Tag Archives: Pacific salmon

Special interest hit piece unfairly targets Southeast fisheries
I was disappointed by what I consider to be a targeted attack on Southeast Alaska salmon fisheries. A report on interceptions of British Columbia salmon in Southeast Alaska salmon fisheries was publicly released on Tuesday by Canadian environmental groups. Many Pacific salmon stocks are highly migratory and often travel across state and international borders. Several stocks migrate into Alaska’s waters to take advantage of the rich marine environment in coastal Southeast Alaska and the Gulf of Alaska where they feed and grow before starting their journey back to their natal streams to spawn. Our quality habitat allows these salmon to thrive and return healthy to their natal streams to renew their life cycle. >click to read< by Doug Vincent-Lang 13:41

Southeast Alaska commercial salmon harvest 4 times higher than last year
Commercial fishermen in Southeast harvested 58 million salmon across the five species this year: almost 7 million chum salmon; 48 million pinks; 1.5 million coho; 1.1 million sockeye and 216,000 king salmon. That’s a marked improvement in harvest for every species. Even the embattled Southeast king salmon had a commercial harvest increase of more than 16,000 fish. In total, commercial salmon fishermen in the region caught and sold 44 million more salmon than last year. Even taking into account the odd-year pink salmon peaks, this year’s pink salmon harvest was more than double 2019’s Southeast Alaska pink salmon catch. >click to read< 19:10

Fishery Closures and the Ghosts of Past Mistakes
The news spread quickly across the calm June waters off the west coast of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, as fishers jumped on the radio to figure out what had just happened. The radio chatter was incessant as fishers wondered aloud where they’d be allowed to fish, if they would be out of business, and what the future would hold. “Everyone was freaking out because all of those questions were unanswered,” Christian says, adding this policy will likely end British Columbia’s commercial salmon industry.,, Under the PSSI, DFO plans to close 57 percent of the 138 Pacific salmon fisheries along the west coast of British Columbia and Yukon. >click to read< 10:06

Commercial harvesters “financially devastated” – 79 B.C. commercial salmon fisheries closed for the 2021 season
The abrupt closure of nearly 60 per cent of B.C. salmon fisheries this summer has left commercial harvesters “financially devastated,” according to a survey by the United Fishermen & Allied Workers’ Union. The survey, which was open to both members and non-members of UFAWU-Unifor, found the unexpected loss of income to have been the biggest blow to harvesters following the effects of the pandemic on the industry.,, For a lot of commercial harvesters, the retirement plan is their boats, gear and licence. In ideal circumstances, if you are a licence-holder, you can sell your licence with your boat when you are ready for retirement,,, >click to read< 15:16

Invasive pink salmon populations are increasing throughout native Atlantic salmon waters
Fisheries biologists have been wringing their hands for decades in cold-water regions of the Pacific Ocean due to the proliferation of farmed Atlantic salmon and the threats they pose to native fish and the health of inshore waters, both in North America off the coasts of the U.S. and Canada, and in South America, where salmon farms are common off the coast of Chile. The threats are real, and there are lots of them,,, But, until recently, the presence of Pacific salmon in the North Atlantic hasn’t moved the “environmental disaster” needle much. That’s changing, thanks to an invasive Pacific salmon that is showing up in larger numbers in traditional Atlantic salmon rivers in Scandinavia, as far south as the British Isles and even to the east coast of Canada. The culprit in question is pink salmon, the smallest and most numerous of the Pacific salmon family. >click to read< 13:20

Warming rivers in US West killing fish, imperiling industry
Salmon fisherman Mike Hudson sits on the bow of his boat at the Berkeley, Calif., Marina on Thursday, July 22, 2021. Baby salmon are dying by the thousands in one river and an entire run of endangered salmon could be wiped out in another. The plummeting catch has led to skyrocketing retail prices for salmon, hurting customers who say they can no longer afford the $35 per pound of fish, said Hudson, who has spent the last 25 years catching and selling salmon at farmers’ markets in Berkeley. “An extreme set of cascading climate events is pushing us into this crisis situation,” said Jordan Traverso, a spokeswoman for the California Department of Wildlife and Fish. 14 photos, >click to read< 10:03

