim Dow, a Bass Harbor lobsterman and board member with Maine Lobstermen’s Association, said Wednesday. “You’re talking a lot of the coast that is going to be affected by it.” The discovery in 2014 of deep-sea corals in the gulf, near Mount Desert Rock and along the Outer Schoodic Ridges, has prompted the New England Fisheries Management Council to consider making those area off-limits to fishing vessels in order to protect the coral from damage. According to Maine Department of Marine Resources, fishermen from at least 15 harbors in Hancock and Washington counties could be affected by the proposed closure. click here to read the story Wake Up, Fishermen! 11:15:30

A milestone in the war over the true state of cod
For years, fishermen from Gloucester to New Bedford have accused the federal government of relying on faulty science to assess the health of the region’s cod population, a fundamental flaw that has greatly exaggerated its demise, they say, and led officials to wrongly ban nearly all fishing of the iconic species.The fishermen’s concerns resonated with Governor Charlie Baker, so last year he commissioned his own survey of the waters off New England, where cod were once so abundant that fishermen would say they could walk across the Atlantic on their backs. Now, in a milestone in the war over the true state of cod in the Gulf of Maine, Massachusetts scientists have reached the same dismal conclusion that their federal counterparts did: The region’s cod are at a historic low — about 80 percent less than the population from just a decade ago. continue reading the story here 08:07
Plan to reopen Maine shrimp fishery in the works
 The Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission is seeking comment on its plan to reopen the northern shrimp fishery, which has been closed for three years. The Arlington, Va.-based regulatory agency’s plan includes options such as changing the way the quota system is managed. The agency noted that earlier proposals had considered establishing a limited entry program. The current proposal eliminates that option and focuses instead on “total allowable catch allocation programs, gear requirements, and other measures to improve management of the northern shrimp fishery and resource.” continue reading the story click here 21:14
The Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission is seeking comment on its plan to reopen the northern shrimp fishery, which has been closed for three years. The Arlington, Va.-based regulatory agency’s plan includes options such as changing the way the quota system is managed. The agency noted that earlier proposals had considered establishing a limited entry program. The current proposal eliminates that option and focuses instead on “total allowable catch allocation programs, gear requirements, and other measures to improve management of the northern shrimp fishery and resource.” continue reading the story click here 21:14

Federal regulators put an end to turbulent season in northern Gulf of Maine scallop fishery
Federal authorities are closing the scallop fishery in the northern Gulf of Maine at 12:01 a.m. Thursday after a contentious three-week season that pitted the interests of part-time, small-boat fishermen from Maine against large, full-time scallop operators. Fisheries regulators announced the closure Wednesday after small-boat fishermen – many of them Maine lobstermen operating 40- to 45-foot boats – met their annual quota of 70,000 pounds. The developments do not apply to the scallop fishery in state waters, which extend to 3 miles from shore. This year’s federal harvest has been contentious because the large, full-time boats are believed to have caught more than 1 million pounds of scallops in the northern Gulf of Maine scallop fishing area, but owing to a quirk in federal rules the fishery could not be closed until the small vessels caught 70,000 pounds. This month’s storms and unseasonable weather had kept the small boats in port, delaying their ability to meet their annual quota and close the area to the larger vessels, who were permitted to continue harvesting large quantities of scallops under federal rules. continue reading the story here 07:57
Small-boat scallop fishermen worry about being overwhelmed by larger boats in the Gulf of Maine
 Since the start of the scallop season this month, Jim Wotton has dragged heavy dredges along the seabed off Gloucester, hauling in as much as 200 pounds a day of the valuable clams, the area’s federal limit for small-boat fishermen. Now, to his dismay, dozens of larger, industrial-sized boats have been steaming into the same gray waters, scooping up as many scallops as they can. Unlike their smaller counterparts, the large vessels have no quota on the amount they can catch; they’re only limited by the number of days they can fish.,, NOAA officials acknowledge the fishermen’s concerns, but have declined to take emergency action to close the fishery.,, Representatives of the larger boats say they have every right to fish in the area, and insist their catch won’t threaten the fishery.,, “The situation this year can’t continue and support a strong fishery year in and year out in the Gulf of Maine,” said Pete Christopher, a supervisory fishery policy analyst at NOAA Fisheries. “The council needs to change the way the fishery operates.” read the story here 18:52
