U.S. Congressman Garret Graves is calling for the U.S. Department of Commerce to immediately declare a “Fishery Disaster Determination” due to both the biological resources and fishery infrastructure sustaining major damage related to Hurricane Ida. Commerce is able to declare the disaster provided by the provisions within the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act and Interjurisdictional Fisheries Act. The declared disaster would provide targeted relief to one of the most impacted sectors of Louisiana’s economy. The funds would help both commercial and recreational fishers begin to recover. >click to read< 18:31
Tag Archives: magnuson-stevens-fishery-conservation-and-management-act
South Carolina shrimpers applaud decision to impose duties on shrimp imported from four countries
 South Carolina shrimpers are celebrating the U.S. International Trade Commission’s recent decision to crack down on frozen shrimp imports from four countries. The ITC voted in favor of issuing countervailing duties on frozen, warm-water shrimp imports from Ecuador, India, and Vietnam after the U.S. Department of Commerce determined those governments were illegally subsidizing the industry. “We’re grateful because it’s an acknowledgment of what we feel and we experience in the industry and we see on a daily basis,” said Bryan Jones, a first-generation shrimper who lives in McClellanville. Jones serves as vice president of the South Carolina Shrimpers Association and was among a group of commercial fishermen who testified before the ITC in Washington, D.C. in October. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 14:20
South Carolina shrimpers are celebrating the U.S. International Trade Commission’s recent decision to crack down on frozen shrimp imports from four countries. The ITC voted in favor of issuing countervailing duties on frozen, warm-water shrimp imports from Ecuador, India, and Vietnam after the U.S. Department of Commerce determined those governments were illegally subsidizing the industry. “We’re grateful because it’s an acknowledgment of what we feel and we experience in the industry and we see on a daily basis,” said Bryan Jones, a first-generation shrimper who lives in McClellanville. Jones serves as vice president of the South Carolina Shrimpers Association and was among a group of commercial fishermen who testified before the ITC in Washington, D.C. in October. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 14:20
New bill to expand federal relief eligibility for fishing/shrimping industry
 “The influx of imported shrimp has resulted in the decline of our fleets and massive job losses and our local businesses are devastated,” said Bryan Jones, the Vice President of the South Carolina Shrimper’s Association. Standing in front of the shrimp boats of Shem Creek, US Congresswoman Nancy Mace (R) introduced the Protect American Fisheries Act on Friday. “Foreign dumping of shrimp filled with contaminants that don’t meet US safety standards is undercutting honest, hardworking, American fisherman,” said Congresswoman Mace. The bipartisan bill proposes to amend the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act to include “economic causes” as a reason for declaring a fishery resource disaster. Video, more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 06:58
“The influx of imported shrimp has resulted in the decline of our fleets and massive job losses and our local businesses are devastated,” said Bryan Jones, the Vice President of the South Carolina Shrimper’s Association. Standing in front of the shrimp boats of Shem Creek, US Congresswoman Nancy Mace (R) introduced the Protect American Fisheries Act on Friday. “Foreign dumping of shrimp filled with contaminants that don’t meet US safety standards is undercutting honest, hardworking, American fisherman,” said Congresswoman Mace. The bipartisan bill proposes to amend the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act to include “economic causes” as a reason for declaring a fishery resource disaster. Video, more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 06:58
Fishermen Who Were Forced to Pay $700 Per Day to Government-Mandated Observers on Their Boats Get Big News from SCOTUS
 Members of the 18th-century British Parliament, unelected by American colonists, tried to take money from those colonists without their consent. Hence, the American Revolution ensued. On Friday, the U.S. Supreme Court overturned a 40-year-old ruling that had allowed unelected federal regulators, acting the part of the British Parliament, to commit such travesties of justice as requiring fishermen to pay for government-mandated regulators on their boats — a requirement that, according to CBS, could cost the fishermen more than $700 per day. The true magnitude of Friday’s ruling, however, involved far more than fishing boats. In fact, it struck at the heart of American progressivism by eviscerating the insidious claim that federal “experts” know best. In so doing, it took one small-but-crucial step towards dismantling the permanent federal state that actually governs in Washington, D.C. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 11:18
Members of the 18th-century British Parliament, unelected by American colonists, tried to take money from those colonists without their consent. Hence, the American Revolution ensued. On Friday, the U.S. Supreme Court overturned a 40-year-old ruling that had allowed unelected federal regulators, acting the part of the British Parliament, to commit such travesties of justice as requiring fishermen to pay for government-mandated regulators on their boats — a requirement that, according to CBS, could cost the fishermen more than $700 per day. The true magnitude of Friday’s ruling, however, involved far more than fishing boats. In fact, it struck at the heart of American progressivism by eviscerating the insidious claim that federal “experts” know best. In so doing, it took one small-but-crucial step towards dismantling the permanent federal state that actually governs in Washington, D.C. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 11:18

