Tag Archives: Gulf of Maine
Feds say “damn the whales” in the Gulf of Maine
 Biden’s Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) proposes to build a huge amount of floating offshore wind in the Gulf of Maine. As required by law, it has published for public comment a draft Environmental Assessment of the area designated for this monster project. But insanely, there is no assessment of the project, just of the area without the project. I am not making this up. This place is properly called the Wind Energy Area (WEA) because that is where the wind energy will come from. BOEM says they plan to issue eight leases initially with a monster development potential of 15,000 MW. Given that 15 MW is the biggest turbine available that amounts to 1,000 or more huge turbines. A second phase might add another thousand of so. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 12:29
Biden’s Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) proposes to build a huge amount of floating offshore wind in the Gulf of Maine. As required by law, it has published for public comment a draft Environmental Assessment of the area designated for this monster project. But insanely, there is no assessment of the project, just of the area without the project. I am not making this up. This place is properly called the Wind Energy Area (WEA) because that is where the wind energy will come from. BOEM says they plan to issue eight leases initially with a monster development potential of 15,000 MW. Given that 15 MW is the biggest turbine available that amounts to 1,000 or more huge turbines. A second phase might add another thousand of so. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 12:29
Reagan Paul: Hope Floats, But Not for UMaine’s VolturnUS Floating Offshore Wind Platform
 Last year, LD 1895 “An Act Regarding the Procurement of Energy from Offshore Wind Resources” passed, which got the ball rolling on Maine’s push for offshore wind port. The port will be the culmination of a more than decade-long taxpayer-funded effort to develop a floating offshore wind research array project, with the goal of eventually turning the Gulf of Maine into an industrialized wind farm. The viability of this technology was to be tested through an array of 12 wind turbines using the patented VolturnUS concrete, semi-submersible floating offshore wind turbine platform design created by Dr. Habib Dagher of the University of Maine, over the last decade. The Portland Press Herald conceded that this floating offshore wind research array project is too cost-prohibitive without an almost billion-dollar dedicated wind port facility off the coast of Maine, which means that a port must be constructed before the state can even move forward with the research array outlined in LD 1895. Enter Sears Island. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 07:46
Last year, LD 1895 “An Act Regarding the Procurement of Energy from Offshore Wind Resources” passed, which got the ball rolling on Maine’s push for offshore wind port. The port will be the culmination of a more than decade-long taxpayer-funded effort to develop a floating offshore wind research array project, with the goal of eventually turning the Gulf of Maine into an industrialized wind farm. The viability of this technology was to be tested through an array of 12 wind turbines using the patented VolturnUS concrete, semi-submersible floating offshore wind turbine platform design created by Dr. Habib Dagher of the University of Maine, over the last decade. The Portland Press Herald conceded that this floating offshore wind research array project is too cost-prohibitive without an almost billion-dollar dedicated wind port facility off the coast of Maine, which means that a port must be constructed before the state can even move forward with the research array outlined in LD 1895. Enter Sears Island. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 07:46
Floating Wind Madness in Maine
 The Government of Maine has really big plans for floating wind, a floating net zero fantasy, in fact. Since floating wind power is the next big green thing, it is worth taking a close look at this ruinous vision. Floating wind is a fad, not an established technology. It has yet to be built at utility scale or tested in a hurricane. The world’s biggest grid-connected system is a tiny 50 MW and just came online off Scotland. The cost of floating wind is necessarily much greater than fixed wind. A fixed wind tower sits on a simple monopile, while a floating tower sits on a huge complex structure called a floater. We are talking about massive 500-foot towers with 500-ton turbines on top and 300-foot blades catching the wind. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 06:17
The Government of Maine has really big plans for floating wind, a floating net zero fantasy, in fact. Since floating wind power is the next big green thing, it is worth taking a close look at this ruinous vision. Floating wind is a fad, not an established technology. It has yet to be built at utility scale or tested in a hurricane. The world’s biggest grid-connected system is a tiny 50 MW and just came online off Scotland. The cost of floating wind is necessarily much greater than fixed wind. A fixed wind tower sits on a simple monopile, while a floating tower sits on a huge complex structure called a floater. We are talking about massive 500-foot towers with 500-ton turbines on top and 300-foot blades catching the wind. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 06:17

