Tag Archives: Wild salmon
Celebrate wild sockeye salmon — the harvest that powers Bristol Bay’s economy and feeds the world
 It’s the time of year again when children have returned to school and seemingly endless daylight gives way to shorter days and cooler nights. In the Bristol Bay region of Alaska, it is viewed less as the end of another summer, and more as the end of another salmon season. Many weeks of hard work harvesting and preserving tens of millions of salmon to feed our families, communities and the rest of the world has come to an end. I can’t think of a better time to pause and celebrate Bristol Bay’s wild salmon. We celebrate the incredible journey every single salmon makes; traveling thousands of miles in its life to return to its birthplace and complete the cycle of life. Over the week of Sept. 9, a diverse coalition of commercial fishermen, business leaders, lodge owners, Alaska Native people and others, all from the Bristol Bay region, is bringing this celebration to the nation’s capital. more, >>CLICK TO READ<<10:15
It’s the time of year again when children have returned to school and seemingly endless daylight gives way to shorter days and cooler nights. In the Bristol Bay region of Alaska, it is viewed less as the end of another summer, and more as the end of another salmon season. Many weeks of hard work harvesting and preserving tens of millions of salmon to feed our families, communities and the rest of the world has come to an end. I can’t think of a better time to pause and celebrate Bristol Bay’s wild salmon. We celebrate the incredible journey every single salmon makes; traveling thousands of miles in its life to return to its birthplace and complete the cycle of life. Over the week of Sept. 9, a diverse coalition of commercial fishermen, business leaders, lodge owners, Alaska Native people and others, all from the Bristol Bay region, is bringing this celebration to the nation’s capital. more, >>CLICK TO READ<<10:15

Commercial fishers and wild salmon advocates celebrate large returns to B.C. waters
Mitch Dudoward has worked in the salmon industry for more than 40 years and says fishing on the Skeena River in northwest B.C. has never been better. “This is the best season I can recall in my lifetime with the numbers we are catching,” said Dudoward, who recently completed a big sockeye haul aboard his gillnetter Irenda. Meanwhile, Bob Chamberlin, chairman of the First Nations Wild Salmon Alliance, said thousands of pink salmon are in Central Coast rivers after years of minimal returns. The strong run comes two years after the closure of two open-net Atlantic salmon farms in the area. “We got them removed and two years later we went from 200 fish in the river to where we have several thousand to date. In our mind and knowledge that is a really clear indicator.” >click to read< 10:41

Canada ignored warnings of virus infecting farmed and wild salmon
Canada was warned in 2012 by its own scientists that a virus was infecting both farmed and wild salmon, but successive governments ignored the expert advice, saying for years that risks to salmon were low. Justin Trudeau’s government has said it will phase out open-pen industrial fish farms off the coast of British Columbia by 2025. But both his government and the previous Conservative government were in possession of a newly released report that linked large-scale farms and wild salmon to the highly contagious Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV). In 2012, biologists with the department of fisheries and oceans investigated the presence of the virus, which has been found in both farmed and wild salmon. but successive governments ignored the expert advice, saying for years that risks to salmon were low. >click to read< 11:48

A virus that flourishes in fish farms is now threatening wild populations.
Wild salmon in British Columbia are in trouble. According to one estimate, some populations have dropped by as much as 93 percent since the early 1990s. Lately, the situation has grown dire.,, Last year, the number of sockeye returning to spawn in the Fraser River crashed to a record low. It’s hard to say exactly why this is happening, though logging, climate change, and overfishing all seem to play a role. Among the most controversial potential factors, however, is the virus Piscine orthoreovirus, or PRV. The virus isn’t necessarily fatal, but infected fish may be weakened and unable to swim as fast, making them more likely to be eaten by predators or fail to migrate upriver in order to spawn,,, Not everyone agrees. Among the dissenters is Fisheries and Oceans Canada-DFO,,, >click to read< Killing Sea Lions to Save the Salmon, February 1,1925, Dorothy G. Bell, >click to read< 19:39