Since the start of the scallop season this month, Jim Wotton has dragged heavy dredges along the seabed off Gloucester, hauling in as much as 200 pounds a day of the valuable clams, the area’s federal limit for small-boat fishermen. Now, to his dismay, dozens of larger, industrial-sized boats have been steaming into the same gray waters, scooping up as many scallops as they can. Unlike their smaller counterparts, the large vessels have no quota on the amount they can catch; they’re only limited by the number of days they can fish.,, NOAA officials acknowledge the fishermen’s concerns, but have declined to take emergency action to close the fishery.,, Representatives of the larger boats say they have every right to fish in the area, and insist their catch won’t threaten the fishery.,, “The situation this year can’t continue and support a strong fishery year in and year out in the Gulf of Maine,” said Pete Christopher, a supervisory fishery policy analyst at NOAA Fisheries. “The council needs to change the way the fishery operates.” read the story here 18:52

Drop in herring a mystery in Maine as bait price booms
Scientists and fishermen are trying to figure out why Maine’s Atlantic herring catch — the largest in the nation — has fallen from 103.5 million pounds in 2014 to 77.2 million last year. The per-pound price of the fish at the dock has gone up 56 percent since 2014, and that price is eventually borne by people who buy lobsters. “The whole dynamic of the fishery has changed,” said Jeff Kaelin, who works in government relations for Lund’s Fisheries, which lands herring in Maine. Kaelin, and others who work in and study the fishery, thinks climate and the way the government manages herring may have played a role in the decline of catch. Atlantic herring are managed via a quota system, and regulators have slashed the quota by more than 40 percent since the early 2000s. Last year, herring were also difficult to catch far offshore, where they are typically caught in large amounts, but they were abundant closer to the New England coast. This led to a bait shortage, because fishermen are only allowed to catch a certain percentage of their quotas in inshore waters. Read the story here 10:15
Out-of-state scallop boats threaten survival of Maine fishermen
 After years of waiting for the northern Gulf of Maine scallop population to flourish, small-boat fishermen from Maine say federal mismanagement of scallop stocks in the area could result in larger boats wiping them out. Hancock fisherman James West said that larger boats, most of which are based out of state, should not be allowed unlimited catches when he is capped at harvesting only 200 pounds of meat a day. And he said he’s angry that the New England Fishery Management Council has known about the regulatory disparity for years and has done nothing to address it. “That’s what makes me so mad about it,” West said Sunday. “I’m shocked the council couldn’t figure out a way to fix this. We’re really getting the shaft.” Council officials say protecting the lucrative resource is a high priority that they plan to address in the coming year. But Maine fishermen say a year could be too late to ensure that federal scallop grounds in the gulf stay productive. continue reading the story here 07:36
After years of waiting for the northern Gulf of Maine scallop population to flourish, small-boat fishermen from Maine say federal mismanagement of scallop stocks in the area could result in larger boats wiping them out. Hancock fisherman James West said that larger boats, most of which are based out of state, should not be allowed unlimited catches when he is capped at harvesting only 200 pounds of meat a day. And he said he’s angry that the New England Fishery Management Council has known about the regulatory disparity for years and has done nothing to address it. “That’s what makes me so mad about it,” West said Sunday. “I’m shocked the council couldn’t figure out a way to fix this. We’re really getting the shaft.” Council officials say protecting the lucrative resource is a high priority that they plan to address in the coming year. But Maine fishermen say a year could be too late to ensure that federal scallop grounds in the gulf stay productive. continue reading the story here 07:36

Northern Shrimp lovers lining up for local catch