Offshore wind farm lease auction plan has Gulf of Maine fishermen feeling brushed aside
The prospect of hundreds of offshore wind turbines generating power in the Gulf of Maine is moving forward with plans to auction eight leases in a large swath of waters off the New England coast. Jerry Leeman III, the CEO of the New England Fishermen’s Stewardship Association, said there’s not enough data to support the areas that have been chosen for wind development. As now laid out, the plan could take away valuable fishing grounds from New England’s fishing fleet, pose navigational hazards and create new environmental threats, he said. “We still have more questions than we have answers,” he said. “Yet we’re moving ahead with the leasing ahead of the science.” more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 12:37

Coddock? Sea sleuths work to uncover mystery of new cod-haddock-like fish
Last summer, I wrote about a very interesting fish, showing up in the Gulf of Maine and promised an update. Well, here it is. We nicknamed it a “coddock” due to its strange shape and coloration. It has the head of a haddock, the lateral line of a cod, the pectoral fin of a cod, and the meat flaked in large pieces like cod. The body shape is that of haddock, and all the other fins look like haddock fins, but it was missing the “thumbprint of God,” which is a large black spot just behind the operculum (gill plates) and above the pectoral (side fin). It also had spotted skin that looked more like a cod than the silvery skin of a haddock. This was abnormal and deserved some investigation. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 06:37
Lobstermen and Scientists See a Fishery in Flux
 While overall the fishery seems stable, some lobstermen are seeing changes that have them worried about its future. Scientists are looking into what role the changing climate may be playing in those changes, but they don’t have definitive answers. “It’s horrible,” said Mike Rego, a lobsterman and owner of the F/V Miss Lilly who operates out of Provincetown. “Last year was the worst year I ever had.” Dana Pazolt, another Provincetown lobsterman who owns the F/V Black Sheep, said that the last four years have been slim for lobsters around the Outer Cape. “You’ve got to hunt for them,” he said. “I can’t tell you why that is.” The surface waters of the Gulf of Maine are warming at a rate of about one degree per decade, faster than 99 percent of the world’s oceans, according to the Gulf of Maine Research Institute. Meanwhile, in other areas, warming has already had an effect — it played a major role in causing the collapse of the lobster fishery in Long Island Sound in 1999. more, >>CICK TO READ<< 21:20
While overall the fishery seems stable, some lobstermen are seeing changes that have them worried about its future. Scientists are looking into what role the changing climate may be playing in those changes, but they don’t have definitive answers. “It’s horrible,” said Mike Rego, a lobsterman and owner of the F/V Miss Lilly who operates out of Provincetown. “Last year was the worst year I ever had.” Dana Pazolt, another Provincetown lobsterman who owns the F/V Black Sheep, said that the last four years have been slim for lobsters around the Outer Cape. “You’ve got to hunt for them,” he said. “I can’t tell you why that is.” The surface waters of the Gulf of Maine are warming at a rate of about one degree per decade, faster than 99 percent of the world’s oceans, according to the Gulf of Maine Research Institute. Meanwhile, in other areas, warming has already had an effect — it played a major role in causing the collapse of the lobster fishery in Long Island Sound in 1999. more, >>CICK TO READ<< 21:20
Warming waters in Casco Bay are driving herring farther from shore
 The Gulf of Maine is warming three times faster than the average global ocean, driving some cold-water species like Atlantic herring, the preferred lobster bait — farther away from its shoreline spawning habitat earlier than usual and attracting species from warmer southern waters, including blue crab and black sea bass, a new survey found. The warmth is stressing some of Maine’s keystone fisheries, according to the Gulf of Maine Research Institute’s report on the Casco Bay ecosystem released recently. The report is the first time the institute took a longer, 10-year look at the pace of environmental changes and their effects on ecosystems close to shore. It found that warming waters related to climate change, along with human activities, ocean acidification and harmful algal blooms, are causing different behaviors in species that could hinder their ability to reproduce and thrive. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 09:52