Bering Sea fishermen press NPFMC on halibut bycatch
After years of deliberations, the North Pacific Fishery Management Council is inching toward a decision on whether to tie halibut bycatch limits in the Bering Sea to abundance indices. The action, known formally as Bering Sea-Aleutian Islands halibut abundance-based management, or ABM, is intended to reduce bycatch of halibut in the Bering Sea by the Amendment 80 trawl fleet when the fish stocks are lower. The Amendment 80 fleet is a group of catcher-processor vessels that are allocated a portion of groundfish harvest. Each year, the fleet is bound to a hard limit on how many halibut they can take as bycatch, known as the prohibited species catch, or PSC limit. >click to read< 08:34

Commerce Department Announces 2021 Appointments to the Regional Fishery Management Councils
The U.S. Department of Commerce today announced the appointment of 31 members to the regional fishery management councils that partner with NOAA Fisheries to manage marine fishery resources. Established by the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act, councils are responsible for developing region-specific fishery management plans that safeguard and enhance the nation’s fisheries resources. Each year, the Secretary of Commerce appoints approximately one-third of the total 72 appointed members to the eight,,, >click here to read< 15:03

NOAA Fisheries Releases Final “Batched” Biological Opinion & North Atlantic Right Whale Conservation Framework
NOAA Fisheries released its Endangered Species Act (ESA) section 7 Biological Opinion on the authorization of eight federal fisheries management plans under the MSA two interstate fishery management plans under the Atlantic Coastal Fisheries Cooperative Management Act, and the implementation of the New England Fishery Management Council’s Omnibus Essential Fish Habitat Amendment 2. We also released the North Atlantic Right Whale Conservation Framework for Federal Fisheries in the Greater Atlantic Region (Conservation Framework). NOAA Fisheries has evaluated the effects of the authorization of the fisheries, as modified by the Conservation Framework, on endangered and threatened species. The 10 fisheries included in the Opinion are: >click to read< 12:22

Huffman Gets Bleak Input on Fisheries
On Oct. 5, North Coast Congressman Jared Huffman held a public meeting in Arcata to discuss updating the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act (MSA), the federal legislation that governs ocean fishing. Huffman brought together a roundtable of regional and local officials, a Humboldt State University professor and a few representatives of the local fishing industry to offer feedback on the failings — and successes — of the MSA. >click to read< 10:22

Council turns down petition sought to protect Adak processor
The North Pacific Fishery Management Council decided not to approve an emergency petition from a group of Aleutian Islands stakeholders at its meeting June 9, instead taking a longer route through a discussion to look at the set-aside options for the area. The petition had sought an emergency quota set-aside of Pacific cod, separate from the general Bering Sea-Aleutian Islands quota, to help sustain the shore-based plant and thus the community. >click to read<09:36
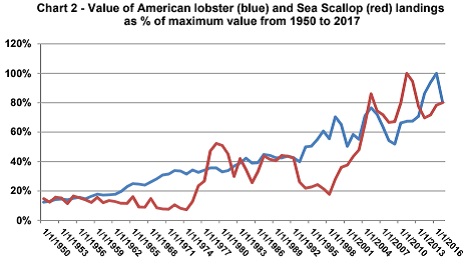
After over forty years of NOAA/NMFS management how are we really doing? Nils Stolpe
The Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act – I have seen the focus of government fisheries manage-ment increasingly shift away from the fishermen to the fish. The provisions of the Act as it was originally written were put in place to allow the U.S. fishing industry to regain control of the fisheries in the United States’ highly productive coastal waters,,, The legislation was singularly effective, so effective that within ten years or so of its passage the greatest portion of our domestic fish and shellfish production was being harvested by U.S. fishermen on U.S. vessels. This success was sold to the U.S. public – and the U.S. politicians – as an assault on the “sanctity” of our coastal waters by a burgeoning environmental industry that was (and still is) engaged in non-governmental empire building. This has resulted in a handful of multi-national ENGOs (Environmental Non-Governmental Organizations) that have become at least as influential as the fishing industry in national and international fisheries management. >click to read, and review the links and graphs<16:10

