Researchers use the North Atlantic Oscillation as a predictive tool for managing Gulf of Maine Cod
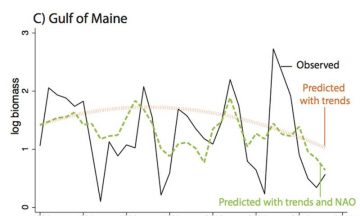 In recent decades, the plight of Atlantic cod off the coast of New England has been front-page news. Since the 1980s in particular, the once-seemingly inexhaustible stocks of Gadus morhua—one of the most important fisheries in North America—have declined dramatically. In 2008, a formal assessment forecasted that stocks would rebound, but by 2012, they were once again on the verge of collapse. Two years later, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration instituted an unprecedented six-month closure of the entire Gulf of Maine cod fishery to allow stocks to recover. While overfishing is one known culprit, a new study co-authored by researchers at UC Santa Barbara and Columbia University finds that the climatological phenomenon known as the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is also a factor. And it contributes in a predictable way that may enable fishery managers to protect cod stocks from future collapse. Read the rest here 17:37
In recent decades, the plight of Atlantic cod off the coast of New England has been front-page news. Since the 1980s in particular, the once-seemingly inexhaustible stocks of Gadus morhua—one of the most important fisheries in North America—have declined dramatically. In 2008, a formal assessment forecasted that stocks would rebound, but by 2012, they were once again on the verge of collapse. Two years later, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration instituted an unprecedented six-month closure of the entire Gulf of Maine cod fishery to allow stocks to recover. While overfishing is one known culprit, a new study co-authored by researchers at UC Santa Barbara and Columbia University finds that the climatological phenomenon known as the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is also a factor. And it contributes in a predictable way that may enable fishery managers to protect cod stocks from future collapse. Read the rest here 17:37
Share this post
Related
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.












































Leave a Reply