The Gulf of Maine is warming three times faster than the average global ocean, driving some cold-water species like Atlantic herring, the preferred lobster bait — farther away from its shoreline spawning habitat earlier than usual and attracting species from warmer southern waters, including blue crab and black sea bass, a new survey found. The warmth is stressing some of Maine’s keystone fisheries, according to the Gulf of Maine Research Institute’s report on the Casco Bay ecosystem released recently. The report is the first time the institute took a longer, 10-year look at the pace of environmental changes and their effects on ecosystems close to shore. It found that warming waters related to climate change, along with human activities, ocean acidification and harmful algal blooms, are causing different behaviors in species that could hinder their ability to reproduce and thrive. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 09:52
Scallop Research Set-Aside Program to Support 14 New Projects; Several 2024 Announcements Include Multi-Year Awards
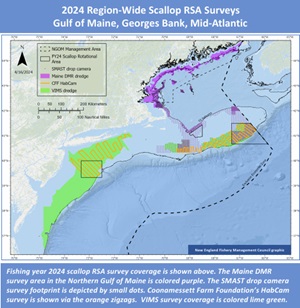 The Atlantic Sea Scallop Research Set-Aside (RSA) Program will support 14 new projects that were selected from the 2024 RSA solicitation. Several awards will support multi-year research, including a four-year regional survey effort. The set-aside harvest is expected to generate $22 million in revenue. Of that total, $5 million will fund the targeted research and $17 million will compensate industry partners who harvest the set-aside scallops. To determine the award amounts, the price of sea scallops was projected to average $14 per pound of meats. Charts, more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 12:38
The Atlantic Sea Scallop Research Set-Aside (RSA) Program will support 14 new projects that were selected from the 2024 RSA solicitation. Several awards will support multi-year research, including a four-year regional survey effort. The set-aside harvest is expected to generate $22 million in revenue. Of that total, $5 million will fund the targeted research and $17 million will compensate industry partners who harvest the set-aside scallops. To determine the award amounts, the price of sea scallops was projected to average $14 per pound of meats. Charts, more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 12:38
State backs lobstermen in urging regulators to reevaluate changes to minimum size
 The rules, which are set to go into effect on Jan. 1, 2025, will increase the minimum size from 3 1/4 inches to 3 5/16 inches, on the gauges that lobstermen use to measure lobsters and determine whether they are allowed to harvest them. A second increase would take effect two years later, bringing the minimum to 3 3/8 inches. The rules also affect the vents in traps that allow undersized lobsters to escape. The Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission says it is making the changes to preserve the long-term future of the lobster population in the Gulf of Maine, which federal data show has sharply dropped. Lobstermen also question the accuracy of the federal data – saying that it was corrected over a small and abnormal time frame that doesn’t indicate the reality of population trends. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 06:23
The rules, which are set to go into effect on Jan. 1, 2025, will increase the minimum size from 3 1/4 inches to 3 5/16 inches, on the gauges that lobstermen use to measure lobsters and determine whether they are allowed to harvest them. A second increase would take effect two years later, bringing the minimum to 3 3/8 inches. The rules also affect the vents in traps that allow undersized lobsters to escape. The Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission says it is making the changes to preserve the long-term future of the lobster population in the Gulf of Maine, which federal data show has sharply dropped. Lobstermen also question the accuracy of the federal data – saying that it was corrected over a small and abnormal time frame that doesn’t indicate the reality of population trends. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 06:23

Fishermen call for a delay to upcoming lobster size rules
Congressman Jared Golden is calling on fishery regulators to delay upcoming rules that will change the minimum catch sizes for lobster in certain parts of Maine. Officials have said the changes are necessary after they observed a troubling decline in the juvenile lobster population over a three-year period. The new management measures are intended to allow sublegal lobsters to reproduce before being harvested. But some Maine fishermen are questioning that data, and on Tuesday, many turned out at a meeting of the Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission to express their concerns. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 05:50
Biden administration plans to tee up offshore wind across the nation’s coastlines