Fishery Disaster Assistance Soon to Be Available to Georgia Shrimpers
The Southern Shrimp Alliance is pleased to inform the Georgia shrimp industry that $1.062m in financial assistance has been made available to address the 2013 Georgia shrimp fishery disaster. Commerce Secretary Wilbur Ross announced the funding in a March 27, 2019 press release. In a February 10, 2014, letter to then U.S. Secretary of Commerce Penny Pritzker, then Georgia Governor Nathan Deal filed a request for fishery disaster assistance pursuant to section 312(a) of the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act (MSA). >click to read<17:07

President Trump Signs Bipartisan Modern Fish Act Into Law
The Modern Fish Act was signed into law on December 31st, 2018, by President Donald Trump. Over 11 million Americans partake in recreational saltwater fishing—with the activity being heavily concentrated in the southeastern U.S. In what is being celebrated as a victory for recreational fishing and boating, this law will be bring much-needed clarification and reforms to the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act. While the bill is not entirely perfect, various stakeholders agree this new law will clarify any confusion previously inset in the law and bring recreational fishing management into the 21st century. The Modern Fish Act was passed unanimously in the U.S. Senate on December 17th, and by overwhelming approval in the House (350-11) on December 19th, 2018. >click to read<15:51

2017 Report to Congress on the Status of U.S. Fisheries
NOAA Fisheries NMFS is pleased to present the 2017 Report to Congress on the Status of U.S. Fisheries managed under the science-based framework established by the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act (MSA). The 2017 report highlights the work toward the goal of maximizing fishing opportunities while ensuring the sustainability of fisheries and fishing communities. Due to the combined efforts of NOAA Fisheries, the eight regional fishery management councils, and other partners, three previously overfished stocks were rebuilt and the number of stocks listed as overfished is at a new all-time low. >click to read<16:04

H.R. 200 – More than one way to manage the nation’s fisheries
For the first time ever, reauthorization of the nation’s overarching marine fishery management law will take into account concerns of America’s recreational anglers. In mid-December, the U.S. House Committee on Natural Resources approved H.R. 200, a bill sponsored by Rep. Don Young, R-Alaska, amending the 1976 Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act. While the vast majority of the public hails progress on the bill as long overdue, an unusual coalition of environmentalists and commercial fishing entities has roundly condemned it, feverishly depicting the bill as an attack on the oceans and a threat to the future of the nation’s marine resources. >click here to read< 20:57
Legislative Hearing on 4 Fishery Bills – Tuesday, September 26, 2017 10:00 AM
 H.R. 200 (Rep. Don Young), To amend the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act to provide flexibility for fishery managers and stability for fishermen, and for other purposes. click here H.R. 2023 (Rep. Garret Graves), To modernize recreational fisheries management Modernizing Recreational Fisheries Management Act of 2017 click here H.R. 3588 (Rep. Garret Graves), To amend the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act to provide for management of red snapper in the Gulf of Mexico, and for other purposes. click here RED SNAPPER Act Discussion Draft of H.R. ____ (Rep. Jared Huffman), To amend and reauthorize the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act, and for other purposes. click here To read the notice, click here 12:29
H.R. 200 (Rep. Don Young), To amend the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act to provide flexibility for fishery managers and stability for fishermen, and for other purposes. click here H.R. 2023 (Rep. Garret Graves), To modernize recreational fisheries management Modernizing Recreational Fisheries Management Act of 2017 click here H.R. 3588 (Rep. Garret Graves), To amend the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act to provide for management of red snapper in the Gulf of Mexico, and for other purposes. click here RED SNAPPER Act Discussion Draft of H.R. ____ (Rep. Jared Huffman), To amend and reauthorize the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act, and for other purposes. click here To read the notice, click here 12:29