Joe Jurek knew his catch would be popular. He just didn’t know how popular. Jurek, a Gloucester-based groundfisherman who specializes in yellow-tail flounder on most fishing days, now holds the rarified position as the only Massachusetts fisherman allowed to fish for northern shrimp in the Gulf of Maine. His tenure as shrimper-in-residence will last only two more weeks, much to the dismay of local northern shrimp lovers — including Mayor Sefatia Romeo Theken — who literally have trooped down to the dock with buckets to try to buy the cold-water delicacies. The local shrimp have disappeared from seafood retail shops in the last four years the shrimp fishery has been closed. “Once people found out about it, it was like a bunch of seagulls,” said Romeo Theken, who along with a couple other dozen friends put in an order for about 230 pounds of the small, sweet shrimp. “Now people know the process, that they have to sign in at the auction and buy it through a seafood dealer.” Jurek said he’s averaging 350 to 400 pounds of the shrimp per fishing day, which he lands at the Cape Ann Seafood Exchange at an average off-the-boat price of about $6.50 a pound. continue reading the story here 07:28
Scallops scuffle pitting small boats against big
 A disagreement over the right to fish for scallops off New England is pitting small boats against big ones in one of the most lucrative fisheries in the U.S. The federal government maintains different rules for the small- and big-boat scallop fisheries, though they work some of the same areas. Small boat fishermen say the conflict has arisen in the northern Gulf of Maine, a critically important fishing area stretching roughly from Boston to the border of Maine and Canada. At issue is the fact that the northern Gulf of Maine is fertile ground for scallops right now, and rules allow the bigger boats to harvest more of them. The smaller boats have a possession limit of 200 pounds, while the largest boats have no such limit, because they are regulated instead by a limited number of days at sea. Continue reading the article here 11:48
A disagreement over the right to fish for scallops off New England is pitting small boats against big ones in one of the most lucrative fisheries in the U.S. The federal government maintains different rules for the small- and big-boat scallop fisheries, though they work some of the same areas. Small boat fishermen say the conflict has arisen in the northern Gulf of Maine, a critically important fishing area stretching roughly from Boston to the border of Maine and Canada. At issue is the fact that the northern Gulf of Maine is fertile ground for scallops right now, and rules allow the bigger boats to harvest more of them. The smaller boats have a possession limit of 200 pounds, while the largest boats have no such limit, because they are regulated instead by a limited number of days at sea. Continue reading the article here 11:48

New SMAST camera can help assess cod stocks in Gulf of Maine
Researchers from UMass Dartmouth say they have successfully tested an underwater video-survey system that they hope will provide an accurate method to assess Atlantic cod stocks. In collaboration with fishermen, the research team recently placed high-resolution cameras in an open-ended commercial trawl net on Stellwagen Bank in the Gulf of Maine, known as one of the world’s most active marine sanctuaries. The cameras captured images of cod and other groundfish as they passed through the net. Periodically, researchers from UMD’s School for Marine Science & Technology closed the net for short periods to collect length, weight, and take other biological samples from some of the fish. The fish are unharmed and are returned to the sea. The system is design to be portable, so scientists can set it up on different fishing vessels. Professor Kevin Stokesbury, head researcher on the project, said the video system is an important tool at a time of uncertainty about the groundfish stock in the Gulf of Maine. Read the story here 17:57 Read the press release and watch the video here
Fishermen and Scientists to collaberate on Trawl Surveys utilizing industry vessels in the Gulf of Maine
 By next year, the Northeast Fisheries Science Center hopes to begin outfitting commercial boats with surveying equipment and paying fishermen to pull in catches that will supplement the regular trawl surveys conducted by government scientists, according to Russell Brown, who heads the center’s population dynamics branch. The gathered data will be fed into the complex process used to set catch quotas. It’s a collaboration that Brown hopes will give regulators a more detailed picture of the fish population and build trust among fishermen, who in turn see it as an opportunity to show the scientists what’s really going on. “It’s really perplexing that you’ve got a set of federal scientists who are sampling the ocean methodically and coming up with a very different picture than the fishermen about what’s going on out in the Gulf of Maine,” Jonathan Labaree of the Gulf of Maine Research Institute said. Read the story here 08:27