 The Biden administration is planning to boost offshore wind energy production, announcing up to a dozen opportunities for industry to bid on chances to build wind turbines in U.S. oceans over the next five years. Interior Secretary Deb Haaland is slated to announce the lease sales at a conference in New Orleans. The 12 potential opportunities Haaland is announcing include sales in the central Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Maine, Gulf of Mexico, the New York Bight and off the coast of Oregon, California, Hawaii and a yet-to-be-determined U.S. territory. These sales were described as potential sales that could occur rather than ones definitely slated to happen, and if former President Trump wins election, he may want to cancel them. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 14:56
The Biden administration is planning to boost offshore wind energy production, announcing up to a dozen opportunities for industry to bid on chances to build wind turbines in U.S. oceans over the next five years. Interior Secretary Deb Haaland is slated to announce the lease sales at a conference in New Orleans. The 12 potential opportunities Haaland is announcing include sales in the central Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Maine, Gulf of Mexico, the New York Bight and off the coast of Oregon, California, Hawaii and a yet-to-be-determined U.S. territory. These sales were described as potential sales that could occur rather than ones definitely slated to happen, and if former President Trump wins election, he may want to cancel them. more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 14:56
Warming Waters Heat Summer’s Feast Well Before It Gets to the Kitchen
 An ever-warming planet is playing havoc with the intricately interconnected web of marine life. Just as climate has long stressed human populations and driven migration, marine populations are stressed and in search of survivable climates too. In New England, scientists and lobstermen alike are studying and living the impacts. Tim Alley has been lobstering in Maine’s coastal waters for 40 years. “There’s been a trend in recent years related to temperatures,” he says. Alley is steeped in the traditions of his home state’s biggest industry and recently dusted off a short film from 1972 in which he starred at age 12, “Alone in My Lobster Boat,” filmed in South Bristol and New Harbor, Maine. Like most lobstermen, he would call himself an environmentalist: they live on the water, they live from the water, they thrive on the water. But they reject the notion that a species – the right whale – is failing because of them. Over 40 years, he says, he has seen exactly one right whale. Photos, Video, more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 14:50
An ever-warming planet is playing havoc with the intricately interconnected web of marine life. Just as climate has long stressed human populations and driven migration, marine populations are stressed and in search of survivable climates too. In New England, scientists and lobstermen alike are studying and living the impacts. Tim Alley has been lobstering in Maine’s coastal waters for 40 years. “There’s been a trend in recent years related to temperatures,” he says. Alley is steeped in the traditions of his home state’s biggest industry and recently dusted off a short film from 1972 in which he starred at age 12, “Alone in My Lobster Boat,” filmed in South Bristol and New Harbor, Maine. Like most lobstermen, he would call himself an environmentalist: they live on the water, they live from the water, they thrive on the water. But they reject the notion that a species – the right whale – is failing because of them. Over 40 years, he says, he has seen exactly one right whale. Photos, Video, more, >>CLICK TO READ<< 14:50

More things to worry about by Jerry Leeman
Wind energy in the Gulf of Maine is going to be a great challenge to all varieties of commercial and recreational fisheries. What disturbs me the most is, in all my travels along the coast in the four major fishing ports in New England, very few commercial fishing Captains were aware of the new talks on changing the management stock areas and the reallocation of codfish. This is a concern for many now that they are aware. This raises the question, if no Captain’s that fish inside the Wind Energy proposed areas were not aware of this future action, then how can the last comment periods on the proposed sights be accurately sighted? Charts graphs, more, >>click to read<< 13:16
Offshore wind threatens centuries of fishing
 Many people today think that offshore wind power will be able to give us abundant (long-lived?) clean energy. The water in the Gulf of Maine is very deep, any turbines sited there will be on floating platforms anchored to the seabed with giant chains. It is important to remember that the Gulf of Maine is the life blood of all our coastal fishing communities. I participated in an interesting project some years ago when the Maine Coast Fishermen’s Association was formed. We worked with Island Institute to document how each fishing community extended far out to sea. Each community has traditional grounds that have been worked for centuries by fishermen from those communities. Fishing sustains coastal New England. If offshore wind industrialization is allowed in these fishing grounds the communities connected to these areas will suffer. by Glen Libby, more, >>click to read<< 10:52