Survivor: Salmon Edition
In 2020, COSEWIC designated seven chinook populations in southern British Columbia as either endangered or threatened. Much the same is true in the Columbia River watershed in the northwestern United States, where chinook populations may have lost more than one-third of their genetic diversity. More worrying still, the rate of young salmon returning as adults to rivers from California to Alaska over the past half-century has plummeted to one-third of earlier levels. It’s a picture that puzzles many researchers. A myriad of variables impact salmon survival and it takes time and research to untangle them. Land use, from mining to damming and irrigation, for example, has affected chinook stocks in the Pacific Northwest at critical life stages, but it can’t be blamed for what’s happening in the northern latitudes. >click to read< 09:05

Pacific salmon recovery report gives 32 recommendations to reverse declines
Wild salmon stocks are being affected by a range of impacts throughout their life cycle, which span from freshwater streams and rivers, to coastal ‘foreshore’ areas and deepwater marine environments, per the report. These threats include habitat degradation, impacts of flood control measures, predation, fishing activity, and threats of disease from fish farms. Based on these findings, the committee provided 32 recommendations to reverse salmon declines, which one witness, Richard Beamish, Scientist Emeritus at DFO’s Pacific Biological Station in Nanaimo, calls the “international Pacific salmon emergency.” >click to read< 07:58

A research expedition returning to Victoria puzzled by a no-show of the fish after an initial big haul
“It is a little difficult for people to accept that scientifically, no catch is sometimes as important as large catches. I think this is the case here,” said Richard Beamish, who is organizing the $1.45-million expedition with fellow B.C. scientist Brian Riddell. “We had relatively large catches of pink, chum and coho early in the survey and there were no salmon in the same area a few weeks later.” It is clear that there are probably large schools of species such as coho that are moving over large areas in response to some factor, Beamish said. The chartered trawler Pacific Legacy No. 1 left Victoria on March 11, headed up to the southern part of the Gulf of Alaska and fished off Dixon Entrance. On Friday, it was 513 miles off Cape Beale, west of Ucluelet. The team expects to return to Victoria on Tuesday. >click to read< 10:32