New Study – B.C. Salmon farms regularly under count sea lice, potentially putting wild salmon at risk
The study shows mandatory sea lice counts performed by the operators of the fish farms drop by between 15 and 50 per cent when they’re not being done during an audit by Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO). “That isn’t really a minor effect. This is a pretty obvious result,” said lead researcher Sean Godwin, who conducted the research for his PhD at Simon Fraser University. Salmon farms are required to perform monthly counts of the sea lice on their fish and make those numbers publicly available. The counts are self-reported, but fisheries officials perform occasional, pre-arranged audits to make sure the numbers are accurate. If the lice counts pass a certain threshold, the operators are required to pay for delousing treatments. >click to read< 15:59

8 more wild salmon restoration projects to receive funding in B.C.
Fisheries Minister Bernadette Jordan addressed the Greater Vancouver Board of Trade on Tuesday, saying climate change and increasing demand for seafood products has put unprecedented pressure on Pacific wild salmon. The latest projects will receive about $10.5 million from the joint federal and provincial fund established in 2018 to help the recovery of stocks in steep decline.,,, “Speaking to British Columbians, I want to assure you that our government is moving ahead with the transition from open-net pens,” she said, adding Ottawa will develop a comprehensive process to ensure all voices are heard in the decision-making process. >click to read< 10:24

How Coronavirus Is Threatening Alaska’s Wild Salmon Fishing Season
A Brooklyn winemaker travels north to Bristol Bay each summer to net the red salmon that support his family. This year he’s faced with a tough ethical and economic choice. Mr. Nicolson, 45, spends much of the year working at Red Hook Winery in Brooklyn, where he is the managing winemaker, but his main income is drawn from Iliamna Fish Company. The business, which he and two cousins own, sells Alaska red salmon directly to thousands of shareholders, most of them in New York and Portland, Ore., as well as to a few high-end restaurants and stores, including the Park Slope Food Co-op in Brooklyn. >click to read< 19:25

How one fisherman brings his wild salmon catch from Alaska to Missouri
Sean Guffey was studying communications at the University of Michigan when he drove to Alaska during the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Soon, he was on a fishing boat with scientists studying the impact of the spill. As he watched, Guffey learned from their observations and concerns about wildlife. Every year since, he has found his way back to Alaska. Today, he is the captain of Watermen, a boat docked in Bristol Bay. And every summer, he catches wild sockeye salmon and brings it back to Missouri to sell. photos, >click to read< 17:22

Thanks for all the fish: a wild salmon story
I live in a place that’s wedded to salmon. Hundreds of local people in this town of 5,000 are commercial salmon fishermen, scores more fish for themselves or work in an industry tied to salmon. So it makes sense that the local calendar runs on these fish. Schools break up in late May so families can prepare for the salmon season. The ebb and flow of boats from the harbour and local boatyards follow salmon. Tourists do too, thronging into town just as the fish start filling local rivers.It might be odd that Homer calls itself the “Halibut Fishing Capital of the World” when it’s salmon that truly captures locals’ hearts. Halibut are dun-coloured flatfish; we think of them as meat that swims. photos, >click to read< 09:12

Alexandra Morton: Mark, set, go—reversing the salmon extinction trend
As a scientist and a grandmother, I want to make sure we don’t give up on wild salmon. This year, 2019, is the worst salmon return in the history of this country and the silence is terrifying. It feels like everyone is giving up. Salmon are masters at the art of thriving. They are so good at it all we need to do is listen to them and here is how. Politics aside, the pattern of the 2019 collapse is so clear Siri could navigate it. The Fraser sockeye, which swim through Atlantic salmon pathogens twice in their life history, crashed to 10 percent of what was forecast, while the Nass,,, >click to read< 09:24

Harvest numbers are mixed as season gets underway. Meanwhile, PWS wild salmon harvest tops 1.5M fish
Prince William Sound landings of wild Alaska salmon have been strong, as the fishery gets under way. Meanwhile sockeye production in Kodiak, Cook Inlet and Chignik is off to a slow start, fisheries economist Garrett Evridge says in his first harvest report of the season. “Year-to-date statewide harvest of sockeye is more than three times the prior year,” said Evridge, an economist with the McDowell Group, >click to read<14:08
PWS wild salmon harvest tops 1.5M fish – As more areas of Prince William Sound opened for commercial fishing, preliminary data compiled by the Alaska Department of Fish and Game put the catch at 1.5 million salmon through June 18, including some 813,942 fish caught in the Copper River. >click to read<