Many people today think that offshore wind power will be able to give us abundant (long-lived?) clean energy. The water in the Gulf of Maine is very deep, any turbines sited there will be on floating platforms anchored to the seabed with giant chains. It is important to remember that the Gulf of Maine is the life blood of all our coastal fishing communities. I participated in an interesting project some years ago when the Maine Coast Fishermen’s Association was formed. We worked with Island Institute to document how each fishing community extended far out to sea. Each community has traditional grounds that have been worked for centuries by fishermen from those communities. Fishing sustains coastal New England. If offshore wind industrialization is allowed in these fishing grounds the communities connected to these areas will suffer. by Glen Libby, more, >>click to read<< 10:52

Massachusetts fishermen say feds are hypocritical in Gulf of Maine wind energy designation
A move to designate two million acres in the Gulf of Maine as a hub for wind energy is snagging a sharp hook from Massachusetts fishermen who say the development overlooks risks to the North Atlantic right whale. A handful of Bay State fishermen advocacy groups are teaming with counterparts from across New England in criticizing the Biden administration’s plans to industrialize the area off the coasts of Massachusetts, New Hampshire and Maine. Fishermen, however, say the industrialization of the two-million-acre area is “flatly inconsistent with a policy of endangered species protection.” “Fishermen are disheartened that the WEA designation favors foreign energy developers over marine mammal protection,” the Gulf of Maine Fishing Associations said in a statement last week. “This preferential treatment is in stark contrast to the federal government’s aggressive campaign to burden commercial fishing needlessly with crushing restrictions to protect whales.” more, >>click to read<< 08:43
Federal Government Picks New England Offshore Wind Power Site, Drawing Cheers and Questions Alike
 The federal government on Friday designated a large area off the New England coast for offshore wind production development, setting the stage for a possible lease sale within the Gulf of Maine. The U.S. Bureau of Ocean Energy Management said in a statement that the New England zone, which renewable energy advocates have identified as crucial for the growth of wind power, “avoids important areas for lobster fishing, North Atlantic right whale habitat, and other important fishing areas and habitats.” The move came a day after the country’s first commercial-scale offshore wind farm opened off Montauk Point, New York. Environmental groups cheered the announcement, but some members of the commercial fishing industry, which has opposed wind development in areas where they trap lobsters, said they still have concerns about locating offshore wind in the area. more, >>click to read<< 12:23
The federal government on Friday designated a large area off the New England coast for offshore wind production development, setting the stage for a possible lease sale within the Gulf of Maine. The U.S. Bureau of Ocean Energy Management said in a statement that the New England zone, which renewable energy advocates have identified as crucial for the growth of wind power, “avoids important areas for lobster fishing, North Atlantic right whale habitat, and other important fishing areas and habitats.” The move came a day after the country’s first commercial-scale offshore wind farm opened off Montauk Point, New York. Environmental groups cheered the announcement, but some members of the commercial fishing industry, which has opposed wind development in areas where they trap lobsters, said they still have concerns about locating offshore wind in the area. more, >>click to read<< 12:23
What You Need to Know About Cod
As a large, naturally abundant fish, cod has been eaten by various human populations for centuries.  While both of America’s Atlantic cod fisheries are overfished, American stocks of Pacific cod (Gadus macrocephalus) are not. What’s more, various other cod fisheries are located around the globe, some over-exploited, others not. The fish’s prevalence, along with its suitability for eating, means that despite dwindling numbers, cod remains a stalwart of many cuisines. However, there are many things about cod that aren’t widely known. It might surprise some people to learn that cod hunt for prey. They eat a variety of animals, ranging from worms to lobsters and even small fish. Such a diet means cod are capable of growing up to an impressive length of six feet and a weight of over 100 pounds. more, >>click to read<< 11:52