By next year, the Northeast Fisheries Science Center hopes to begin outfitting commercial boats with surveying equipment and paying fishermen to pull in catches that will supplement the regular trawl surveys conducted by government scientists, according to Russell Brown, who heads the center’s population dynamics branch. The gathered data will be fed into the complex process used to set catch quotas. It’s a collaboration that Brown hopes will give regulators a more detailed picture of the fish population and build trust among fishermen, who in turn see it as an opportunity to show the scientists what’s really going on. “It’s really perplexing that you’ve got a set of federal scientists who are sampling the ocean methodically and coming up with a very different picture than the fishermen about what’s going on out in the Gulf of Maine,” Jonathan Labaree of the Gulf of Maine Research Institute said. Read the story here 08:27
Gloucester fisherman chosen for Gulf of Maine northern shrimp research project
 Joe Jurek is no stranger to the Gulf of Maine northern shrimp fishery, having incorporated shrimping into his annual fishing calendar even after moving to Gloucester about a decade ago to groundfish. “When sectors started in 2009, we would catch our groundfish quota as quickly as we could and then go fish the other fisheries, including the northern shrimp fishery,” Jurek said Tuesday. “I shrimped long before that, though. You could say it’s kind of my background.” Jurek, owner and skipper of the 42-foot F/V Mystique Lady, will be the lone Massachusetts representative in the upcoming Gulf of Maine winter shrimp sampling program that will produce the only legal shrimping in 2017 in the Gulf of Maine. The Mystique Lady is one of 10 trawlers participating in the sampling program, along with eight from Maine and one from New Hampshire captained by Mike Anderson of Rye. Read the story here 09:56
Joe Jurek is no stranger to the Gulf of Maine northern shrimp fishery, having incorporated shrimping into his annual fishing calendar even after moving to Gloucester about a decade ago to groundfish. “When sectors started in 2009, we would catch our groundfish quota as quickly as we could and then go fish the other fisheries, including the northern shrimp fishery,” Jurek said Tuesday. “I shrimped long before that, though. You could say it’s kind of my background.” Jurek, owner and skipper of the 42-foot F/V Mystique Lady, will be the lone Massachusetts representative in the upcoming Gulf of Maine winter shrimp sampling program that will produce the only legal shrimping in 2017 in the Gulf of Maine. The Mystique Lady is one of 10 trawlers participating in the sampling program, along with eight from Maine and one from New Hampshire captained by Mike Anderson of Rye. Read the story here 09:56
Warming trend continues in waters off Atlantic Canada
 Warmer ocean temperatures off Atlantic Canada continued in 2016, maintaining a trend that started earlier this decade, according to survey results from Canada’s Department of Fisheries and Oceans. On the Scotian Shelf off Nova Scotia, temperatures last year were as high as three degrees above the 30-year average used to establish climatic norms. “It’s not quite the same [record] level of 2012, but it’s getting close to it,” said Dave Hebert, a research scientist with DFO. He added that 2016 was probably the second warmest year on record. Scientists have struggled to explain what is causing the most intriguing aspect of the recent trend: the warming of ocean bottom water, which is not influenced by surface weather events. Hebert said the latest theory is based on model results that see the Gulf Stream moving northward and intersecting with the tail of the Grand Banks. “That is stopping the cold Labrador Sea water from coming around the tail of the Grand Banks,” he said. “That’s where we normally get the cold water that refreshes the [Scotian] Shelf. That hasn’t been happening. Read the story here 16:48
Warmer ocean temperatures off Atlantic Canada continued in 2016, maintaining a trend that started earlier this decade, according to survey results from Canada’s Department of Fisheries and Oceans. On the Scotian Shelf off Nova Scotia, temperatures last year were as high as three degrees above the 30-year average used to establish climatic norms. “It’s not quite the same [record] level of 2012, but it’s getting close to it,” said Dave Hebert, a research scientist with DFO. He added that 2016 was probably the second warmest year on record. Scientists have struggled to explain what is causing the most intriguing aspect of the recent trend: the warming of ocean bottom water, which is not influenced by surface weather events. Hebert said the latest theory is based on model results that see the Gulf Stream moving northward and intersecting with the tail of the Grand Banks. “That is stopping the cold Labrador Sea water from coming around the tail of the Grand Banks,” he said. “That’s where we normally get the cold water that refreshes the [Scotian] Shelf. That hasn’t been happening. Read the story here 16:48