International Scientific Expedition to probe Pacific salmon survival
“While we recognize that ocean and climate conditions are major factors regulating salmon abundances, the mechanisms regulating abundances in the ocean are not known,” B.C. scientists Richard Beamish and Brian Riddell,, Scientists are seeking to provide more accurate forecasts of salmon returns during what Beamish and Riddell say might be the most difficult time in recent history for stewardship of Pacific salmon.,, The survey takes place as B.C. fishermen fear disastrous returns this year following poor returns for much of the coast last year. >click to read< 18:56
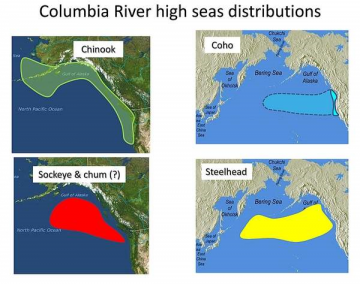
Ghost of ‘the Blob’ haunts Pacific salmon
The initial period after ocean entry for Columbia River basin juvenile salmon and steelhead is when most of the mortality occurs during their lives at sea, so ocean conditions — temperatures and nutrient supplies — during that period are critical to how many of the fish will return to the river as adults one to three years later. The path the fish take after they enter the ocean makes a difference, according Laurie Weitkamp of NOAA Fisheries’ Northwest Fisheries Science Center, Newport Field Station, especially lately with the “strange” ocean conditions. >click here to read< 10:31
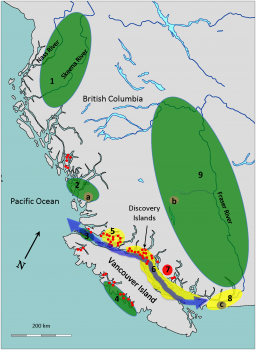
New research shows wild salmon exposed to fish farms have ‘much higher’ rate of disease
Wild salmon exposed to open-net fish farms are much more likely to be infected with piscine reovirus (PRV) than those that don’t have that contact, a new study has concluded. The data also show that the virus makes it more difficult for wild salmon to swim upstream to their spawning grounds, which has major implications for the sustainability of the populations. “The government has to remove this industry from the key salmon migration routes or we risk the complete loss of wild salmon in this province,” said Alexandra Morton, lead author on the report and an outspoken advocate for wild salmon. click here to read the story 18:07
The effect of exposure to farmed salmon on piscine orthoreovirus infection and fitness in wild Pacific salmon in British Columbia, Canada – click here to read the study
Public urged to remain vigilant after Pacific salmon found in Irish rivers
 Thirty Pacific salmon have been found in nine Irish river systems since the first one was recorded in late June. Fisheries chiefs said one of the most recent non-native fish to be captured was a mature male, which was ready to spawn when it was found on August 9 on the Erriff in Co Mayo. It has been suggested that some of the Pacific species have made their way south after “straying” from rivers in northern Norway or Russia. They were introduced to some Russian fisheries in the 1960s and have colonised west along Arctic coasts. click here to read the story 09:02
Thirty Pacific salmon have been found in nine Irish river systems since the first one was recorded in late June. Fisheries chiefs said one of the most recent non-native fish to be captured was a mature male, which was ready to spawn when it was found on August 9 on the Erriff in Co Mayo. It has been suggested that some of the Pacific species have made their way south after “straying” from rivers in northern Norway or Russia. They were introduced to some Russian fisheries in the 1960s and have colonised west along Arctic coasts. click here to read the story 09:02
Update: No Fukushima Contamination Detected in Pacific Salmon Off North American Coast
 The Integrated Fukushima Ocean Radionuclide Monitoring (InFORM) project is a network involving academic, governmental, and non-governmental organizations, as well as citizen scientists. InFORM is acquiring data to support a thorough radiological impact assessment for Canada’s west coast stemming from the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant (FD-NPP) accident, and to effectively communicate these results to the public. Read the rest here 16:00
The Integrated Fukushima Ocean Radionuclide Monitoring (InFORM) project is a network involving academic, governmental, and non-governmental organizations, as well as citizen scientists. InFORM is acquiring data to support a thorough radiological impact assessment for Canada’s west coast stemming from the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant (FD-NPP) accident, and to effectively communicate these results to the public. Read the rest here 16:00
Salmon in NY waters have complex natural instincts
 Chinook, or king, salmon are stocked in New York waters. These fish actually are Pacific salmon that are raised in state hatcheries, said Matt Sanderson, a regional fisheries biologist with the New York Department of Environmental Conservation. Brown trout and coho salmon also are stocked by the state. [email protected] 08:40
Chinook, or king, salmon are stocked in New York waters. These fish actually are Pacific salmon that are raised in state hatcheries, said Matt Sanderson, a regional fisheries biologist with the New York Department of Environmental Conservation. Brown trout and coho salmon also are stocked by the state. [email protected] 08:40
Opinion: Some students learn from mistakes – Jack Emberly, retired teacher, local author and environmentalist.
Maple Ridge News – In the 1960s, the DFO paid $15 for harbor seal “snouts,” proof an enemy of Pacific salmon had been killed. Bounty hunters – commercial and recreational fishermen eager to help the cause – shot thousands of animals. Many seals sank before they could give up their noses. Dr. Lance Barrett-Lennard, biologist Vancouver Aquarium, recalls this culling campaign as an example of government tinkering with a perfectly self-regulating bio-system. alrighty then ,,,,,,,,,continued













