Modern Fish Act: boon to recreational fishing or risk to U.S. fishery?
The Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act sets strict, scientifically adjusted, annual catch limits on U.S. commercial, charter and recreational fisheries in order to sustain saltwater fish stocks, and is seen as a model of fishery management globally. The Modern Fish Act (MFA), a bill introduced in the U.S. House in April, would do away with limits on recreational fishermen, who argue they have no impact on fishery stocks. Environmentalists, however, say the MFA introduces legal loopholes that would allow for uncontrolled fishing at potentially unsustainable levels that could cause stocks to crash. Critics also say that the MFA muddies the waters between federal and state management, and allows political and economic considerations to override science in management decisions. The bill is still moving through Congress, and its chances for passage are presently unknown. click here to read the story 08:55

Fish Stocks And Our Balance Of Payments
Our balance of payments is overly burdened by our consumption of seafood: We import approximately 90% of the seafood that we eat. Given our natural resources, we should be net exporters of seafood. The total value of edible and non-edible fishery imports in the United States was $35.8 billion in 2016. The total value of edible and non-edible exports was $21.3 billion. The imbalance does not imply only a shipment of dollars abroad. It also implies a number of jobs exported, a number of jobs that could be created in this country, were we not to import that much more seafood than we export.,,, The reason for the imbalance in our accounts with other nations is not due to lack of fish in our waters. Not to put too fine a point on it, the imbalance is due to rules and regulations imposed by our National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS) that prevent our fishermen from catching fish. click here to read the article by Carmine Gorga 09:21
MSA – Fishing rule gives regional councils more flexibility on catch limits
 The rule, already under fire from environmental groups in a rare conflict with the administration, could help mollify the recreational fishing industry and its Republican allies in Congress. They’ve criticized the administration for not relaxing restrictions on catches, given that many fish stocks have rebounded dramatically over the past few years. Officials with the fisheries division of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, said the change, years in the making, strikes an appropriate balance between current law, which has helped rescue dozens of once over-fished stocks, and the needs of the economically vital recreational and commercial industry. Some environmental groups oppose the change, saying that giving more “flexibility” to the eight regional councils that set catch limits in federal waters could soften protections that have worked well. “Unfortunately, the new rules weaken the foundations of U.S. sustainable fisheries management,” said Meredith Moore, director of the fish conservation program at Ocean Conservancy. “By allowing risky management decisions that leave stocks at low levels, we leave fish populations and fishing communities vulnerable.” Read the story here. Read the NOAA press release – NOAA announces revisions to federal fishery management guidelines click here 20:07
The rule, already under fire from environmental groups in a rare conflict with the administration, could help mollify the recreational fishing industry and its Republican allies in Congress. They’ve criticized the administration for not relaxing restrictions on catches, given that many fish stocks have rebounded dramatically over the past few years. Officials with the fisheries division of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, said the change, years in the making, strikes an appropriate balance between current law, which has helped rescue dozens of once over-fished stocks, and the needs of the economically vital recreational and commercial industry. Some environmental groups oppose the change, saying that giving more “flexibility” to the eight regional councils that set catch limits in federal waters could soften protections that have worked well. “Unfortunately, the new rules weaken the foundations of U.S. sustainable fisheries management,” said Meredith Moore, director of the fish conservation program at Ocean Conservancy. “By allowing risky management decisions that leave stocks at low levels, we leave fish populations and fishing communities vulnerable.” Read the story here. Read the NOAA press release – NOAA announces revisions to federal fishery management guidelines click here 20:07
Ninth Circuit Sides With Cook Inlet Fishermen