Moving salmon farms on land vital
You may have heard that the federal government has a new minister of Fisheries, Oceans and Canadian Coast Guard. Unlike his predecessor from the east, Jonathan Wilkinson is a West Coast man. Also unlike his predecessor, he will understand what the wild salmon mean to all of us on the B.C. coast. From Indigenous communities to whom the salmon have given physical and spiritual sustenance for millennia, to tourist and commercial fishing, and all of us who want to eat wild salmon that is unadulterated from chemicals; to bears and marine animals who depend on the wild runs, and the forests who are fed by salmon carcasses, the wild salmon is part of who we all are. by Paula Foot >click to read<12:00

Wild salmon return to Bay Area markets
Local wild king salmon are back in Bay Area markets and restaurants after the commercial season reopened last week from Pigeon Point (near Half Moon Bay) south to the Mexico border. “The fleet just found a school of beautiful salmon,” San Francisco fisherwoman Sarah Bates said via a text from her boat, the Bounty. This current window of commercial salmon season is scheduled to last from June 19 to June 30. Bates said the fleet had to wait until about the third day of the opener to start fishing, once the school moved south of the Pigeon Point line with the movement of prevailing currents and feed. >click to read<19:43

It’s wild salmon health vs. money and jobs as B.C.’s fish farm fight comes to a head
For some, salmon farms are a blight on the landscape. Not for the way they look, but because of the threat they believe these large aquaculture operations pose to wild salmon. “We’re pretty confident this place will have to be dismantled,” says Ernest Alfred, pointing at the farm from the boat. “And I’ll be here to watch it.” The government is currently reviewing the leases of 20 fish farms that expire on June 20. Alfred and other opponents are upping the pressure on the NDP leadership in hopes they will commit to ending fish farming in the ocean. But supporters of the farms say that would be a huge blow to an industry worth billions of dollars to the province. >click to read<12:01
Meanwhile, in Scotland, A bid by the Scottish Government to resolve fierce arguments over how fish farms harm wild salmon has been dismissed as a public relations stunt by campaigners. The population of wild salmon in Scotland has fallen by 50 per cent from around 1.25 million in the 1960s to 600,000 in 2016. Angling groups point out that most of the decline is on the west coast, close to where salmon farms are located. >click to read<

Pacific salmon ‘more abundant than ever’, new study claims
Pacific salmon are generally “more abundant than ever.” That is the provocative conclusion of a new paper published in Marine and Coastal Fisheries by Greg Ruggerone of Seattle’s Natural Resources Consultants and James Irvine of the Department of Fisheries and Oceans. The study used historical commercial catch and escapement data for the entire Pacific region for both wild and commercial hatchery salmon over a 90-year period, up to 2015. There is one caveat, however: Ruggerone and Irvine analyzed only data for pink, chum and sockeye salmon. >click to read<09:13