While both of America’s Atlantic cod fisheries are overfished, American stocks of Pacific cod (Gadus macrocephalus) are not. What’s more, various other cod fisheries are located around the globe, some over-exploited, others not. The fish’s prevalence, along with its suitability for eating, means that despite dwindling numbers, cod remains a stalwart of many cuisines. However, there are many things about cod that aren’t widely known. It might surprise some people to learn that cod hunt for prey. They eat a variety of animals, ranging from worms to lobsters and even small fish. Such a diet means cod are capable of growing up to an impressive length of six feet and a weight of over 100 pounds. more, >>click to read<< 11:52
Feds announce areas where offshore wind can go in Gulf of Maine
 Federal regulators have made a final designation of roughly 2 million acres in the Gulf of Maine where offshore wind turbines can be deployed to help provide power to New England. The boundary set by the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management does not include any part of the federal lobster management area 1. That fishing area extends from state waters about three miles offshore to about 40 miles. The closest the designated federal wind energy area comes to Maine’s coast is just outside the fishing zone. The Maine Lobstermen’s Association said Friday that it appreciates that the fishing zone is excluded from the wind area approved by BOEM. But it said that it remains “steadfast” in its position that industrial wind power development does not belong anywhere in the Gulf of Maine. more, >>click to read<< 12:39
Federal regulators have made a final designation of roughly 2 million acres in the Gulf of Maine where offshore wind turbines can be deployed to help provide power to New England. The boundary set by the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management does not include any part of the federal lobster management area 1. That fishing area extends from state waters about three miles offshore to about 40 miles. The closest the designated federal wind energy area comes to Maine’s coast is just outside the fishing zone. The Maine Lobstermen’s Association said Friday that it appreciates that the fishing zone is excluded from the wind area approved by BOEM. But it said that it remains “steadfast” in its position that industrial wind power development does not belong anywhere in the Gulf of Maine. more, >>click to read<< 12:39
Maine Lobstermen’s Association tallies its victories, future risks at annual meeting
 “Every year, there is a new issue facing the industry,” Tristan Porter, president of the Maine Lobstermen’s Association (MLA), said as the trade organization opened its 70th annual meeting during the Maine Fishermen’s Forum on March 1. For lobstermen and the commercial lobster fishery, there are three big issues facing the industry: protecting North Atlantic right whales, maintaining a sustainable fishery and the federal leasing in the Gulf of Maine for floating offshore wind energy — plus the myriad of federal and state regulations and public hearings and, at times, lawsuits, that go with them. 8 photos, more, >>click to read<< 08:44
“Every year, there is a new issue facing the industry,” Tristan Porter, president of the Maine Lobstermen’s Association (MLA), said as the trade organization opened its 70th annual meeting during the Maine Fishermen’s Forum on March 1. For lobstermen and the commercial lobster fishery, there are three big issues facing the industry: protecting North Atlantic right whales, maintaining a sustainable fishery and the federal leasing in the Gulf of Maine for floating offshore wind energy — plus the myriad of federal and state regulations and public hearings and, at times, lawsuits, that go with them. 8 photos, more, >>click to read<< 08:44
Commercial fisheries landings increased more than $25 million in value in 2023
 Preliminary numbers for commercial seafood landings in 2023 released today show a strong year for the industry, with commercial fishermen earning $611,277,692 — an increase of $25 million — for 204,684,775 pounds of seafood brought in to state docks. Despite a warming Gulf of Maine, intense storms and the damage to working waterfronts and lower lobster landings, “the Maine seafood industry continues to be a powerful economic engine for our state,” said Governor Janet Mills. Statewide, 93,734,116 pounds of lobsters landed on docks for a $461,371,720 value, an increase of about $72 million. The value represents what is paid at the docks to fishermen, dollars that flow throughout local communities and the state’s overall economy. Stonington is the top port for commercial seafood value this year, bringing in $47.37 million of value, and the second port, behind Portland, for pounds — 13.98 million. more, >>click to read<< 12:54
Preliminary numbers for commercial seafood landings in 2023 released today show a strong year for the industry, with commercial fishermen earning $611,277,692 — an increase of $25 million — for 204,684,775 pounds of seafood brought in to state docks. Despite a warming Gulf of Maine, intense storms and the damage to working waterfronts and lower lobster landings, “the Maine seafood industry continues to be a powerful economic engine for our state,” said Governor Janet Mills. Statewide, 93,734,116 pounds of lobsters landed on docks for a $461,371,720 value, an increase of about $72 million. The value represents what is paid at the docks to fishermen, dollars that flow throughout local communities and the state’s overall economy. Stonington is the top port for commercial seafood value this year, bringing in $47.37 million of value, and the second port, behind Portland, for pounds — 13.98 million. more, >>click to read<< 12:54