 The Ninth Circuit ruled Wednesday that the federal government must manage fisheries in federal waters that require conservation, unless a fishery-management plan cedes control to a state. Reversing a decision from the Alaska Federal Court, the Ninth Circuit panel held that the National Marine Fisheries Service is required by the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act to include the Cook Inlet in its fishery-management plan. It may not hand over control of the inlet to the state of Alaska without first drawing up a plan, according to the 20-page ruling. The North Pacific Fishery Management Council has jurisdiction over Cook Inlet. In 2011, the Council voted and passed Amendment 12 to remove the net-fishing areas from its plan, arguing that the plan was vague on management goals and that the state was the most appropriate management authority. However, the amendment was opposed by the United Cook Inlet Drift Association and the Cook Inlet Fishermen’s Fund, two groups of commercial fishermen. However, the amendment was opposed by the United Cook Inlet Drift Association and the Cook Inlet Fishermen’s Fund, two groups of commercial fishermen. They argued that the state’s failure to deal with carnivorous northern pike and its improper escapement management have contributed to a 51 percent reduction in the sockeye salmon catch since 1981. Read the story here 08:14
The Ninth Circuit ruled Wednesday that the federal government must manage fisheries in federal waters that require conservation, unless a fishery-management plan cedes control to a state. Reversing a decision from the Alaska Federal Court, the Ninth Circuit panel held that the National Marine Fisheries Service is required by the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act to include the Cook Inlet in its fishery-management plan. It may not hand over control of the inlet to the state of Alaska without first drawing up a plan, according to the 20-page ruling. The North Pacific Fishery Management Council has jurisdiction over Cook Inlet. In 2011, the Council voted and passed Amendment 12 to remove the net-fishing areas from its plan, arguing that the plan was vague on management goals and that the state was the most appropriate management authority. However, the amendment was opposed by the United Cook Inlet Drift Association and the Cook Inlet Fishermen’s Fund, two groups of commercial fishermen. However, the amendment was opposed by the United Cook Inlet Drift Association and the Cook Inlet Fishermen’s Fund, two groups of commercial fishermen. They argued that the state’s failure to deal with carnivorous northern pike and its improper escapement management have contributed to a 51 percent reduction in the sockeye salmon catch since 1981. Read the story here 08:14
Pacific Council on proposed Marine Monument
Today, the  Pacific Fishery Management Council sent a letter to President Obama expressing concern about “how these National Monument designations would impact our fishery management efforts in the west coast Exclusive Economic Zone.” In it, the Council stresses: 1. All of the areas proposed for designation already have significant protections from specific fishing activities. For example – Essential Fish Habitat requirements under the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act; and Cowcod Conservation Areas off the Southern California coast. 2. Fishery management decisions are best done in a thoroughly transparent public process rather than being done with limited involvement of certain stakeholders. 3. The social and economic importance of those areas cannot be understated. Read the letter from the PFMC, and the letter from the Council Coordination Committee by clicking here 07:44
Pacific Fishery Management Council sent a letter to President Obama expressing concern about “how these National Monument designations would impact our fishery management efforts in the west coast Exclusive Economic Zone.” In it, the Council stresses: 1. All of the areas proposed for designation already have significant protections from specific fishing activities. For example – Essential Fish Habitat requirements under the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act; and Cowcod Conservation Areas off the Southern California coast. 2. Fishery management decisions are best done in a thoroughly transparent public process rather than being done with limited involvement of certain stakeholders. 3. The social and economic importance of those areas cannot be understated. Read the letter from the PFMC, and the letter from the Council Coordination Committee by clicking here 07:44
Longstanding fisheries act doesn’t need changing says Hogarth and Murawski, Sam Parisi disagrees
 Those who catch ocean fish, dine on the country’s marine bounty or simply appreciate the remarkable improvement in the state of America’s fisheries can thank the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act. From its passage in 1976, the nation’s premier fisheries law has been remarkably free of the party politics so often exhibited these days. And that’s exactly why we need to be careful about some current initiatives to change it. As we approach the transition to a new administration, however, a number of proposals have emerged to revise the law or change its administrative guidelines. Unfortunately, these would loosen effective protections that have been so successful in eliminating overfishing and rebuilding stocks. Read the rest here Fishermen take another hit. NOAA wins again. How can you beat them? It seems like the deck is stacked against fishermen. Take the case in New Hampshire (”Judge rules for government in monitoring suit,” July 29). The judge ruled under the law he does not have to take into account any other scientific data. In other words, what NOAA research vessels say is the bottom line. First of all, ask a real fishermen with 20 or more years experience if those on the NOAA research vessel know what they are doing. They will tell you perhaps not. If the judge was ruling because of the way the law is written, then we need to change the law .It has been more than 50 years since the Magnuson-Stevens Act was passed. A lot has changed. We need to review the act and if necessary modify it, or our fishermen will never be able to beat NOAA in a court of law. Sam Parisi Gloucester 14:20