Participants in cooperative winter sampling program for Gulf of Maine northern shrimp announced
 The program, coordinated by the Maine Department of Marine Resources, New Hampshire Fish and Game Department, and Massachusetts Division of Marine Fisheries, is designed to provide biological data on the shrimp fishery which is closed for the fourth year in a row. These Maine fishermen were chosen from over 60 applicants based on a random drawing of those fully qualified in each region. Preference was given to trawlers willing to participate in a test of a compound grate for harvesting. The sampling program will include the participation of 10 trawlers (eight Maine trawlers, one Massachusetts trawler and one New Hampshire trawler) and five Maine trappers fishing for eight weeks from mid-January to mid-March. Read the story here 08:15
The program, coordinated by the Maine Department of Marine Resources, New Hampshire Fish and Game Department, and Massachusetts Division of Marine Fisheries, is designed to provide biological data on the shrimp fishery which is closed for the fourth year in a row. These Maine fishermen were chosen from over 60 applicants based on a random drawing of those fully qualified in each region. Preference was given to trawlers willing to participate in a test of a compound grate for harvesting. The sampling program will include the participation of 10 trawlers (eight Maine trawlers, one Massachusetts trawler and one New Hampshire trawler) and five Maine trappers fishing for eight weeks from mid-January to mid-March. Read the story here 08:15

There are more fish in the sea – A high-tech battle for the future of the New England fishing industry
The high-tech battle for the future of the Massachusetts fishing industry is being waged aboard a western-rigged stern trawler named the Miss Emily. Onboard the commercial groundfish vessel, in addition to the satellite positioning system and other sophisticated tools that have become standard in the industry, are at least five computer monitors and a $14,000 fish-measuring board that has halved the time it takes to gauge the catch. State officials say it’s money well spent. Federal catch limits — caps on how many fish each boat can catch — have devastated the state’s most iconic commercial sector, fishermen say. In response to an outcry from the struggling local groundfishing industry, environmental officials are now using the Miss Emily to try to come up with a new — and, they say, more accurate — estimate of codfish in the Gulf of Maine. Under a survey launched last April, local fishermen hope new technology and an aggressive timetable will yield what they have concluded based on their own anecdotal evidence: There are more fish in the sea. Read the story here 09:59
Coral plan threatens fishing grounds
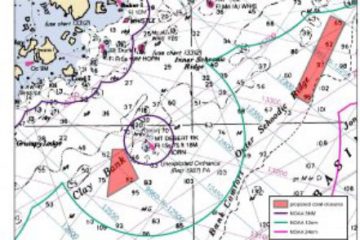 The NEFMC is working with the Mid-Atlantic Fishery Management Council and the South Atlantic Fishery Management Council to preserve deep-sea corals from the Canadian border to Virginia. Area lobstermen could lose valuable fishing grounds if a federal proposal to close four areas of Gulf of Maine waters comes to fruition. The New England Fishery Management Council (NEFMC) has drafted a plan that would close a span of 161 square miles offshore to commercial fishing in an effort to conserve deep-sea coral there. Two of those areas, Mount Desert Rock in Lobster Management Zone B and Outer Schoodic Ridge in Lobster Management Zone A, are preferred fishing grounds for local fishermen when lobster head further offshore in the winter. The other proposed offshore closure areas lie in Jordan Basin and Lindenkohl Knoll to the south. Read the story here 09:34
The NEFMC is working with the Mid-Atlantic Fishery Management Council and the South Atlantic Fishery Management Council to preserve deep-sea corals from the Canadian border to Virginia. Area lobstermen could lose valuable fishing grounds if a federal proposal to close four areas of Gulf of Maine waters comes to fruition. The New England Fishery Management Council (NEFMC) has drafted a plan that would close a span of 161 square miles offshore to commercial fishing in an effort to conserve deep-sea coral there. Two of those areas, Mount Desert Rock in Lobster Management Zone B and Outer Schoodic Ridge in Lobster Management Zone A, are preferred fishing grounds for local fishermen when lobster head further offshore in the winter. The other proposed offshore closure areas lie in Jordan Basin and Lindenkohl Knoll to the south. Read the story here 09:34