Floating offshore wind experts say they want to coexist with Maine lobstermen, but lobstermen say no thanks
 Lobstermen asked pointed questions Thursday about a planned offshore floating wind array that they fear will take away fishing grounds and potentially disrupt the species they rely on to make a living. “Offshore wind overall we have a lot of issues with,” Virginia Olsen, political director of the Maine Lobstering Union said. “We know it will be industrializing our ocean and as fishermen we just don’t want to see that happen.” During the Thursday presentation, state officials and consultants working on the floating array emphasized they want to work toward “coexistence” between the new technology and the fishing industry. But that didn’t sit well with some of the lobstermen, who said they don’t want to co-exist with the turbines. more, >>click to read<< 06:50
Lobstermen asked pointed questions Thursday about a planned offshore floating wind array that they fear will take away fishing grounds and potentially disrupt the species they rely on to make a living. “Offshore wind overall we have a lot of issues with,” Virginia Olsen, political director of the Maine Lobstering Union said. “We know it will be industrializing our ocean and as fishermen we just don’t want to see that happen.” During the Thursday presentation, state officials and consultants working on the floating array emphasized they want to work toward “coexistence” between the new technology and the fishing industry. But that didn’t sit well with some of the lobstermen, who said they don’t want to co-exist with the turbines. more, >>click to read<< 06:50
Maine’s lobster fishermen struggle with efforts to save right whales
 Willis Spear stands in the backyard of his Yarmouth, Maine home. Behind him are dozens of yellow and green lobster traps. Spear, 67, spends most of the winter preparing these traps to be deployed in the Gulf of Maine come April. It’s a task this lifelong lobster fisherman has carried out each year since he was a child. “The water gives us life,” Spear said on an unusually warm winter day in late February. Over the last decade, lobster fishermen in Maine have faced increasingly stronger financial headwinds, from the price of fuel to the revenue they are receiving for the lobster themselves. The lobster-fishing industry generates hundreds of millions of dollars for Maine’s economy each year. Video, more, >>click to read<< 18:37
Willis Spear stands in the backyard of his Yarmouth, Maine home. Behind him are dozens of yellow and green lobster traps. Spear, 67, spends most of the winter preparing these traps to be deployed in the Gulf of Maine come April. It’s a task this lifelong lobster fisherman has carried out each year since he was a child. “The water gives us life,” Spear said on an unusually warm winter day in late February. Over the last decade, lobster fishermen in Maine have faced increasingly stronger financial headwinds, from the price of fuel to the revenue they are receiving for the lobster themselves. The lobster-fishing industry generates hundreds of millions of dollars for Maine’s economy each year. Video, more, >>click to read<< 18:37

A day on the ocean with Maine’s tough winter scallopers
Their day began in the 5:30 a.m. darkness, when Josh Todd and his father, Alex Todd, steamed the F/V Jacob & Joshua from Chebeague Island to Littlejohn Island, where they picked up Blanchard. As Alex Todd piloted his boat to the day’s fishing ground west of Eagle Island, Josh Todd and Blanchard readied the vessel’s eight-foot, 1,500-pound dredge where it hung from scaffolding at the stern. Once in position, Blanchard lowered the dredge on a quarter-inch steel cable. The Jacob & Joshua shuddered, and the rigging groaned, as the dredge bit into the graveled sea floor, roughly 80 feet below. 8 photos, more, >>click to read<< 08:15
Scotian Shelf shrimp fishery braces for another cut
 For a third straight year, the shrimp fishery off eastern Nova Scotia is facing a big quota cut with ocean conditions to blame. The recent scientific assessment for northern shrimp on the eastern Scotian Shelf showed environmental factors — including warmer ocean water due to climate change — are contributing to the poor condition of the stock, he says. And the response, he predicts, will be a reduction in the total allowable catch. The Department of Fisheries and Oceans (DFO) is expected to announce the 2024 shrimp quota in several weeks. more, >>click to read<< 10:59
For a third straight year, the shrimp fishery off eastern Nova Scotia is facing a big quota cut with ocean conditions to blame. The recent scientific assessment for northern shrimp on the eastern Scotian Shelf showed environmental factors — including warmer ocean water due to climate change — are contributing to the poor condition of the stock, he says. And the response, he predicts, will be a reduction in the total allowable catch. The Department of Fisheries and Oceans (DFO) is expected to announce the 2024 shrimp quota in several weeks. more, >>click to read<< 10:59