Those who catch ocean fish, dine on the country’s marine bounty or simply appreciate the remarkable improvement in the state of America’s fisheries can thank the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act. From its passage in 1976, the nation’s premier fisheries law has been remarkably free of the party politics so often exhibited these days. And that’s exactly why we need to be careful about some current initiatives to change it. As we approach the transition to a new administration, however, a number of proposals have emerged to revise the law or change its administrative guidelines. Unfortunately, these would loosen effective protections that have been so successful in eliminating overfishing and rebuilding stocks. Read the rest here Fishermen take another hit. NOAA wins again. How can you beat them? It seems like the deck is stacked against fishermen. Take the case in New Hampshire (”Judge rules for government in monitoring suit,” July 29). The judge ruled under the law he does not have to take into account any other scientific data. In other words, what NOAA research vessels say is the bottom line. First of all, ask a real fishermen with 20 or more years experience if those on the NOAA research vessel know what they are doing. They will tell you perhaps not. If the judge was ruling because of the way the law is written, then we need to change the law .It has been more than 50 years since the Magnuson-Stevens Act was passed. A lot has changed. We need to review the act and if necessary modify it, or our fishermen will never be able to beat NOAA in a court of law. Sam Parisi Gloucester 14:20
COMMENTARY: 40 years after Magnuson-Stevens, not all promises kept
 The Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act turned 40 last week and federal and state fishery managers marked that event with an opinion piece in the Alaska Dispatch News on April 12 extolling the successes of the Magnuson-Stevens Act and its implementation in Alaska as a “global model of sustainability.” As the authors point out, the Magnuson-Stevens Act sets up a “transparent governing process” intended to ensure that “science is behind every fishery management decision” in Alaska. Indeed, the Magnuson-Stevens Act sets up national standards ensuring that all fisheries are managed to achieve “optimum yield from each fishery” with management decisions “based on the best scientific information available,” and guided by carefully considered fishery management plans. BUT,,, Read the rest here 16:31
The Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act turned 40 last week and federal and state fishery managers marked that event with an opinion piece in the Alaska Dispatch News on April 12 extolling the successes of the Magnuson-Stevens Act and its implementation in Alaska as a “global model of sustainability.” As the authors point out, the Magnuson-Stevens Act sets up a “transparent governing process” intended to ensure that “science is behind every fishery management decision” in Alaska. Indeed, the Magnuson-Stevens Act sets up national standards ensuring that all fisheries are managed to achieve “optimum yield from each fishery” with management decisions “based on the best scientific information available,” and guided by carefully considered fishery management plans. BUT,,, Read the rest here 16:31
Magnuson-Stevens – Editorial: At 40, landmark fishery law needs revamping
 This Wednesday is the 40th anniversary of the of 1976. Writing on behalf of the At-sea Processors Association, a columnist offers an enthusiastic opinion that the act sets the “gold standard” for U.S. and world fisheries. But it remains a disappointment in a variety of ways. This is perhaps most obvious on the East Coast, where groundfish stocks are a small fraction of what they were in 1976. Fisheries on the West Coast, and the U.S. in general, continue to struggle. Read the editorial here 08:46
This Wednesday is the 40th anniversary of the of 1976. Writing on behalf of the At-sea Processors Association, a columnist offers an enthusiastic opinion that the act sets the “gold standard” for U.S. and world fisheries. But it remains a disappointment in a variety of ways. This is perhaps most obvious on the East Coast, where groundfish stocks are a small fraction of what they were in 1976. Fisheries on the West Coast, and the U.S. in general, continue to struggle. Read the editorial here 08:46