Warming waters have fish on the move. Regulators need to act now! Captain Sam Novello, Gulf of Maine Fisherman
 T0 NOAA & NEFMC – Because of our warming ocean temperatures fish & squid stocks are moving into north for cooler waters to survive. In the near future , these stocks will be moving into the waters and these stocks will be more abundant there than in the southern waters. Most Gulf of Maine fishermen have very little quota of these stocks and most have no quota at all! Our regulators and the NEFMC should be addressing the issue now. Today in the Gulf of Maine, most of fishermen and boats are now out of commercial fishing. At one time there was 2500 fishing permits in the fishing industry. Today I believe there about 200 active permits left. Most of these permits are small family day boats who are struggling to stay in business fishing. It would be a devastating disaster to our natural fishing resources and having Gulf of Maine fishermen dump these fish because of lack of quota. Regulators and Management should consider using incidental catch limits on new stocks. Example- 2000 lbs, per trip. All Gulf of Maine communities and fishermen would benefit by using incidental catch limits in Gulf of Maine waters! Captain Sam Novello, Gulf of Maine Fisherman 15:01
T0 NOAA & NEFMC – Because of our warming ocean temperatures fish & squid stocks are moving into north for cooler waters to survive. In the near future , these stocks will be moving into the waters and these stocks will be more abundant there than in the southern waters. Most Gulf of Maine fishermen have very little quota of these stocks and most have no quota at all! Our regulators and the NEFMC should be addressing the issue now. Today in the Gulf of Maine, most of fishermen and boats are now out of commercial fishing. At one time there was 2500 fishing permits in the fishing industry. Today I believe there about 200 active permits left. Most of these permits are small family day boats who are struggling to stay in business fishing. It would be a devastating disaster to our natural fishing resources and having Gulf of Maine fishermen dump these fish because of lack of quota. Regulators and Management should consider using incidental catch limits on new stocks. Example- 2000 lbs, per trip. All Gulf of Maine communities and fishermen would benefit by using incidental catch limits in Gulf of Maine waters! Captain Sam Novello, Gulf of Maine Fisherman 15:01

New net opens a way to help fishermen and protect cod
Catching the wrong fish, or catching too much of a low-quota fish like cod, can end a season for a commercial fisherman. In recent years, the interstate New England Fishery Management Council has slashed the number of cod that can be landed from the Gulf of Maine from about 1,550 metric tons in 2014 to 280 metric tons now. Fishermen who catch too many, even by accident, can be shut down for the season. A team of scientists and fishermen led by the Gulf of Maine Research Institute has created a new kind of fishing net that can catch popular flatfish like yellowtail flounder without busting strict quotas set to protect the Atlantic cod from overfishing. The net redesign team was led by Eayrs, himself a former commercial fisherman in Australia, and Massachusetts state fisheries biologist Michael Pol. The team included four commercial fishermen from Massachusetts and New Hampshire, two other scientists and a Rhode Island netmaker. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Saltonstall-Kennedy program funded the $265,000 project in 2015, when it awarded $22 million in fisheries grants. Read the story here 07:57
Effort to protect deep-sea coral has lobster industry on alert
 Over 400 Maine lobstermen could lose their traditional fishing territory under a proposal to protect deep-sea corals in the Gulf of Maine. The New England Fishery Management Council is considering a plan that would ban fishing in four designated coral zones spanning about 161 miles of federal waters in the Gulf of Maine – Mount Desert Rock, Outer Schoodic Ridge, Jordan Basin and Lindenkohl Knoll. Here, often on steep rock walls deep under water where sunlight cannot penetrate, scientists have found dense, delicate and slow-growing coral gardens of sea whips, fans and pens. During the cold-weather months, when 52-year-old Jim Dow usually fishes for hard-shell lobsters in deep federal waters, his buoys will encircle Mount Desert Rock, where the lobster is so plentiful that boats will sail for hours to drop traps there. As a result, fishermen call it the Meeting Grounds. He said word is just starting to spread about the coral protection plan, but he said the fishermen he has talked with say they didn’t even know there was coral in the deep canyons below. Read the rest here 10:16