Wide-ranging meeting covers gauge changes, ropeless gear, damage repair – DMR to lobstermen: We need your data
 The Maine Department of Marine Fisheries held its January 29 Lobster Zone C Council meeting in Stonington Town Hall, drawing more than four dozen fishermen, marine scientists and local politicians eager to weigh in on a number of policy initiatives. Among the topics: the timeline for changes to gauge and vent sizes that were triggered due to declining juvenile lobster abundance; challenges to Canadian management practices; and plans to spend $17 million allocated last year by Congress to develop better science around lobstering’s impact on North Atlantic right whale mortality. Keliher kicked off the meeting with a discussion of impending gauge-size changes under Addendum XXVII, a management strategy adopt by the Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission (ASMFC) to increase protection of the Gulf of Maine/Georges Bank spawning stock. more, >>click to read<< 07:57
The Maine Department of Marine Fisheries held its January 29 Lobster Zone C Council meeting in Stonington Town Hall, drawing more than four dozen fishermen, marine scientists and local politicians eager to weigh in on a number of policy initiatives. Among the topics: the timeline for changes to gauge and vent sizes that were triggered due to declining juvenile lobster abundance; challenges to Canadian management practices; and plans to spend $17 million allocated last year by Congress to develop better science around lobstering’s impact on North Atlantic right whale mortality. Keliher kicked off the meeting with a discussion of impending gauge-size changes under Addendum XXVII, a management strategy adopt by the Atlantic States Marine Fisheries Commission (ASMFC) to increase protection of the Gulf of Maine/Georges Bank spawning stock. more, >>click to read<< 07:57
NOAA Fisheries Extends Emergency Measures for Gulf of Maine Haddock Quota through Remainder of Fishing Year 2023
 Effective January 9, 2024 – At the New England Fishery Management Council’s request, NOAA Fisheries took emergency action to increase the Gulf of Maine (GOM) haddock acceptable biological catch (ABC) for the 2023 fishing year. NOAA Fisheries increased the fishing year 2023 ABC to the fishing mortality associated with the maximum sustainable yield (FMSY) (2,515 mt). The emergency measures were included in the final rule for Framework Adjustment 65 (88 FR 56527; August 18, 2023). The emergency measures will expire on February 14, 2024, under the Magnuson-Stevens Act’s initial 180-day limit on the duration of an emergency action. more, links, >>click to read<< 19:40
Effective January 9, 2024 – At the New England Fishery Management Council’s request, NOAA Fisheries took emergency action to increase the Gulf of Maine (GOM) haddock acceptable biological catch (ABC) for the 2023 fishing year. NOAA Fisheries increased the fishing year 2023 ABC to the fishing mortality associated with the maximum sustainable yield (FMSY) (2,515 mt). The emergency measures were included in the final rule for Framework Adjustment 65 (88 FR 56527; August 18, 2023). The emergency measures will expire on February 14, 2024, under the Magnuson-Stevens Act’s initial 180-day limit on the duration of an emergency action. more, links, >>click to read<< 19:40
‘When the Island Had Fish’ is a portrait of Vinalhaven through its most prominent industry
 Vinalhaven Island sits like a plug between the Gulf of Maine’s offshore gyre and the estuaries, marshes and shallows of upper Penobscot Bay. After the melting of the continental ice sheet 13,000 years ago, these waters became some of the richest fishing grounds on earth. “When the Island Had Fish” tells the story of fish and fishing around Vinalhaven, focusing on the industry’s impact on the people of this singular place. It’s presented as history, garnished with some science and statistics, but at heart, this is an ethnography of a Maine fishing community. Janna Malamud Smith is the participant-observer, and her friends and acquaintances on Vinalhaven, where she summered for 30 years, are her informants. more, >>click to read<< 14:10
Vinalhaven Island sits like a plug between the Gulf of Maine’s offshore gyre and the estuaries, marshes and shallows of upper Penobscot Bay. After the melting of the continental ice sheet 13,000 years ago, these waters became some of the richest fishing grounds on earth. “When the Island Had Fish” tells the story of fish and fishing around Vinalhaven, focusing on the industry’s impact on the people of this singular place. It’s presented as history, garnished with some science and statistics, but at heart, this is an ethnography of a Maine fishing community. Janna Malamud Smith is the participant-observer, and her friends and acquaintances on Vinalhaven, where she summered for 30 years, are her informants. more, >>click to read<< 14:10















