Hatchery Fish Often Fail in the Wild. Now We Might Know Why
Wild salmon are struggling to get their groove back.,, For years, Canada has tried to help bolster the salmon population by releasing hatchery-raised juvenile fish, or smolts, into the wild. Scientists know these hatchery smolts don’t do well in the wild—the fish tend to die younger than their wild brethren and reproduce less, but it’s unclear why. In a recent study, however, researchers think they’ve hit upon a possible explanation.,, In Washington State, hatchery-spawned steelhead also do poorly in the wild. click here to read the story 12:31
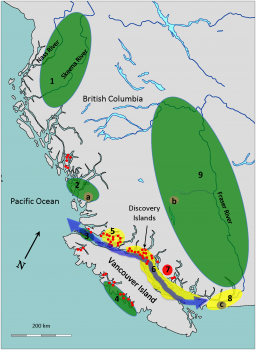
New research shows wild salmon exposed to fish farms have ‘much higher’ rate of disease
Wild salmon exposed to open-net fish farms are much more likely to be infected with piscine reovirus (PRV) than those that don’t have that contact, a new study has concluded. The data also show that the virus makes it more difficult for wild salmon to swim upstream to their spawning grounds, which has major implications for the sustainability of the populations. “The government has to remove this industry from the key salmon migration routes or we risk the complete loss of wild salmon in this province,” said Alexandra Morton, lead author on the report and an outspoken advocate for wild salmon. click here to read the story 18:07
The effect of exposure to farmed salmon on piscine orthoreovirus infection and fitness in wild Pacific salmon in British Columbia, Canada – click here to read the study
Fish traps of past may help future of Columbia salmon
 The once-outlawed commercial fishing technique has been generating fresh interest in the face of declining wild salmon runs and might offer a less lethal way of handling wild salmon while harvesting hatchery fish for the consumer. Fish traps were once used broadly in the Northwest during the early part of the last century to harvest salmon for the canneries, but they were eventually outlawed because they caught too many fish.,, Jim Wells is a member of the lower Columbia River gill-net fleet, and after the conservation group published its findings on the traps he did a little bit of research. Using the catch data from the trap, he figured just how many sell-able fish they had caught during this last season. click here to read the story 14:52
The once-outlawed commercial fishing technique has been generating fresh interest in the face of declining wild salmon runs and might offer a less lethal way of handling wild salmon while harvesting hatchery fish for the consumer. Fish traps were once used broadly in the Northwest during the early part of the last century to harvest salmon for the canneries, but they were eventually outlawed because they caught too many fish.,, Jim Wells is a member of the lower Columbia River gill-net fleet, and after the conservation group published its findings on the traps he did a little bit of research. Using the catch data from the trap, he figured just how many sell-able fish they had caught during this last season. click here to read the story 14:52