Over 400 Maine lobstermen could lose their traditional fishing territory under a proposal to protect deep-sea corals in the Gulf of Maine. The New England Fishery Management Council is considering a plan that would ban fishing in four designated coral zones spanning about 161 miles of federal waters in the Gulf of Maine – Mount Desert Rock, Outer Schoodic Ridge, Jordan Basin and Lindenkohl Knoll. Here, often on steep rock walls deep under water where sunlight cannot penetrate, scientists have found dense, delicate and slow-growing coral gardens of sea whips, fans and pens. During the cold-weather months, when 52-year-old Jim Dow usually fishes for hard-shell lobsters in deep federal waters, his buoys will encircle Mount Desert Rock, where the lobster is so plentiful that boats will sail for hours to drop traps there. As a result, fishermen call it the Meeting Grounds. He said word is just starting to spread about the coral protection plan, but he said the fishermen he has talked with say they didn’t even know there was coral in the deep canyons below. Read the rest here 10:16
Atlantic States Marine Fishery Commission votes to extend closing the Gulf of Maine to shrimping
 The ASMFC’s shrimp section, the panel responsible for setting the northern shrimp regulations, voted to extend the closure throughout 2017 and to establish a 53-ton research set-aside that effectively will produce the only shrimp harvested in the next year from the Gulf of Maine. The 53-ton research set-aside more than doubles the 2016 RSA of 22 metric tons. The panel unanimously approved the motion by Terry Stockwell of Maine that calls for eight trawlers fishing from Maine and one trawler each from Massachusetts and New Hampshire to fish for eight weeks from mid-January to mid-March. The vessels will be limited to one trip per week and a catch of 1,200 pounds of northern shrimp per trip. The RSA also will allow trap fishing, with five trappers allowed to fish for eight weeks, with a limited catch of 500 pounds per week. Vessels will be limited to 40 traps and “preference will be given to individuals in the lottery with double grates and having history prior to the June 7, 2011 control date.” Read the story here 09:32
The ASMFC’s shrimp section, the panel responsible for setting the northern shrimp regulations, voted to extend the closure throughout 2017 and to establish a 53-ton research set-aside that effectively will produce the only shrimp harvested in the next year from the Gulf of Maine. The 53-ton research set-aside more than doubles the 2016 RSA of 22 metric tons. The panel unanimously approved the motion by Terry Stockwell of Maine that calls for eight trawlers fishing from Maine and one trawler each from Massachusetts and New Hampshire to fish for eight weeks from mid-January to mid-March. The vessels will be limited to one trip per week and a catch of 1,200 pounds of northern shrimp per trip. The RSA also will allow trap fishing, with five trappers allowed to fish for eight weeks, with a limited catch of 500 pounds per week. Vessels will be limited to 40 traps and “preference will be given to individuals in the lottery with double grates and having history prior to the June 7, 2011 control date.” Read the story here 09:32
Atlantic States Marine Fishery Commission will decide status Gulf of Maine shrimp fishery
 The commission is scheduled to meet Nov. 10 in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, first to review the most recent stock status report for northern shrimp and technical recommendations from the shrimp advisory panel. It will then set the specifications for the upcoming season. The stock status reports dating back to 2012 reveal a species in free fall, with record low levels of abundance and biomass and poor recruitment since 2012. Those assessments showed problems with overfishing, warming water temperatures and a dwindling number of spawning females. Maine harvesters dominated the fishery the last time it was open in 2013. Of the 207 vessels permitted to shrimp in the Gulf of Maine, 180 had hailing ports in Maine, while Massachusetts and New Hampshire each had 13. Read the story here 07:45
The commission is scheduled to meet Nov. 10 in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, first to review the most recent stock status report for northern shrimp and technical recommendations from the shrimp advisory panel. It will then set the specifications for the upcoming season. The stock status reports dating back to 2012 reveal a species in free fall, with record low levels of abundance and biomass and poor recruitment since 2012. Those assessments showed problems with overfishing, warming water temperatures and a dwindling number of spawning females. Maine harvesters dominated the fishery the last time it was open in 2013. Of the 207 vessels permitted to shrimp in the Gulf of Maine, 180 had hailing ports in Maine, while Massachusetts and New Hampshire each had 13. Read the story here 07:45