Why ‘normal’ salmon don’t get as many parasites
New research reveals the inherent ability of salmon to avoid infection through their first line of defense—behavior. In the rapidly growing fish-farming industry, parasite outbreaks cause production inefficiencies, poor welfare for billions of fish, and negative consequences for wild populations when diseases spread. “Parasite outbreaks in wild fish have been induced by farmed fish in major farming systems, such as sea lice infestations on wild salmon in Europe and North America,” says Tim Dempster, associate professor in the School of BioSciences at the University of Melbourne. click here to read the story 15:25
We’re On Board with These Two Fishermen – Salmon Fishing Season Starts Today
 Our town of Cordova, Alaska is humming with the sounds of diesel engines firing up, big trucks hurrying around the harbor and fishermen catching up with each across the docks. This week holds so much excitement and anticipation here. Today, May 18th, the fleet of 540 fishermen from this tiny coastal community take off for the Gulf of Alaska where we’ll be setting our nets to catch the first wild salmon making their way back to the Copper River. The Alaska Department of Fish and Game carefully monitors our fishery for long term sustainability and have designated the salmon season to start this week with a 12 hour commercial fishing period starting bright and early at 7 am on Thursday. Click here to read the story 07:42
Our town of Cordova, Alaska is humming with the sounds of diesel engines firing up, big trucks hurrying around the harbor and fishermen catching up with each across the docks. This week holds so much excitement and anticipation here. Today, May 18th, the fleet of 540 fishermen from this tiny coastal community take off for the Gulf of Alaska where we’ll be setting our nets to catch the first wild salmon making their way back to the Copper River. The Alaska Department of Fish and Game carefully monitors our fishery for long term sustainability and have designated the salmon season to start this week with a 12 hour commercial fishing period starting bright and early at 7 am on Thursday. Click here to read the story 07:42
Voices of Alaska: Future of wild salmon depends on decisions made today, by Commercial Fisherman Steve Harrison
 Our state is home to the nation’s last stronghold of wild salmon and, for the most part, we have managed our fisheries well. For generations Alaskans have sustainably harvested millions of wild salmon while this amazing fish continues to return to their native streams, spawn and rejuvenate the population every year. Tasked with developing policies that protect our salmon resource, the Alaska Board of Fish uses the basic principles of sustainable yield and conservative management to drive decision-making and, by-and-large, it has worked. But managing the harvest of salmon is only part of the equation. Ensuring our salmon runs remain strong also means protecting the habitat they depend on, from the wetlands at the headwaters of the streams they spawn all the way to the ocean where they spend the majority of their lives. In recent years, pressure to allow mining and damming interests to set up shop in and around our prolific salmon streams has increased greatly, with proposed projects like the Pebble Mine, Susitna dam, and the Chuitna Coal strip mine leading the charge. Read the rest here 17:15
Our state is home to the nation’s last stronghold of wild salmon and, for the most part, we have managed our fisheries well. For generations Alaskans have sustainably harvested millions of wild salmon while this amazing fish continues to return to their native streams, spawn and rejuvenate the population every year. Tasked with developing policies that protect our salmon resource, the Alaska Board of Fish uses the basic principles of sustainable yield and conservative management to drive decision-making and, by-and-large, it has worked. But managing the harvest of salmon is only part of the equation. Ensuring our salmon runs remain strong also means protecting the habitat they depend on, from the wetlands at the headwaters of the streams they spawn all the way to the ocean where they spend the majority of their lives. In recent years, pressure to allow mining and damming interests to set up shop in and around our prolific salmon streams has increased greatly, with proposed projects like the Pebble Mine, Susitna dam, and the Chuitna Coal strip mine leading the charge. Read the rest here 17:15
What are the fish telling us: the story of the world’s largest wild salmon fishery
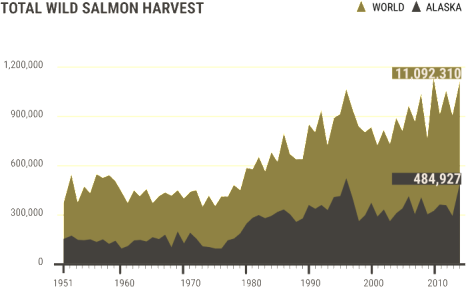 The myth (it was a myth) goes that when Christopher Columbus sailed to the Americas in 1492, he and his crew couldn’t sleep because of the perpetual whack of sea turtles bumping against the hull of their ship. Now, 500 years later, nearly every species of sea turtle is listed as endangered. In fact, so many plants and animals have become endangered or extinct in recent years, that researchers and environmentalists have started referring to it as the sixth mass extinction. Read the rest here 12:38
The myth (it was a myth) goes that when Christopher Columbus sailed to the Americas in 1492, he and his crew couldn’t sleep because of the perpetual whack of sea turtles bumping against the hull of their ship. Now, 500 years later, nearly every species of sea turtle is listed as endangered. In fact, so many plants and animals have become endangered or extinct in recent years, that researchers and environmentalists have started referring to it as the sixth mass extinction. Read the rest here 12:38
California wild salmon harvest continues to dwindle with drought
 It’s still a little too early to tell for sure, but the news on the California wild salmon front is not good. A combination of low water levels in streams because of the drought and high summer temperatures resulted in a massive die-off of young salmon in Northern California. Read the rest here 13:57
It’s still a little too early to tell for sure, but the news on the California wild salmon front is not good. A combination of low water levels in streams because of the drought and high summer temperatures resulted in a massive die-off of young salmon in Northern California. Read the rest here 13:57
Escapees change the wild salmon
For the first time, scientists have managed to quantify how escaped salmon have interbred with wild salmon in Norwegian rivers. These results provide a basis for reassessing the impact that escapees from fish farms have on the wild salmon in Norwegian rivers. more@instituteofmarineresearch 00:28
Wild salmon: Are their best days all behind them?

Chinook salmon returns are setting records on the Columbia this year. But 80 percent are hatchery fish. Thirteen wild salmon populations in the region are listed as endangered and 11 are threatened. The latest threat, warming waters, comes on top of the longstanding dangers of hydropower for salmon. more@crosscut 20:29
B.C. Indian Chiefs: Wild salmon is the first and foremost priority by Dan Bacher
“It is completely unacceptable and First Nations cannot continue to stand idly by as the wild salmon runs die off,” said Chief Bob Chamberlin, Vice-President of the Union of BC Indian Chiefs continue reading
















































